Archaeologists have unearthed relics, including stone-casting molds for bronze artifacts, at the Yoshinogari ruins in the western prefecture of Saga, Japan, potentially making them the oldest of their kind in the country.
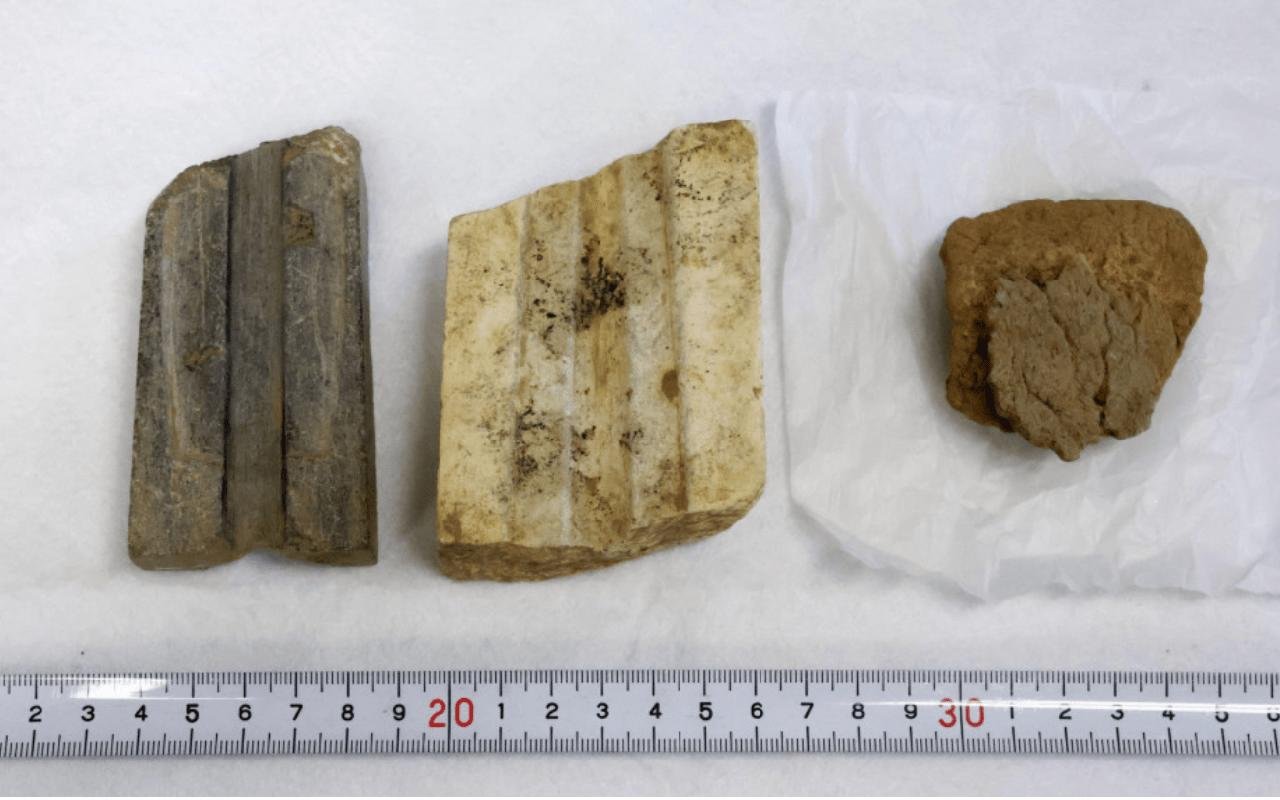 This pH๏τo shows relics — stone molds to cast bronze artifacts and a piece of clay vessel (right) — discovered at the Yoshinogari ruins in Japan. Credit: Saga Prefectural Government
This pH๏τo shows relics — stone molds to cast bronze artifacts and a piece of clay vessel (right) — discovered at the Yoshinogari ruins in Japan. Credit: Saga Prefectural Government
The local government revealed that one of the molds could potentially date back to around 200 BCE, aligning with the Yayoi period in Japanese history, known for its cultural advancements spanning from 300 BCE through 250 BCE.
This discovery comes after a series of excavations conducted between September and October, following the finding of a stone coffin tomb in April believed to have belonged to an individual of high status. The mysterious coffin raised questions among experts, igniting speculation about its occupant and contributing to the ongoing debate over the location of Japan’s ancient Yamatai kingdom. However, a subsequent announcement in June stated that no human bones or burial accessories providing clues to the occupant’s idenтιтy or the burial period were found.
