A team of archaeologists, geologists, and historians from various Spanish insтιтutions has uncovered the remarkable engineering prowess behind the Menga Dolmen, an ancient burial mound near Antequera, Málaga, Spain.
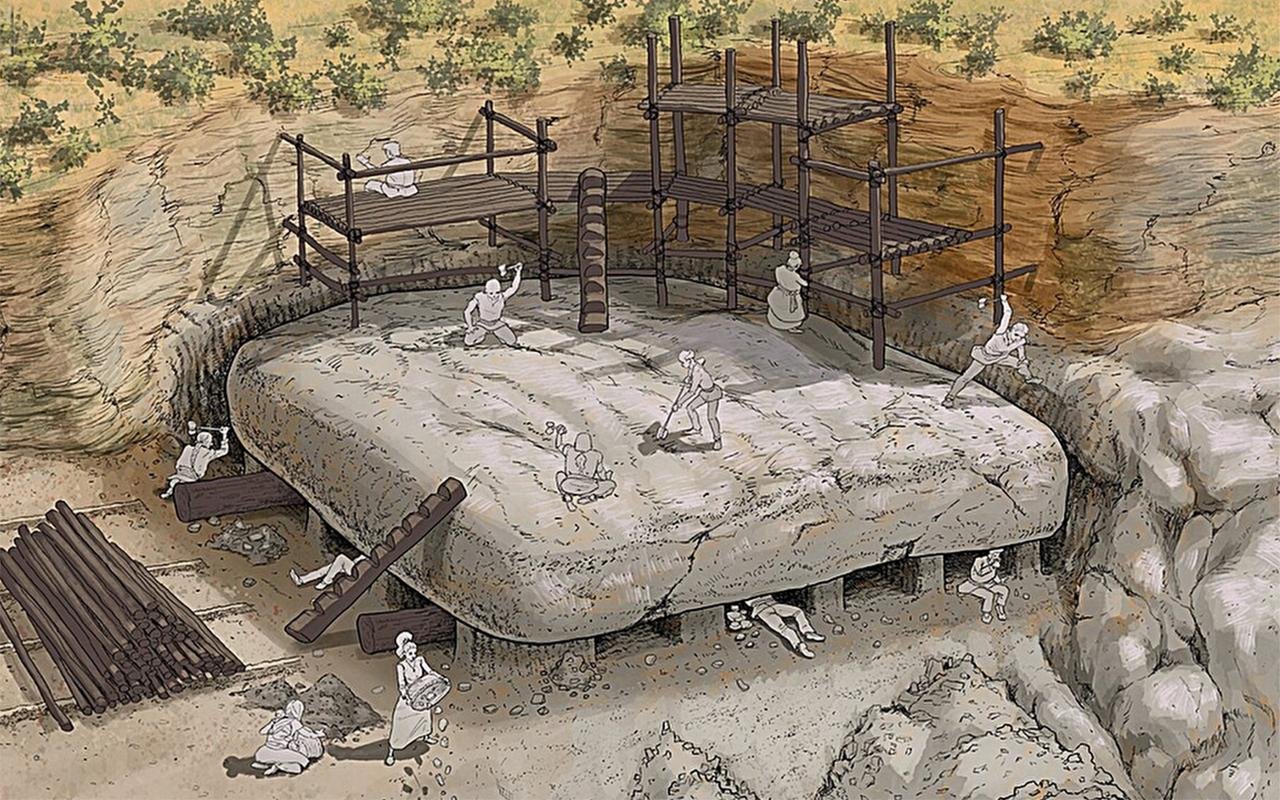 Artistic representation of quarrying activities for the extraction the capstone C-5 in Cerro de la Cruz Quarry, Drawing: Moisés Bellilty under guidance of José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez and Leonardo García Sanjuán. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
Artistic representation of quarrying activities for the extraction the capstone C-5 in Cerro de la Cruz Quarry, Drawing: Moisés Bellilty under guidance of José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez and Leonardo García Sanjuán. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
Published in Scientific Reports, the research explores the intricate engineering behind this Neolithic burial mound, revealing it as one of the most remarkable achievements of its time, dating back approximately 5,700 years.
The Menga Dolmen, part of a UNESCO World Heritage site, stands as one of Europe’s largest megalithic structures, captivating researchers with its colossal stones, some exceeding 100 tons in weight. The recent study employed cutting-edge technology, including petrographic and stratigraphic analyses, to delve into the composition, origin, and construction methods of these monumental stones.
