Neanderthals, our ancient relatives, were not just simple cave dwellers, but rather complex beings with symbolic and artistic expression. Recent research has unveiled the oldest known engravings made by Neanderthals on a cave wall in La Roche-Cotard, France.
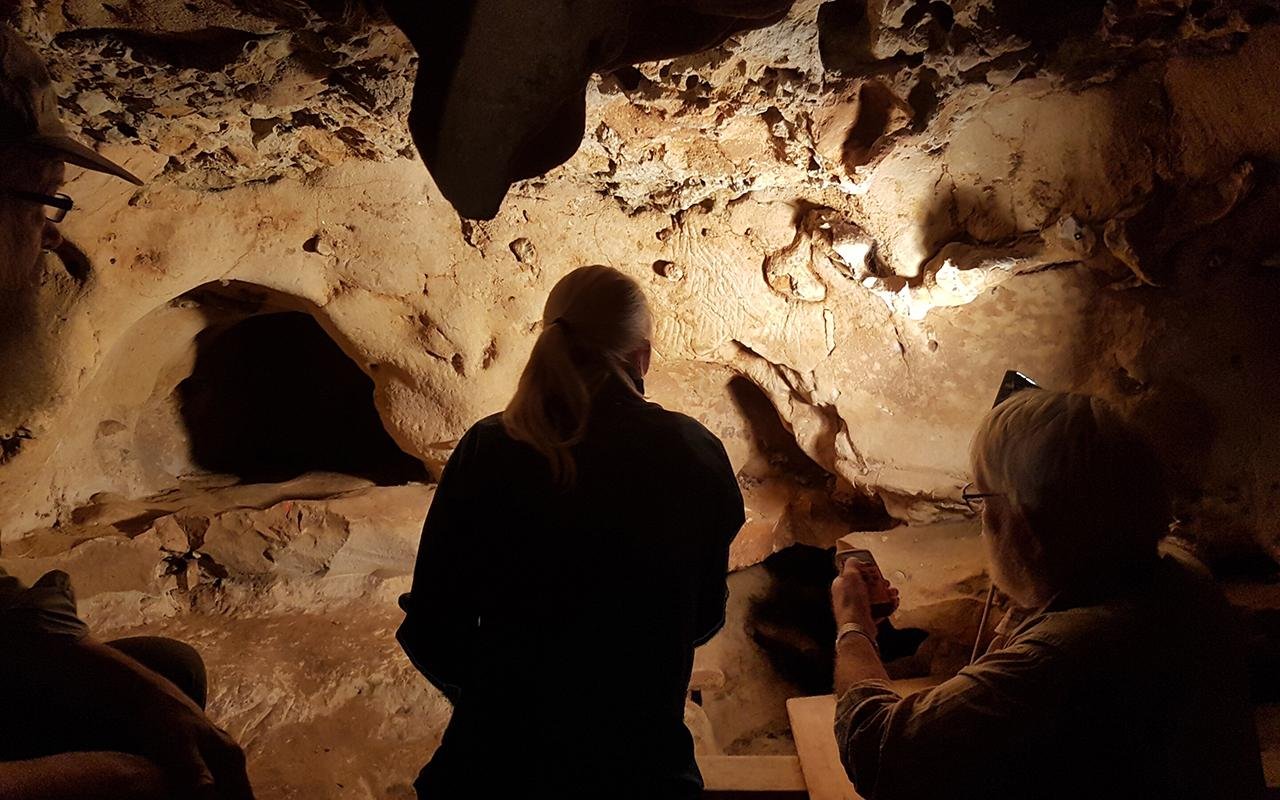 Scientists discuss the Neanderthal markings on the walls of the cave. Credit: Kristina Thomsen, CC-BY 4.0
Scientists discuss the Neanderthal markings on the walls of the cave. Credit: Kristina Thomsen, CC-BY 4.0
The study, published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, confirms that these markings are deliberate, organized, and intentional shapes created by human hands.
The cave, discovered in 1846 during quarrying work, has revealed fascinating insights into the lives of Neanderthals. While previous excavations in 1912 uncovered animal bones and Neanderthal stone tools, it was only in recent decades that the full extent of the cave and its significance became apparent.
The third chamber of the cave features hundreds of finger flutings, non-figurative markings made by running fingers across the soft brown film that covers the crumbly limestone walls.
By analyzing the shape, spacing, and arrangement of these engravings, researchers concluded that they were purposeful creations.
The team used pH๏τogrammetry to create 3D models of the markings and compared them with known human and experimental markings, further confirming their intentional nature. The sediments within the cave were dated using optically-stimulated luminescence dating, showing that the cave became sealed off around 57,000 years ago, well before the arrival of Homo sapiens in the region.
Additionally, the stone tools found in the cave belong to the Mousterian technology, typically ᴀssociated with Neanderthals, providing strong evidence that these engravings were indeed the work of Neanderthals.
The significance of these non-figurative symbols and their intended meaning remains unclear. However, their age places them in the same timeframe as cave engravings made by Homo sapiens in other parts of the world, suggesting that Neanderthals’ behavior and activities were similarly complex and diverse as those of our own ancestors.
