An excavation at Tell Timai in northern Egypt has unearthed evidence of a battleground fought over between the ancient Egyptians and the Ptolemaic Kingdom, which is mentioned in the Rosetta Stone.
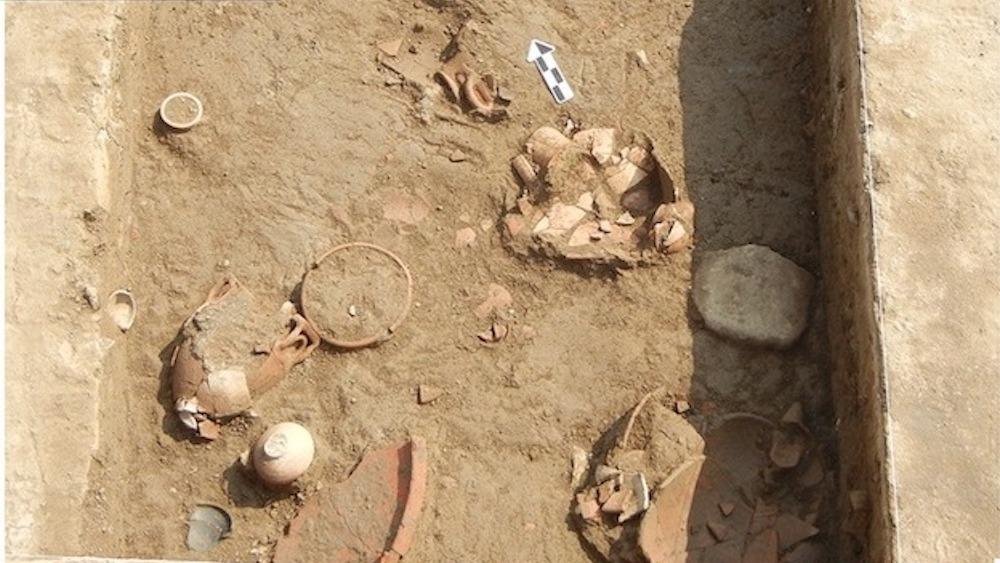 A view of the Tell Timai excavation site littered with pottery shards and other artifacts. Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
A view of the Tell Timai excavation site littered with pottery shards and other artifacts. Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
Archaeologists have long known about the Great Revolt, a battle between the ancient Egyptians and the Ptolemaic Kingdom that lasted from 207 BCE to 184 BCE.
The Rosetta Stone is a granodiorite stele inscribed with three versions of a decree issued in Memphis, Egypt, in 196 BCE during the Ptolemaic dynasty. This stele contains a wealth of information about life in Ptolemaic Egypt.
Archaeologists have now identified the exact location of one of the revolt’s battles. Archaeologists began excavating at the site in 2009, where an ancient Greco-Roman industrial city called Thmouis was located on Egypt’s Nile Delta. The team’s findings were published in the Journal of Field Archaeology on December 27, 2022.
