Archaeologists excavating in France have discovered evidence of a 6,300-year-old fortified compound and residential site used by Europe’s first megalithic builders.
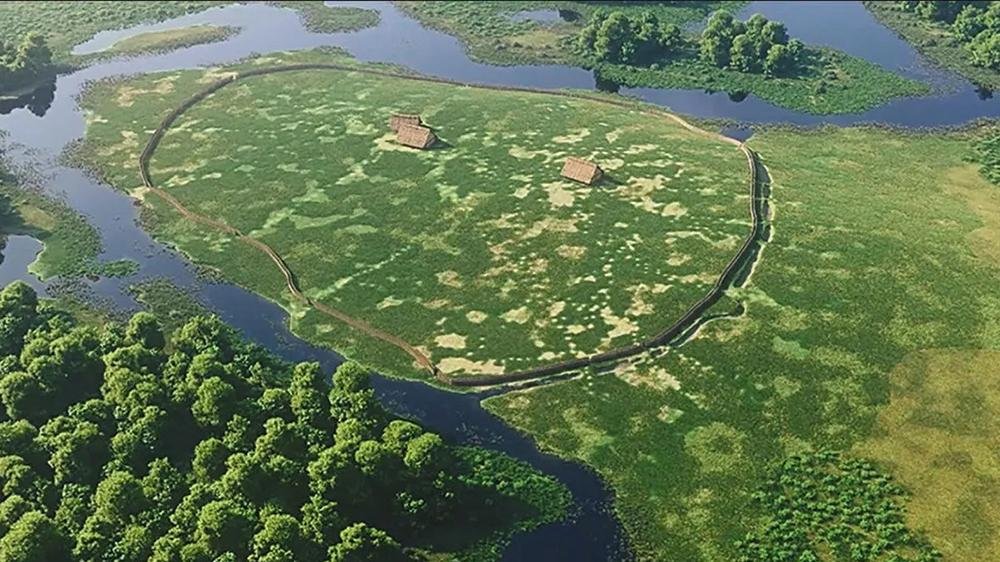 3D reconstruction of the enclosure of Le Peu and its environment from archaeological data. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
3D reconstruction of the enclosure of Le Peu and its environment from archaeological data. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
People in west-central France built barrows and dolmens during the Neolithic period, and the people who built these structures have long been admired for their engineering prowess. Archaeologists have been trying to figure out where they lived for over a century.
A team of researchers has now identified the elusive Le Peu enclosure in southwestern France as where some of them lived. The site was discovered in 2011.
The researchers discovered evidence of an early settlement during an aerial survey of the Le Peu enclosure. Their findings were published in the journal Antiquity, along with a digital reconstruction of the site where these megalithic workers lived, just a few kilometers from their work site.
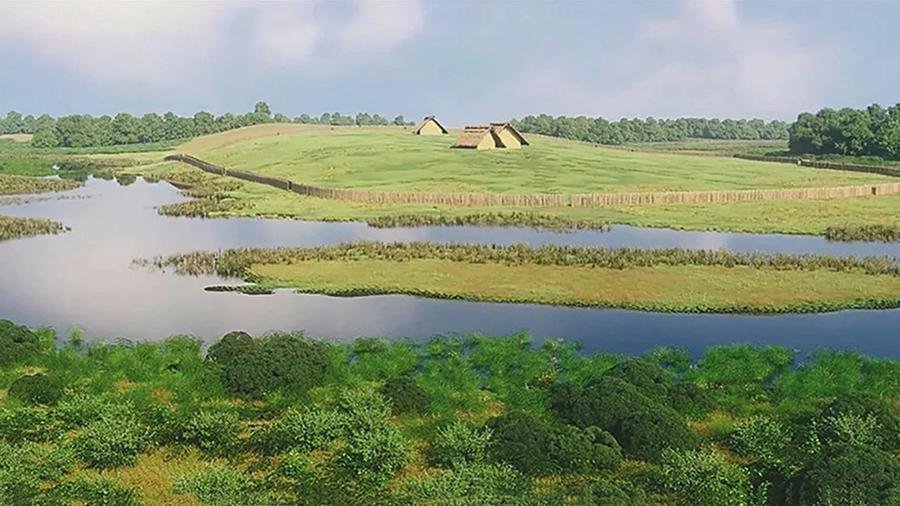 3D reconstruction of the enclosure of Le Peu and its environment from archaeological data. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
3D reconstruction of the enclosure of Le Peu and its environment from archaeological data. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
The study uncovered a palisade encircling several timber homes built during the fifth millennium BC. At least three homes, each about 13 meters long, were discovered clustered together near the top of a small hill surrounded by the palisade.
This makes them the region’s oldest wooden structures and the first residential site contemporary with the Neolithic monument builders.
The researchers put together information about the settlement, the people who lived there, and potential cause of the site’s destruction. An analysis of the palaeosols recovered from the site suggests that it was located on a promontory bordered by marsh. These natural defenses were reinforced by a ditch palisade wall with two monumental structures guarding the enclosure’s entrance.
About 4,400 BC, all of the buildings at the site were destroyed by fire, suggesting that the defenses at Le Peu weren’t able to defend the inhabitants during a conflict.
“In fact, this fortified compound at the Le Peu archaeological site near Charmé, a village in southwestern France, is one of hundreds of enclosures erected between the Loire and Dordogne rivers thousands of years ago,” said Dr. Vincent Ard from the French National Centre for Scientific Research, lead author of a paper published Tuesday in the journal Antiquity.
