In a recent study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 15, 2023, researchers from the Austrian Academy of Sciences, led by Lyndelle Webster, have unveiled new radiocarbon dates that provide detailed insights into the ancient city of Gezer.
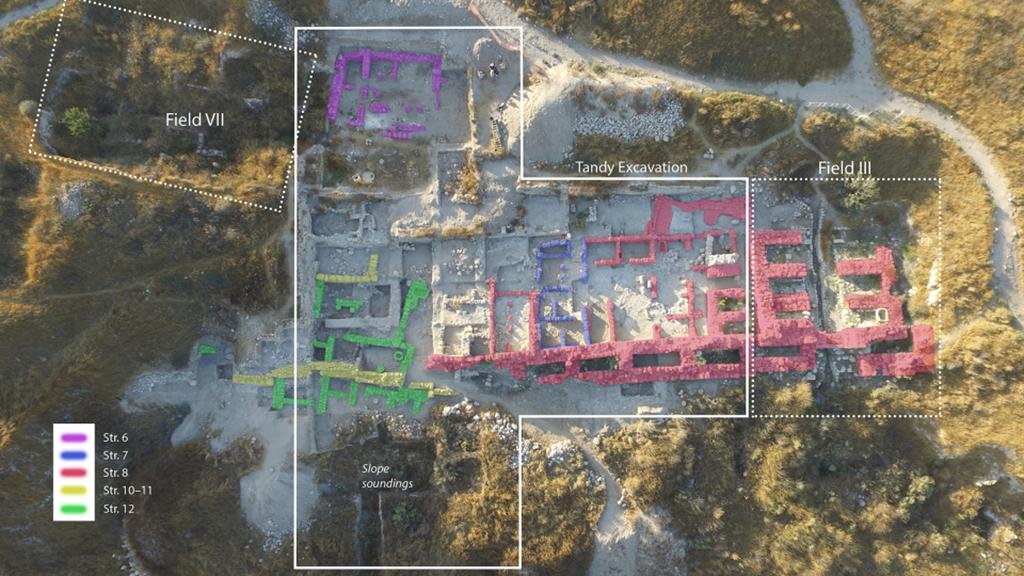 The chronology of Gezer from the end of the late bronze age to iron age II. Credit: PLOS ONE, Lyndelle Webster and colleagues
The chronology of Gezer from the end of the late bronze age to iron age II. Credit: PLOS ONE, Lyndelle Webster and colleagues
Gezer, a southern Levantine city mentioned in Egyptian, ᴀssyrian, and Biblical texts, has long been ᴀssociated with power struggles, conquests, and historical figures such as Joshua and Solomon.
The importance of Gezer lies in its strategic location at the crossroads of the ancient coastal trade route connecting Egypt with Syria, Anatolia, and Mesopotamia, as well as the road to Jerusalem and Jericho. The city, now a national park and archaeological site, has revealed a rich archaeological record spanning the Bronze Age and Iron Age.
The recent excavations at Gezer, have unearthed a continuous stratigraphic sequence, offering a unique opportunity to establish an absolute chronology for the city’s events. The findings, which include over 35 radiocarbon dates obtained from organic materials like seeds across seven distinct stratigraphic layers, span from the 13th to the 9th centuries BCE. This critical timeframe covers various transformative events in Gezer, such as destructive episodes, rebuilding phases, and fortifications.
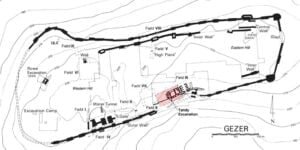 Location of the Tandy excavation relative to previous archaeological fieldwork at Gezer. Credit: Webster et al., PLOS ONE, 2023
Location of the Tandy excavation relative to previous archaeological fieldwork at Gezer. Credit: Webster et al., PLOS ONE, 2023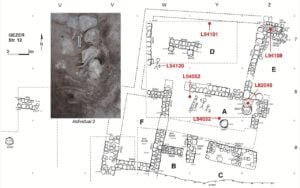 Plan of Tandy excavation stratum 12B elite residence with radiocarbon dated contexts marked. Credit: Webster et al., PLOS ONE, 2023
Plan of Tandy excavation stratum 12B elite residence with radiocarbon dated contexts marked. Credit: Webster et al., PLOS ONE, 2023
One key aspect highlighted by the study is the correlation between certain events and figures mentioned in ancient texts. For instance, the research suggests a plausible connection between a destructive episode and the actions of the pharaoh Merneptah, while discounting the proposed link between another episode and the campaign of Hazael.
Webster emphasizes the significance of this research, stating, “The development of a radiocarbon-based chronology at Tel Gezer illustrates the crucial role radiocarbon dating can and must play in reconstructing individual site histories, resolving long-running debates and testing possible correlations between archaeological remains and written sources.”
Gezer’s idenтιтy as “Tell Jezer” is supported by boundary inscriptions and impressive remains, providing an opportunity to compare text and archaeology. The city is mentioned in Egyptian, ᴀssyrian, and biblical texts, each carrying varying weight for reconstructing history. While Egyptian and ᴀssyrian texts are generally accepted as describing real events, biblical texts, written centuries later, spark debates over the historical realities behind them.
The collaborative efforts of Austrian archaeologists, led by Lyndelle Webster, have provided a groundbreaking radiocarbon dataset that not only refines the absolute chronology of Gezer but also contributes significantly to the broader understanding of the interplay between archaeological remains and ancient texts in the southern Levant.
More information: Webster LC, Wolff SR, Ortiz SM, Barbosa M, Coyle C, Arbino GP, et al. (2023) The chronology of Gezer from the end of the late bronze age to iron age II: A meeting point for radiocarbon, archaeology egyptology and the Bible. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293119.