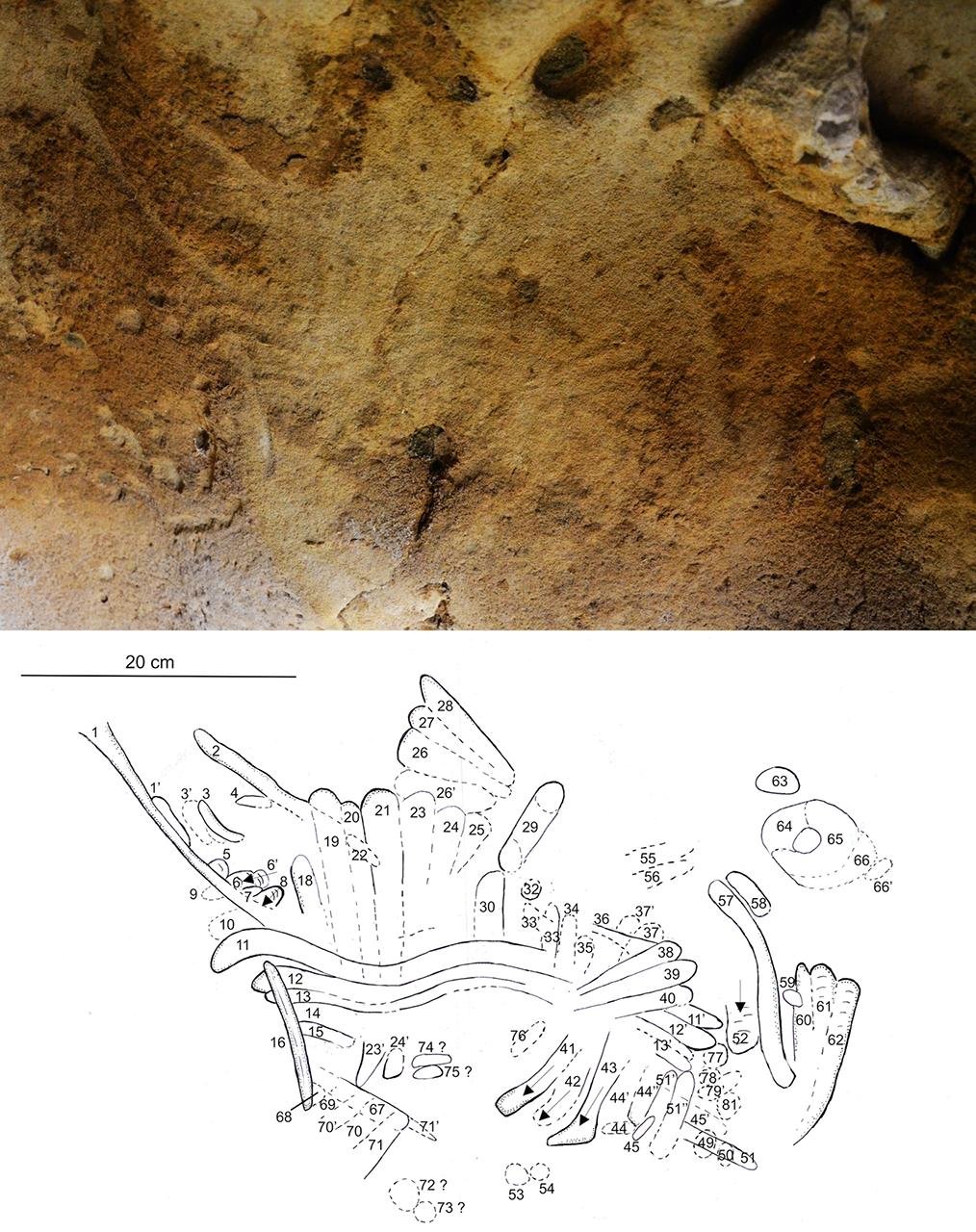 A line drawing of the cave engravings. The arrows indicate the direction of the pᴀssage of the finger.. Credit: Marquet et al, PLoS ONE 2023
A line drawing of the cave engravings. The arrows indicate the direction of the pᴀssage of the finger.. Credit: Marquet et al, PLoS ONE 2023
The discovery of these engravings makes La Roche-Cotard the oldest decorated cave in France, if not all of Europe.
Jean-Claude Marquet, one of the archaeologists involved in the research, acknowledges that understanding the meaning behind these ancient Neanderthal tracks is challenging. Nevertheless, he emphasizes the importance of such discoveries in recognizing and appreciating our shared history with Neanderthals, even though we are genetically distinct from them.
The findings from La Roche-Cotard contribute to a broader shift in our understanding of Neanderthals’ capabilities and cultural complexity. While they were previously underestimated and considered simple beings, recent studies have demonstrated their diverse skill set.
For instance, evidence suggests that Neanderthals regularly hunted elephants using stone tools and even hunted crabs in rock pools in Portugal. The discovery of these ancient engravings adds further weight to the argument that Neanderthals were capable of complex and intentional artistic expression.
More information: Marquet J-C, Freiesleben TH, Thomsen KJ, Murray AS, Calligaro M, Macaire J-J, et al. (2023). The earliest unambiguous Neanderthal engravings on cave walls: La Roche-Cotard, Loire Valley, France, PLOS ONE. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286568.