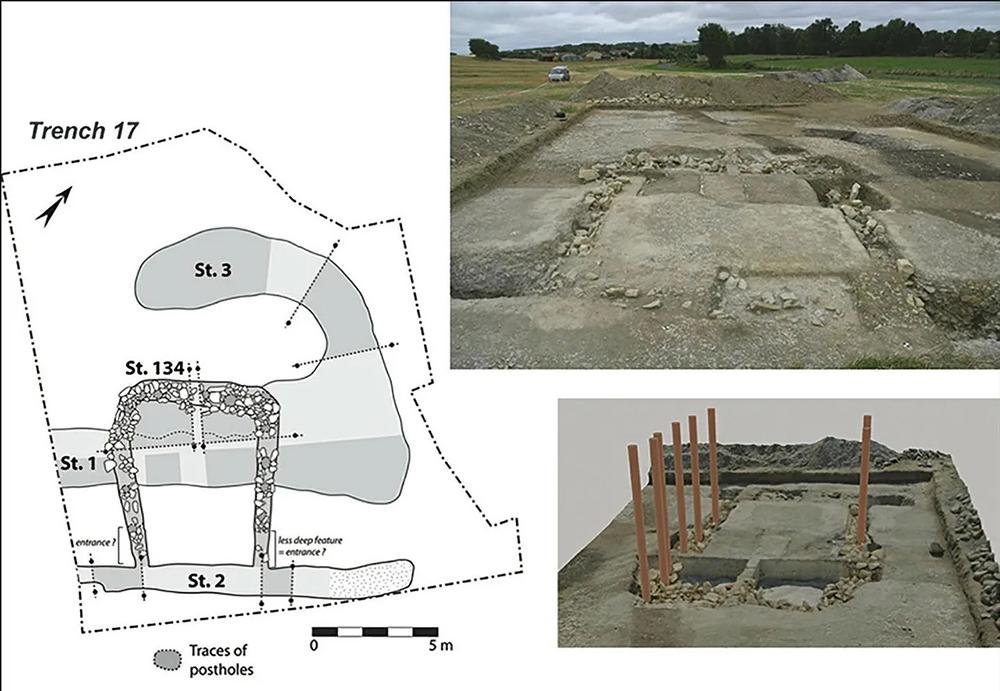
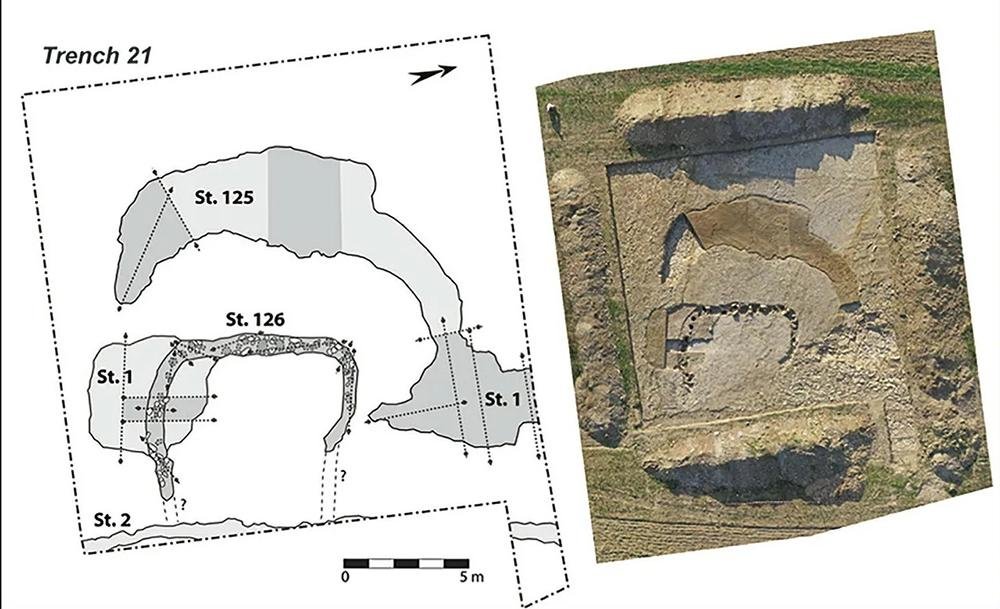 Plans and views of the entrances to two of the monumental buildings. CAD: V. Ard; orthopH๏τography and 3D model: A. Laurent. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
Plans and views of the entrances to two of the monumental buildings. CAD: V. Ard; orthopH๏τography and 3D model: A. Laurent. Credit: Vincent Ard et al / Antiquity Publications Ltd
Radiocarbon study has been done at these sites, he said, but he and his colleagues believe the Le Peu enclosure, the homes, and palisade date back to the fourth or fifth millennium B.C.E.
Researchers are divided as to whether such monumental construction arose independently in Europe or spread from the Near East, where impressively mᴀssive stone complexes first appeared at least 12,000 years ago; anyway, for decades archaeologists have questioned how the people who built these things lived.
“The site reveals the existence of unique monumental architectures, probably defensive. This demonstrates a rise in Neolithic social tensions,” Dr. Ard added.
More information: Ard, V., Onfray, M., Aoustin, D., Bouchet, É, Bruniaux, G., Dandurand, G., . . . Vitté, H. (2023). The emergence of monumental architecture in Atlantic Europe: A fortified fifth-millennium BC enclosure in western France. Antiquity, 97(391), 50-69. doi:10.15184/aqy.2022.169





