Archaeologists from the University of California at San Diego and the University of Haifa have discovered the oldest known Iron Age ship cargoes found in a known port city in Israel, yielding direct, rare evidence of maritime trade in the eastern Mediterranean. The discovery, published in Antiquity, redefines what was known about seaborne trade during the Iron Age and reveals how shifts in regional power influenced trade between Egypt, Phoenicia, and the southern Levant.
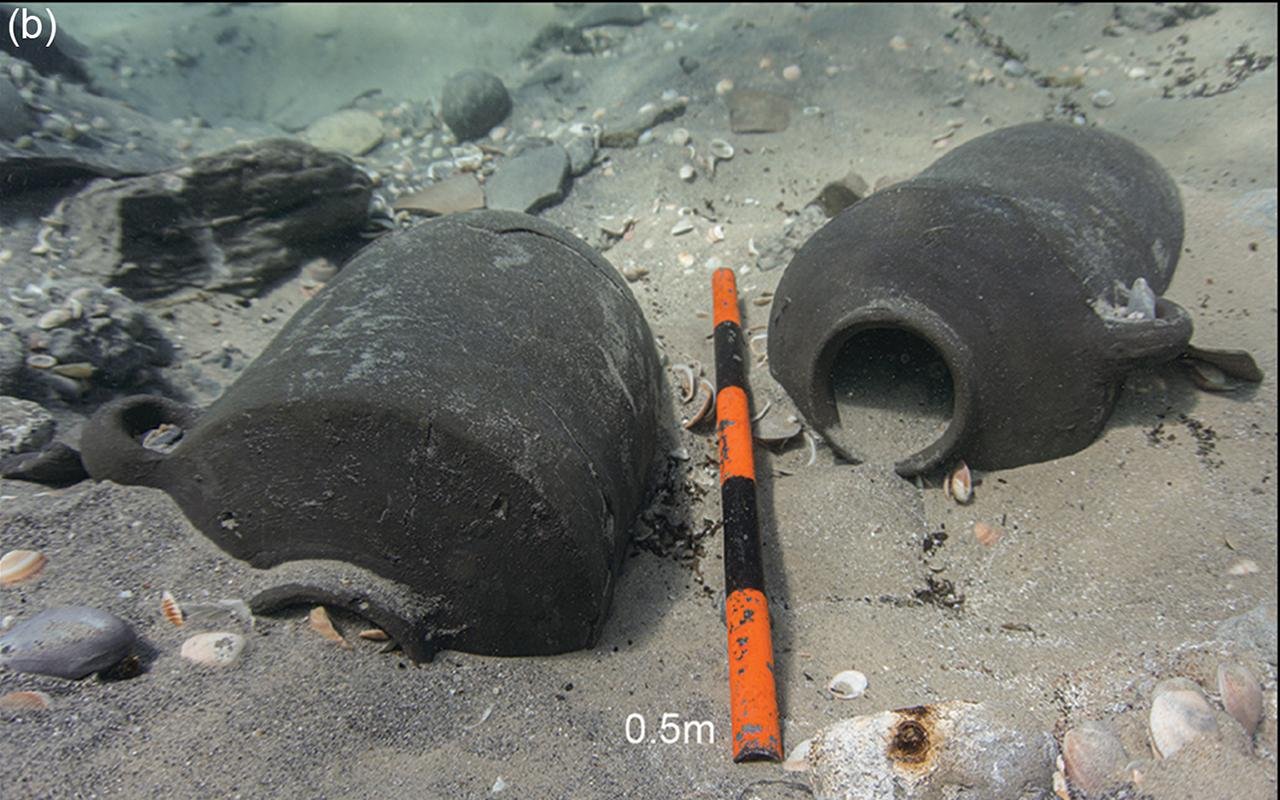 In situ storage jars. Archaeologists discovered the oldest known Iron Age ship cargoes in a port city in Israel. Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
In situ storage jars. Archaeologists discovered the oldest known Iron Age ship cargoes in a port city in Israel. Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
The finds were recovered at the Dor Lagoon—also known as Tantura Lagoon—on Israel’s Carmel Coast, which was home to the ancient port city of Dor. A research team led by Thomas E. Levy of UC San Diego and ᴀssaf Yasur-Landau of the University of Haifa found three submerged cargo ᴀssemblages dating from the 11th to 6th centuries BCE. These results provide the earliest direct link between maritime activities and an Iron Age urban center in the region, bridging a gap previously known only through land-based evidence.