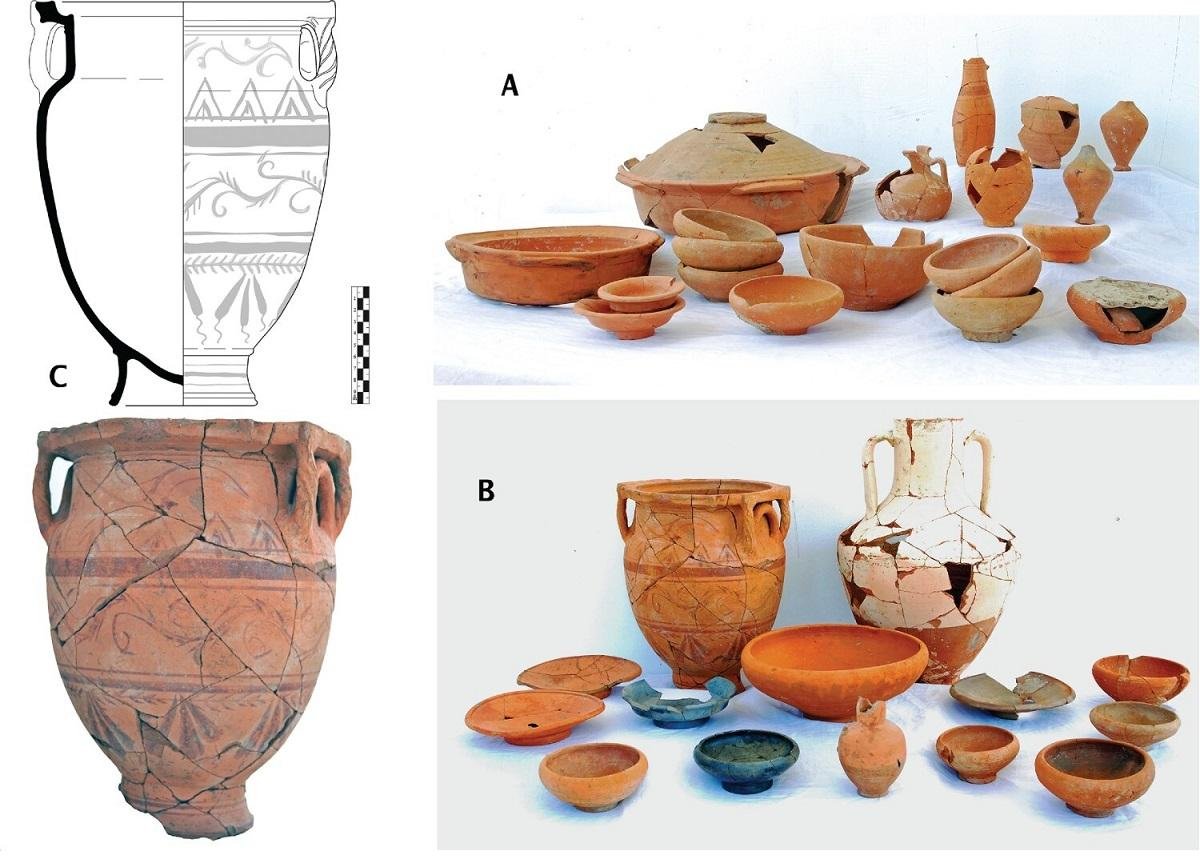 A) Deposit B ceramic ᴀssemblage; B) Deposit C ceramic ᴀssemblage; and, C) column krater from Deposit C (Hudson 2016a). Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
A) Deposit B ceramic ᴀssemblage; B) Deposit C ceramic ᴀssemblage; and, C) column krater from Deposit C (Hudson 2016a). Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
Jay Silverstein, project co-director and an archaeologist and senior lecturer at Nottingham Trent University, said that traces of burned buildings, weapons, stones thrown by siege engine, hidden coins, and a broken statue have been found at the site of the ancient city of Thmuis.
“At first I was seeing things that piqued my curiosity and began to realize that we were looking at the destruction layer,” Silverstein told Live Science. “And then we started finding bodies
Using some of the artifacts recovered from the site, including coins found from beneath a home’s floorboards, along with the discovery of an abandoned kiln complex where pottery was produced, archaeologists were able to better determine the time period of the battle based on when the coins were minted.
Unburied bodies were also discovered: the remains of a young man were unearthed with his legs sticking out of a kiln, while the body of a man in his 50s was found sitting upright after a fight to the death.