The latest excavation in the designated “mystery area,” previously inaccessible due to the presence of a shrine, revealed three remarkable items from the Yayoi period – casting molds made of serpentinite and quartz-porphyry, along with a clay vessel used to contain molten metal. These molds, possibly employed in the casting of swords and spears, were discovered within a range of about 5 to 10 meters from where the stone coffin was unearthed.
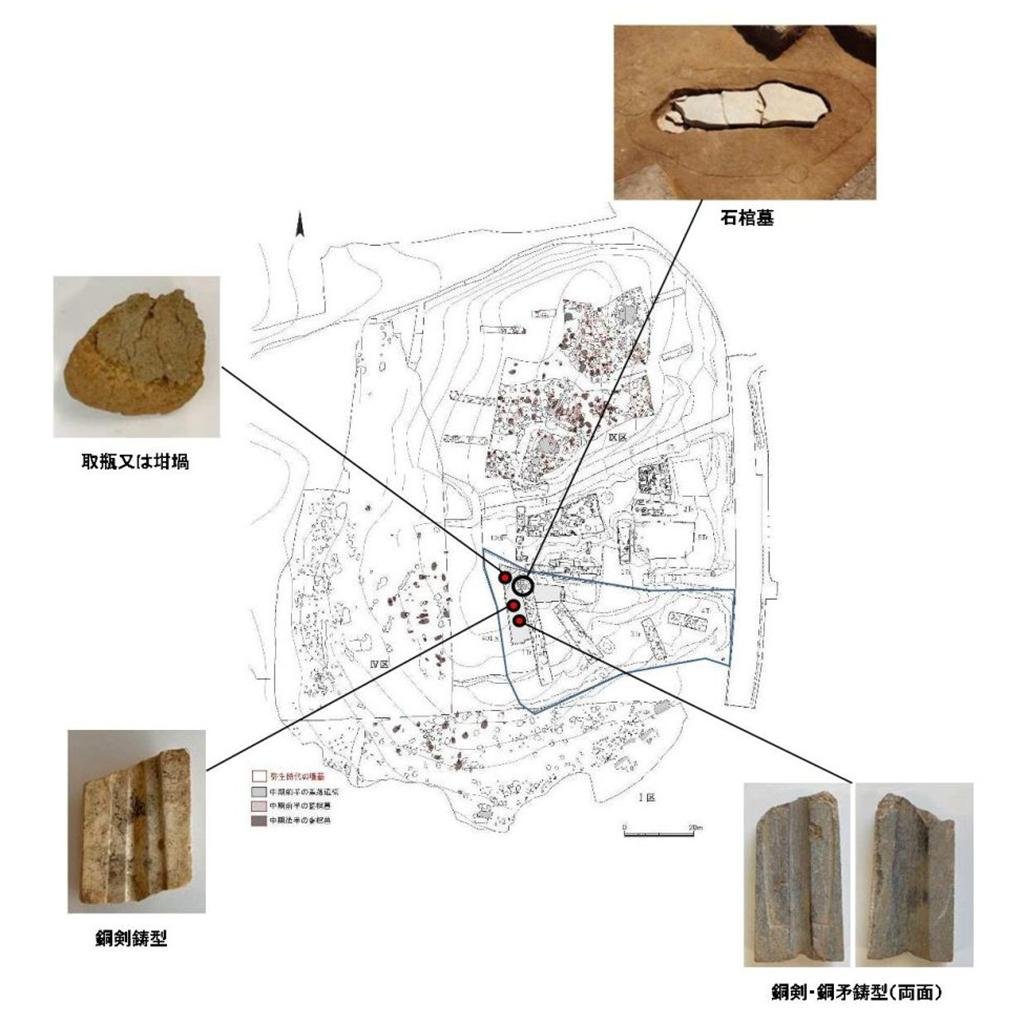 Location of items related to bronze casting at the Yoshinogari ruins. Credit: Saga Prefectural Government
Location of items related to bronze casting at the Yoshinogari ruins. Credit: Saga Prefectural Government
Chuhei Takashima, an archaeologist specializing in the Yoshinogari ruins, noted the significance of the find, stating that the serpentinite molds likely preceded those made of quartz-porphyry. He suggested that this technological shift could have been influenced by the Korean Peninsula, adding depth to the understanding of Yoshinogari as a site for manufacturing bronze artifacts and introducing advanced technology during the Yayoi period.
“It is an extremely significant discovery in understanding distinct features of the structure (of ruins) and the changes,” emphasized a prefectural official, highlighting the importance of these artifacts in unraveling the history and transformations of the Yoshinogari site.
The Yoshinogari ruins, designated a national historic site in 1991, currently welcome visitors as the Yoshinogari Historical Park.