Geological investigations pinpointed the source of the stones to the Cerro de la Cruz quarries, approximately 1 km away from the construction site. Petrological examinations revealed that the stones were predominantly calcarenites, a type of soft sedimentary rock. This particular choice of material, considered fragile in modern terms, underscores the engineering challenges faced by ancient builders.
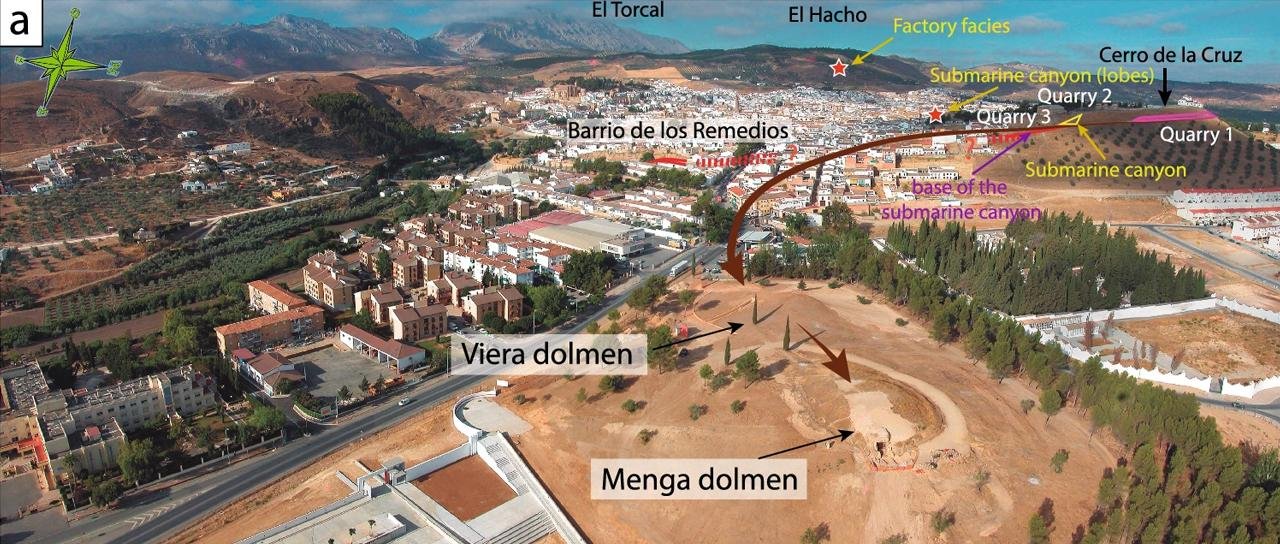 Overview of Menga, Viera, Los Remedios neighbourhood and Cerro de la Cruz from the NE. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
Overview of Menga, Viera, Los Remedios neighbourhood and Cerro de la Cruz from the NE. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
Researchers emphasized the complexity involved in transporting these mᴀssive stones without causing damage. The study suggests that the Neolithic engineers meticulously planned the movement of stones, requiring not only smooth roads but also the use of scaffolds and ropes for precise placement.
The heart of the dolmen’s engineering marvel lies in its capstone, weighing an astonishing 150 tons, strategically positioned as the roof of the burial chamber. According to the researchers, “Moving and placing such large stones from Cerro de la Cruz to the hill of Menga must have demanded intensive planning, highly accurate logistics, and enormous labor investments.”
The dolmen’s alignment with nearby mountains served a dual purpose. It not only created intricate light patterns within the chamber but also indicated intentional orientation by its builders. This aligning technique reflects the advanced understanding of astronomy and architectural planning among the ancient engineers.