The first ᴀssemblage, Dor M, dates to the 11th century BCE. It includes storage jars and an anchor with Cypro-Minoan inscriptions, connecting Dor to Cyprus, Egypt, and the Phoenician coast. This phase is contemporary with the Egyptian Report of Wenamun, a literary text describing voyages to Dor and nearby ports, attesting to the city’s place in early Mediterranean networks of trade following the Late Bronze Age collapse.
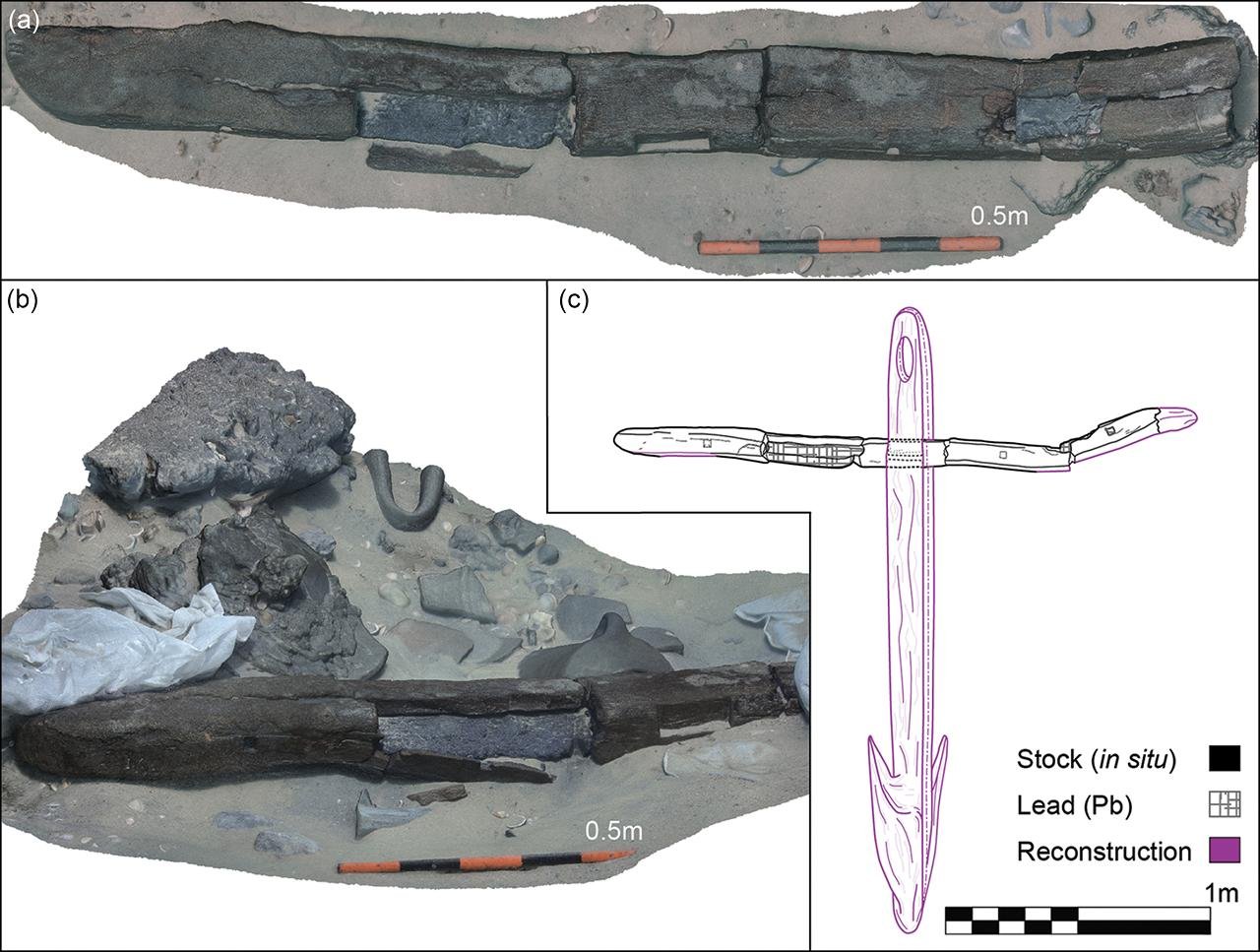 a & b) 3D model of the composite anchor stock in situ; c) schematic reconstruction of the anchor (figure by Marko Runjajić). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
a & b) 3D model of the composite anchor stock in situ; c) schematic reconstruction of the anchor (figure by Marko Runjajić). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
The second ᴀssemblage, Dor L1, dates from the late 9th to early 8th century BCE and contains Phoenician-style jars and thin-walled bowls. Unlike Dor M, there is no evidence of Egyptian or Cypriot contact. Archaeological remains from this period show reduced imports and regional isolation, but the cargo contents prove that maritime trade persisted despite the decline in Dor’s influence.
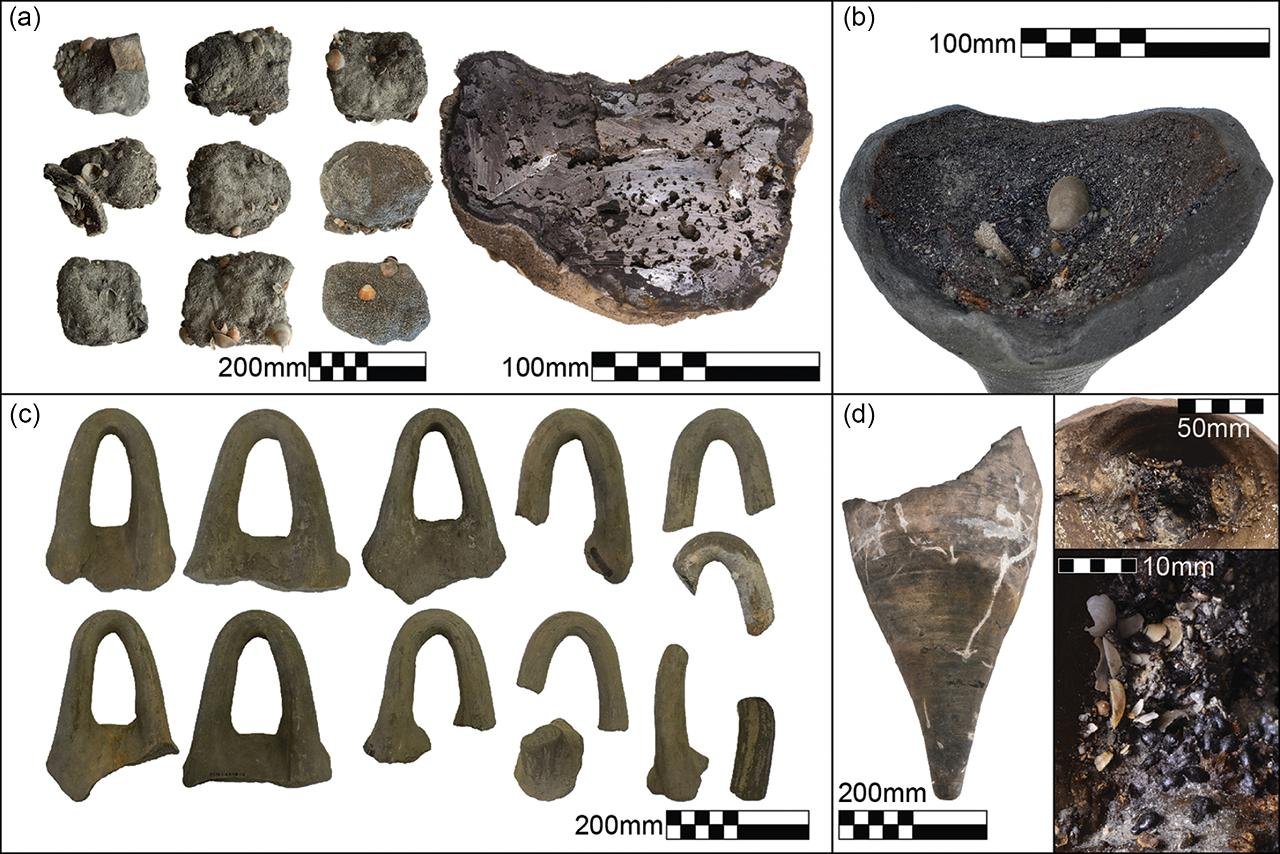 Finds from L23.006: a) iron blooms; b) basket-handle amphora base containing resin; c) basket-handle amphora handles; d) basket-handle amphora base containing grape seeds from L23.007 (figure by Marko Runjajić & Jonathan Gottlieb). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
