The remains of dozens of child sacrifice victims have been discovered in Peru, and many more are likely to be discovered, Live Science reported.
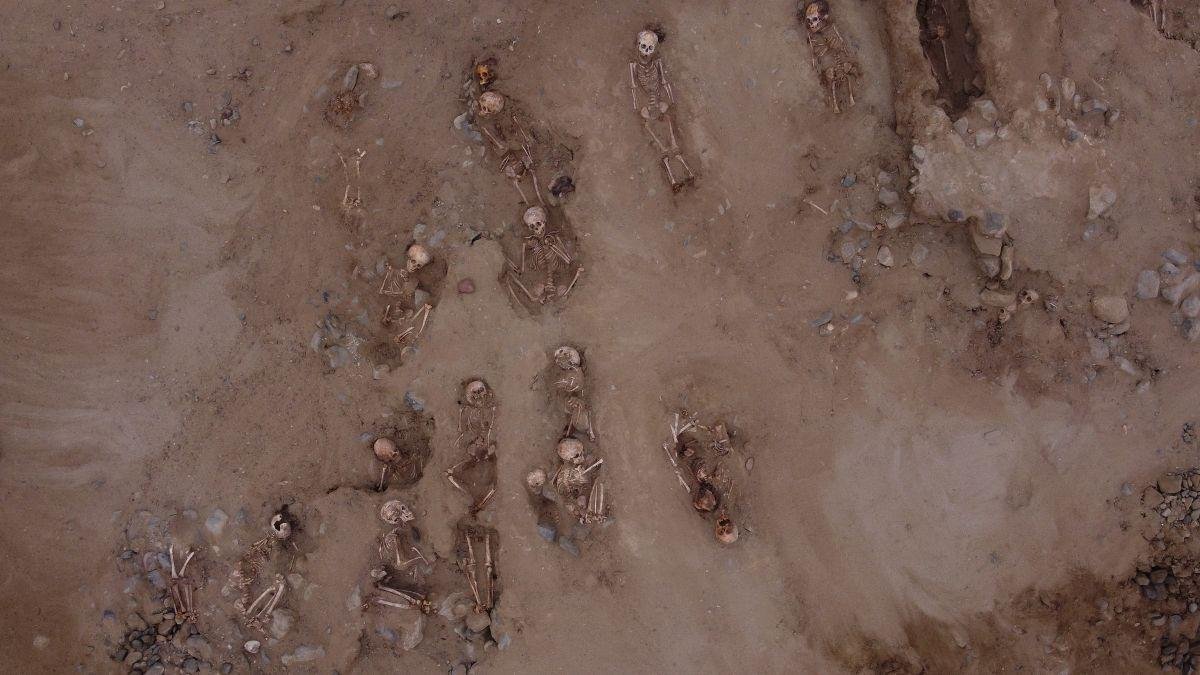 76 child sacrifices were recently discovered during ongoing excavations near Huanchaco, Peru. Image credit: Huanchaco Archaeological Program
76 child sacrifices were recently discovered during ongoing excavations near Huanchaco, Peru. Image credit: Huanchaco Archaeological Program
“These children were put to death by sacrifice. If you look at the skeleton, it is clear that the hearts of the children were taken out,” stated Gabriel Prieto, an ᴀssistant professor at the University of Florida, excavated at Pampa la Cruz near Huanchaco, where the children’s remains were discovered. “All 76 skeletons had a transversal clean cut, indicating that the rib cage was opened and then the heart was removed,” he explained.
“They have been buried on an extended position, with the feet toward the east,” Prieto told Reside Science in an e-mail. “They have been buried on top rated of an artificial mound.” It’s unclear why the sacrifices were placed in this position in this location. “We believed that the region, and specifically the mound, was no cost of Chimu kid sacrifices, but we located the opposite,” Prieto added.
So far, 323 children’s skeletons have been discovered. In addition, 137 other children and three adults were discovered at a nearby location known as Las Lamas.
Radiocarbon dating needs to be done on the 76 newly uncovered skeletons, but previously found victims at Pampa La Cruz dated between A.D. 1100 and 1200, Prieto said. Around this time, the Chimu people flourished in the area, known for their fine metalwork and the city Chan Chan.
It is unclear why the Chimu would have engaged in such large-scale child sacrifice in this area, but the Chimu also built an artificial irrigation system and new agricultural fields nearby, and some of the sacrifices may have been done to “sanctify” this agricultural system.
Human sacrifice was also practiced in Huanchaco during the first millennium A.D., said Richard Sutter, president of anthropology at Indiana University-Purdue University Fort Wayne and member of the Huanchaco team.
At the same time, scholars who did not participate in the excavation said that the discoveries in Huanchaco are significant. “what is striking here is the scale, of course,” Peter Eeckhout, a professor of pre-Columbian art and archaeology at Belgium’s Université libre de Bruxelles, told Live Science in an email.
It’s difficult to say why the child sacrifices were carried out, Eeckhout said, noting that writing was not used in Peru at the time, thus there are no written records detailing the children’s deaths. Climate or environmental changes that may have disrupted agriculture in the area, could have played a role in the sacrifice., Eeckhout said.
“It’s an incredible site with the potential to help us understand much better what was going on at this time in prehistory,” independent bioarchaeologist Catherine Gaither told Live Science in an email. “I think the reason for the sacrifices was likely related in some way to a cultural response to environmental changes that brought about significant cultural upheaval. There may have been ᴀssociations with environmental events like an El Niño, for example,” a climate cycle in which warm water in the Pacific Ocean shifts closer to South America causing changes in the weather, she said.
The team is requesting permission from Peru’s Ministry of Culture to transport some samples abroad for testing to determine more precise dates.