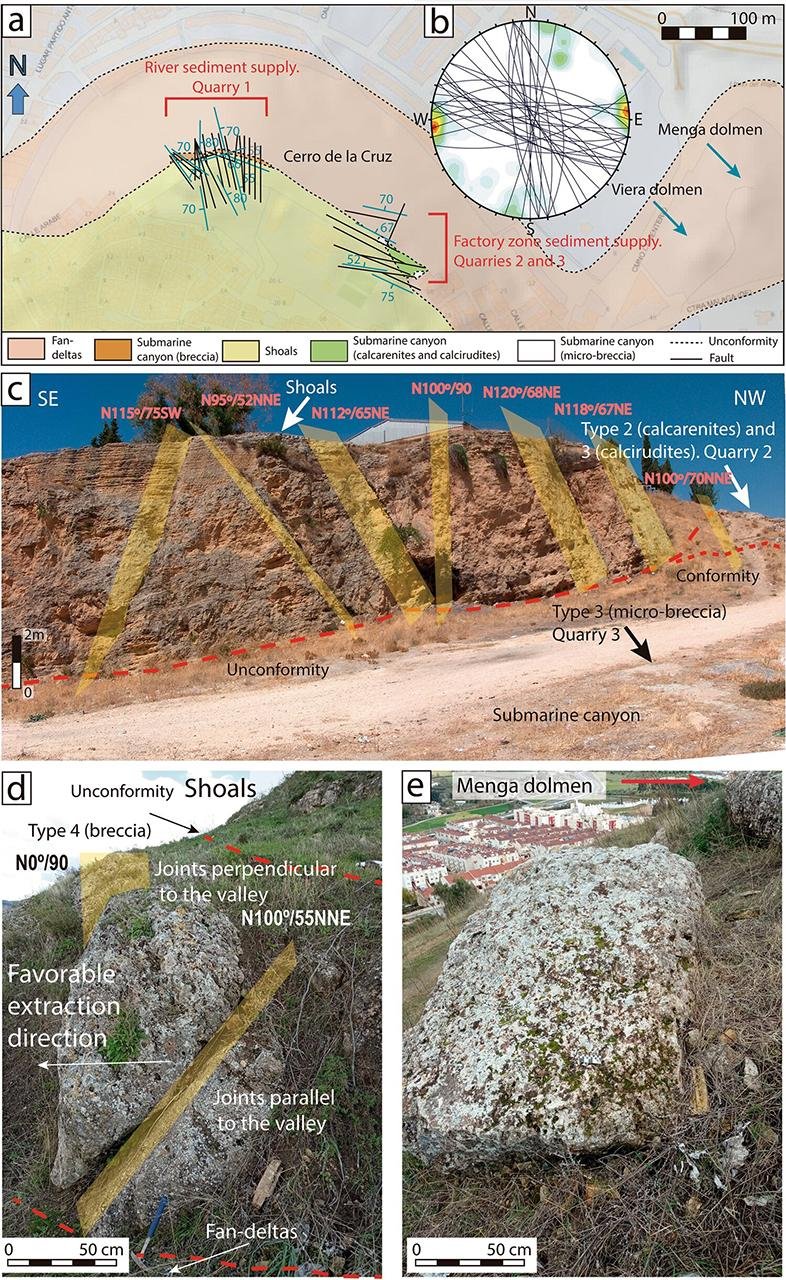 (a) Geological map of tectonic jointing on DTM, showing the location of Menga and Viera and the likely quarrying areas at Cerro de la Cruz. (b) Stereographic representation of the groups of joints. (c) Overview of the tectonic fracturing present in quarry areas #2 and #3. (d) Groups of joints observed in Quarry #1. (e) Example of a possible discarded megalithic stone at Quarry #1. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
(a) Geological map of tectonic jointing on DTM, showing the location of Menga and Viera and the likely quarrying areas at Cerro de la Cruz. (b) Stereographic representation of the groups of joints. (c) Overview of the tectonic fracturing present in quarry areas #2 and #3. (d) Groups of joints observed in Quarry #1. (e) Example of a possible discarded megalithic stone at Quarry #1. Credit: Rodríguez et al., Scientific Reports (2023).
The study also unraveled the ingenious method employed to combat erosion. Stones were interlocked at the chamber’s edges, channeling away water seepage and safeguarding the dolmen from the elements. The construction of a waterproof tumulus further attests to the builders’ deliberate efforts to preserve the soft stones.
Menga’s construction, detailed in the study, stands as a testament to the meticulous planning, labor coordination, technical expertise, and calculations involved in erecting such a colossal structure. According to the researchers, “The woodwork ᴀssociated with the construction process must have demanded the use of large amounts of timber,” underscoring the multidimensional nature of the Neolithic engineering achievement.
Comparisons with other megalithic sites worldwide, such as Stonehenge and Easter Island, highlight the importance of studying stone provenance for understanding ancient architectural practices. The Menga Dolmen’s unique features, including its colossal stones, intentional orientation, and waterproofing techniques, distinguish it as a pinnacle of megalithic engineering in European prehistory.
More information: Rodríguez, J.A.L., Sanjuán, L.G., Álvarez-Valero, A.M. et al. (2023). The provenance of the stones in the Menga dolmen reveals one of the greatest engineering feats of the Neolithic. Sci Rep 13, 21184.