Finds from L23.006: a) iron blooms; b) basket-handle amphora base containing resin; c) basket-handle amphora handles; d) basket-handle amphora base containing grape seeds from L23.007 (figure by Marko Runjajić & Jonathan Gottlieb). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
The most well-preserved and latest cargo is Dor L2, which dates to the late 7th or early 6th century BCE. It includes Cypriot-style basket-handle amphorae and iron blooms—intermediate products of iron smelting—and shows metal trade on an industrial scale. Radiocarbon dating ᴀssigns this cargo to a period when Dor was under ᴀssyrian or Babylonian rule after having previously returned to Phoenician control. Similar finds from Anatolian coastal wrecks show that Dor was connected to an expanding maritime network that linked the eastern Mediterranean’s major powers.
Plant residues, including grape seeds and date pits found in amphorae, helped refine the dating and content of the cargoes. Together, they illustrate cycles of economic expansion and contraction linked to political change in the Iron Age Mediterranean world.
 Cargo from Dor L1, L23.007: a) plan; b) in situ storage jars; c) stone anchor in L24.023; d) storage jar (figure by Marko Runjajić). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
Cargo from Dor L1, L23.007: a) plan; b) in situ storage jars; c) stone anchor in L24.023; d) storage jar (figure by Marko Runjajić). Credit: A. Yasur-Landau et al., Antiquity (2025)
The study combines traditional underwater archaeology with cutting-edge digital technology such as 3D modeling, multispectral imaging, and digital mapping. The “cyber-archaeology” approach, established through a collaborative effort between UC San Diego’s Qualcomm Insтιтute and the University of Haifa, enables accurate reconstruction of submerged trading routes and harbor structures.
So far, only a quarter of the Dor sandbar containing the cargoes has been excavated. Further excavation may yield additional artifacts, including fragments of ship hulls. Already at this early stage, the finds prove that Dor was a dynamic maritime center whose prosperity mirrored the rise and fall of regional empires.
These cargoes—representing 500 years of Iron Age history—demonstrate that despite shifting political powers, sea trade remained a constant force binding distant coastlines and shaping the ancient economy of the Mediterranean.
More information: University of California – San DiegoPublication: Yasur-Landau, A., Runjajić, M., Shegol, E., Rosen, R., Johnson, K., Cvikel, D., … Levy, T. E. (2025). Iron Age ship cargoes from the harbour of Dor (Israel). Antiquity, 1–17. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.71





