Marine archaeologists surveying the bottom of Norway’s largest lake believe they have discovered the wreckage of a ship, the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment stated earlier this month.
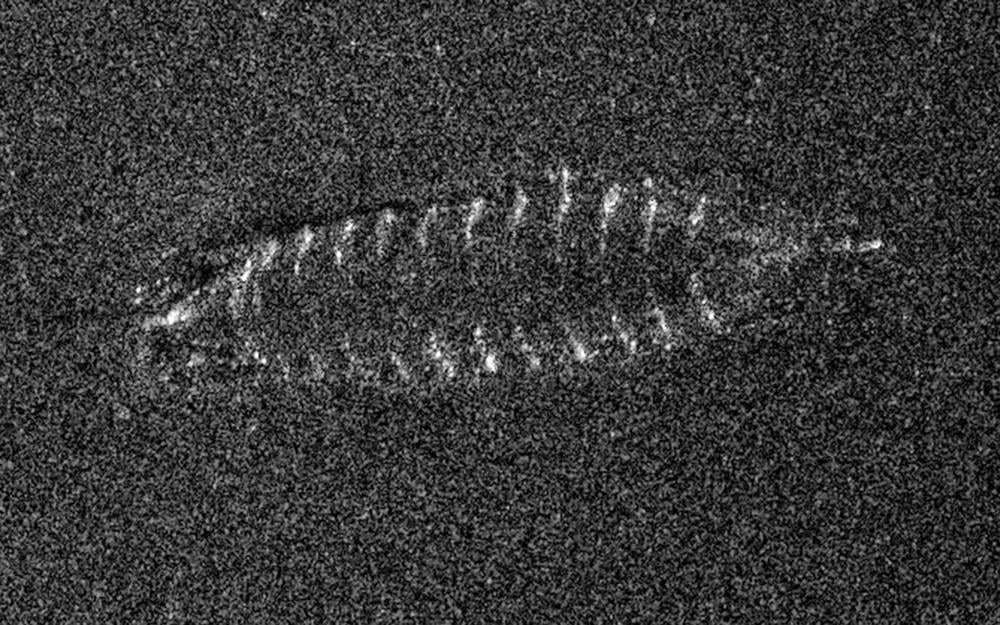 Sonar pictures show the wooden ship’s hull at a depth of about 1,350 feet (410 meters) beneath the surface of Lake Mjøsa. Credit: FFI/NTNU
Sonar pictures show the wooden ship’s hull at a depth of about 1,350 feet (410 meters) beneath the surface of Lake Mjøsa. Credit: FFI/NTNU
They believe the ship was built between 1300 and 1850. Sonar pictures show the wooden ship’s hull at a depth of about 1,350 feet (410 meters) beneath the surface of Lake Mjøsa, about 60 miles (100 kilometers) north of the Norwegian capital.
Since at least the Viking Age (the eighth to 11th centuries), the lake has also served as a vital trade route between wealthy communities.
Based on the fact that the stern of the ship was distinct from the bow, archaeologists believe the ship was built after 1300. Viking ships are much more likely to be similar on both ends and to date before 1300. Other features distinguishing this ship from a Viking one include it having a central rudder, whereas a Viking ship’s rudder or steering oar would most likely be on the starboard side of the hull.
“Because this is a freshwater lake, the wood in such a ship is preserved,” Øyvind Ødegård, a maritime archaeologist at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, told Science Norway. “The metal may rust, and the ship may lose its structure, but the wood is intact. A similar ship to the one we now found would not have survived for more than a few decades if it had gone down on the coast,” he added.
Ødegård is part of a project led by the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI) and NTNU to find and map hundreds of tons of surplus ammunition dumped in Lake Mjøsa from the 1940s to the 1970s.
“Finding the wreck was almost a byproduct of the original mission to map dumped munitions,” he said. “I expected to find some things — that’s why I was participating in the project.
The two-week mapping only covered about 40 square kilometers of the lake’s 360 square kilometers. More ships may be discovered in the coming days as the researchers analyze more of the data collected, or during the next field trip in the spring.
“Finding the wreck was almost a byproduct of the original mission to map dumped munitions,” Ødegård tells Live Science’s Tom Metcalfe. “I expected to find some things—that’s why I was participating in the project.”
“If we are going to find a Viking shipwreck in Norway, then Mjøsa is probably the place with the most potential for such a find,” he said.