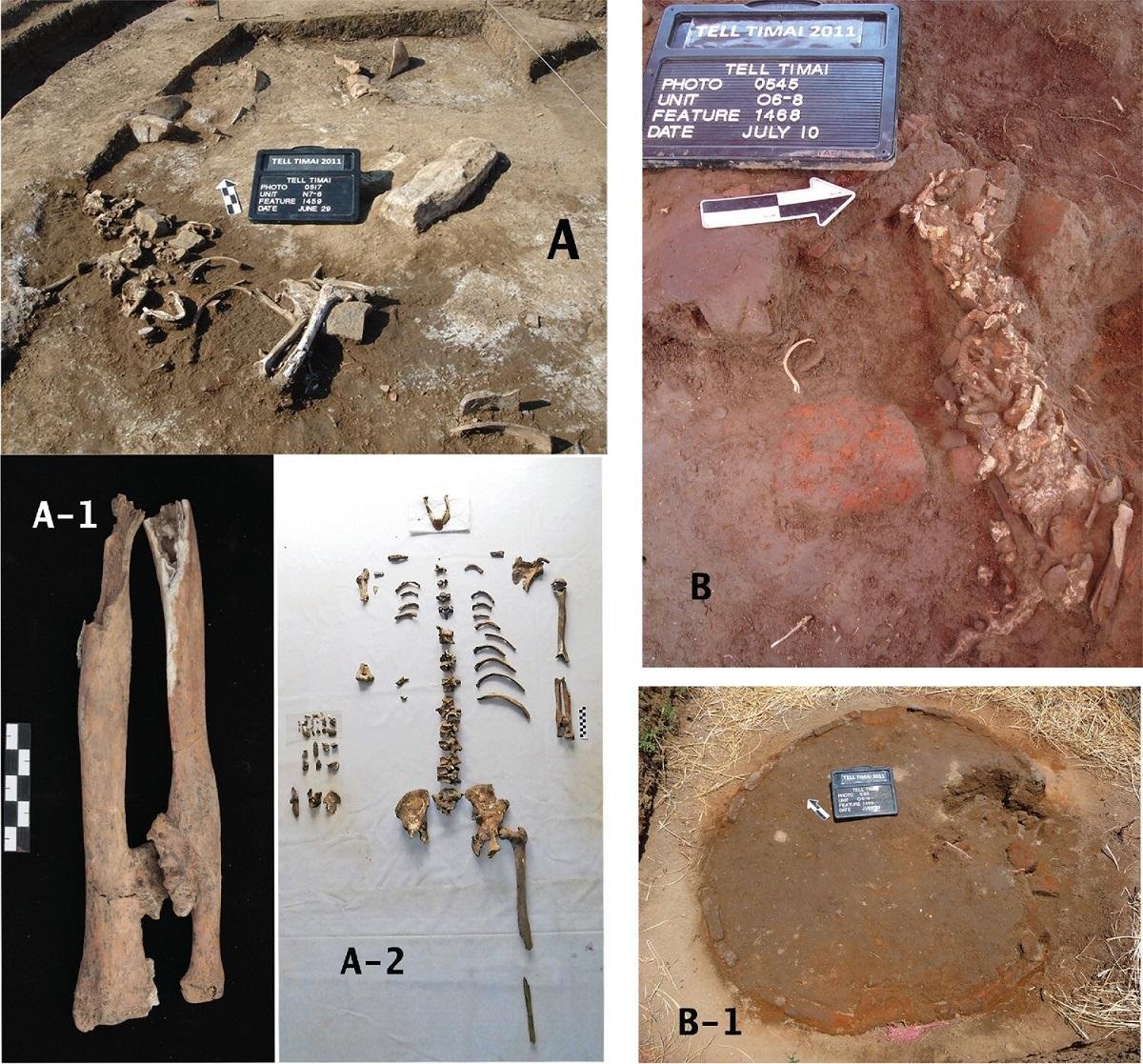 A) Remains recovered from N7-6-F1461: A-1) remains from N7-6-F1461 in anatomical position and A-2) closeup of left forearm. B) Remains recovered from the kiln at O6-8: B-1) post-excavation of remains at Kiln O6-8 showing that remains are aligned with the kiln opening in the southeast. Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
A) Remains recovered from N7-6-F1461: A-1) remains from N7-6-F1461 in anatomical position and A-2) closeup of left forearm. B) Remains recovered from the kiln at O6-8: B-1) post-excavation of remains at Kiln O6-8 showing that remains are aligned with the kiln opening in the southeast. Credit: J. Silverstein, R. Littman
“Archaeological evidence from the [revolt] is quite rare,” Silverstein told The Art Newspaper. “There are of course a number of decrees and inscriptions, like the Rosetta Stone, some historical accounts, and a few papyri with indirect references,” he explained.
“But when it comes to finding the locations where the sword meets the bone, as far as I can tell, this is the first that has been recognized.”
 The Rosetta Stone is currently housed in The British Museum. Credit: Hans Hillewaert via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0.
The Rosetta Stone is currently housed in The British Museum. Credit: Hans Hillewaert via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0.
“The evidence of conflict and destruction at northern Thmouis is unequivocal, and the timing is well-placed … and thus coincides with the Great Revolt,” the study authors wrote in their paper.





