Archaeologists discovered an unfinished ancient Egyptian tomb with a chapel exactly aligned with the sunrise on the winter solstice. This crypt is said to have been built some 3,800 years ago by ancient architects.
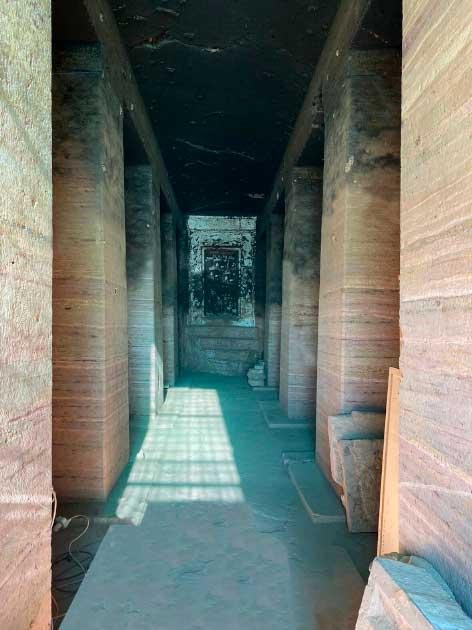 The tomb’s chapel, part of which is seen here. Credit: University of Jaén and Málaga
The tomb’s chapel, part of which is seen here. Credit: University of Jaén and Málaga
Scholars say this is the oldest known tomb in Egypt that is aligned with the winter solstice, revealing that ancient Egyptian architects were “enormously skilled” and had “extensive knowledge of the solar cycle.”
According to Phys.org, archaeologists from the UJA excavated the tomb between 2008 and 2018. Since that time, it has been studied by researchers with different specializations.
The tomb is located in the necropolis of Qubbet el-Hawa, which lies 500 kilometers south of Cairo on the bank of the Nile River.
It was constructed during Egypt’s 12th dynasty, known as the “Middle Kingdom.” Many of the treasures put in the tomb, including the governors’ mummies, were plundered by graverobbers in ancient times.
The tomb’s entrance is precisely orientated to the winter solstice sunrise, which happens on December 21, so the sun’s rays land on a section designed to house a statue.
The winter solstice was significant for the ancient Egyptians since it marked the shortest day of the year.
“The winter solstice marked the beginning of the daily victory of light against darkness, culminating in the summer solstice, the longest day on the earthly plane,” study lead author María Dolores Joyanes Díaz, a researcher at the University of Málaga in Spain, told Live Science.
According to the team’s study published in the journal Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry, the tomb’s chapel features a niche that was originally intended to house a statue of the ruler who erected the tomb.
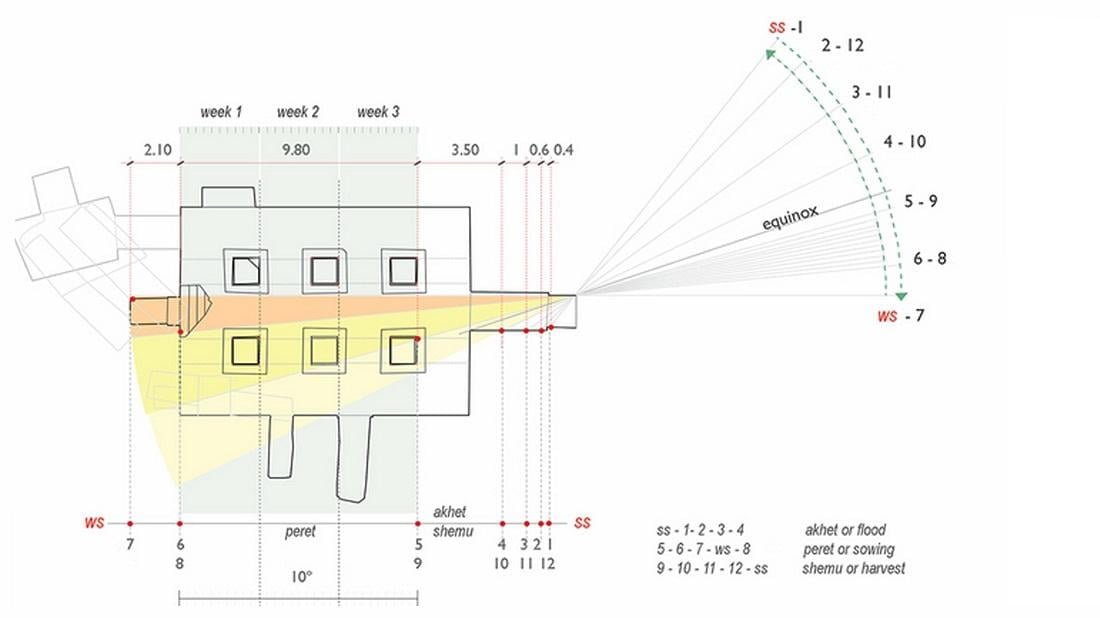 The tomb and the statue were never completed, study co-author Alejandro Jiménez-Serrano, an Egyptologist and archaeologist at the University of Jaén, who directs the team’s excavations at the site, told Live Science in an email.
The tomb and the statue were never completed, study co-author Alejandro Jiménez-Serrano, an Egyptologist and archaeologist at the University of Jaén, who directs the team’s excavations at the site, told Live Science in an email.
Just outside the tomb, the team discovered an incomplete statue that was supposed to be completed and put in the niche, said Jiménez-Serrano added, noting that it’s unclear why the tomb was left unfinished.
More information: Joyanes-Díaz, M., Martínez-De Dios, J., Mozas-Calvache, A., Ruíz-Jaramillo, J., Muñoz-González, C., & Jiménez-Serrano, A. (2022). solar geometry and the organization of the annual cycle through architecture and the funerary landscape in Qubbet el Hawa. Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6815469
Tags: Ancient EgyptArchaeoastronomy





