Archaeologists conducting a re-examination of a mummified teen mother who died in childbirth over 1,500 years ago have uncovered a tragic tale of maternal mortality and unexpected twins.
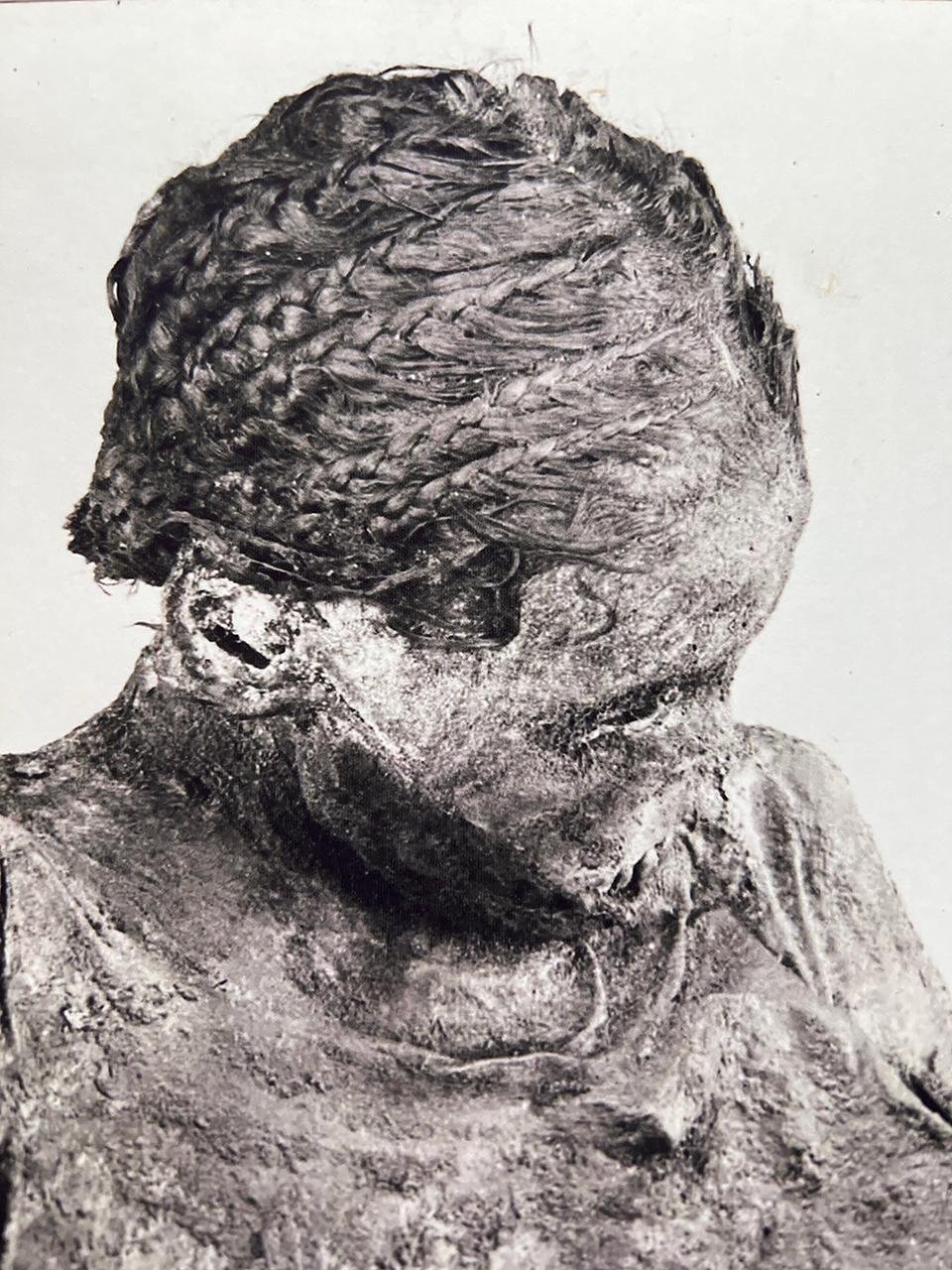 The mummified remains were discovered in 1908 at the El Bagawat cemetery in Egypt’s Kharga Oasis. Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
The mummified remains were discovered in 1908 at the El Bagawat cemetery in Egypt’s Kharga Oasis. Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
The mummified remains initially discovered in 1908 at the El Bagawat cemetery in Egypt’s Kharga Oasis, belonged to a young woman, aged 14 to 17, who was laid to rest with the remains of two infants, suggesting the dangers of pregnancy and childbirth in ancient Egypt.
The findings, detailed in a study published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, were led by a team from George Washington University, who conducted computed tomography (CT) scans on the mummy.
These scans revealed a shocking scenario – the young mother was in the process of delivering twins when she tragically pᴀssed away. The head of the first baby became stuck in the birth canal, resulting in the deaths of both infants and the mother.
 (a) CT scan of the mummy. Arrow indicates remains outside chest cavity, lodged in mummified tissue. Circle indicates fetal skull, ribs and long bones. (b) X-ray of chest cavity of female mummy USNM 258601. Note fetal bones, including a neural arch and a metacarpal that migrated outside the chest cavity (arrow) and the fetal remains in the left chest cavity (circle). Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
(a) CT scan of the mummy. Arrow indicates remains outside chest cavity, lodged in mummified tissue. Circle indicates fetal skull, ribs and long bones. (b) X-ray of chest cavity of female mummy USNM 258601. Note fetal bones, including a neural arch and a metacarpal that migrated outside the chest cavity (arrow) and the fetal remains in the left chest cavity (circle). Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
Francine Margolis, one of the study authors, said: “This is a rare find. There are several examples of women dying during childbirth in the archaeological record (one was a twin pregnancy). However, there has never been one found in Egypt.”
The CT scans further disclosed that the infant between the woman’s legs was missing its head, leading to the conclusion of a “traumatic fetal decapitation.” The researchers believe that the baby was born in a breech position, complicating the delivery process. Breech births, where the baby emerges feet first, can sometimes lead to the entrapment of the baby’s head in the birth canal, resulting in tragic outcomes.
As for the second fetus found in the woman’s chest cavity, the researchers speculate that the embalmers might not have been aware of the twin pregnancy, leading them to overlook the second unborn child during the mummification process. The dissolving diaphragm during mummification could have allowed the second fetus to migrate from the womb to the chest cavity.
The tragic discovery sheds light on the perilous nature of pregnancy and childbirth in ancient Egypt. Childbirth during this time was considered a religious event rather than a medical one. While medical practices in ancient Egypt are well documented, pregnancy remains a less-explored aspect.
The cultural aversion to twin births in ancient Egypt is discernible through spells and incantations designed to prevent the birth of twins. The Oracular Amuletic Decree, an ancient papyrus, contains a spell emphasizing the desire to keep women safe from irregular births and giving birth to twins.
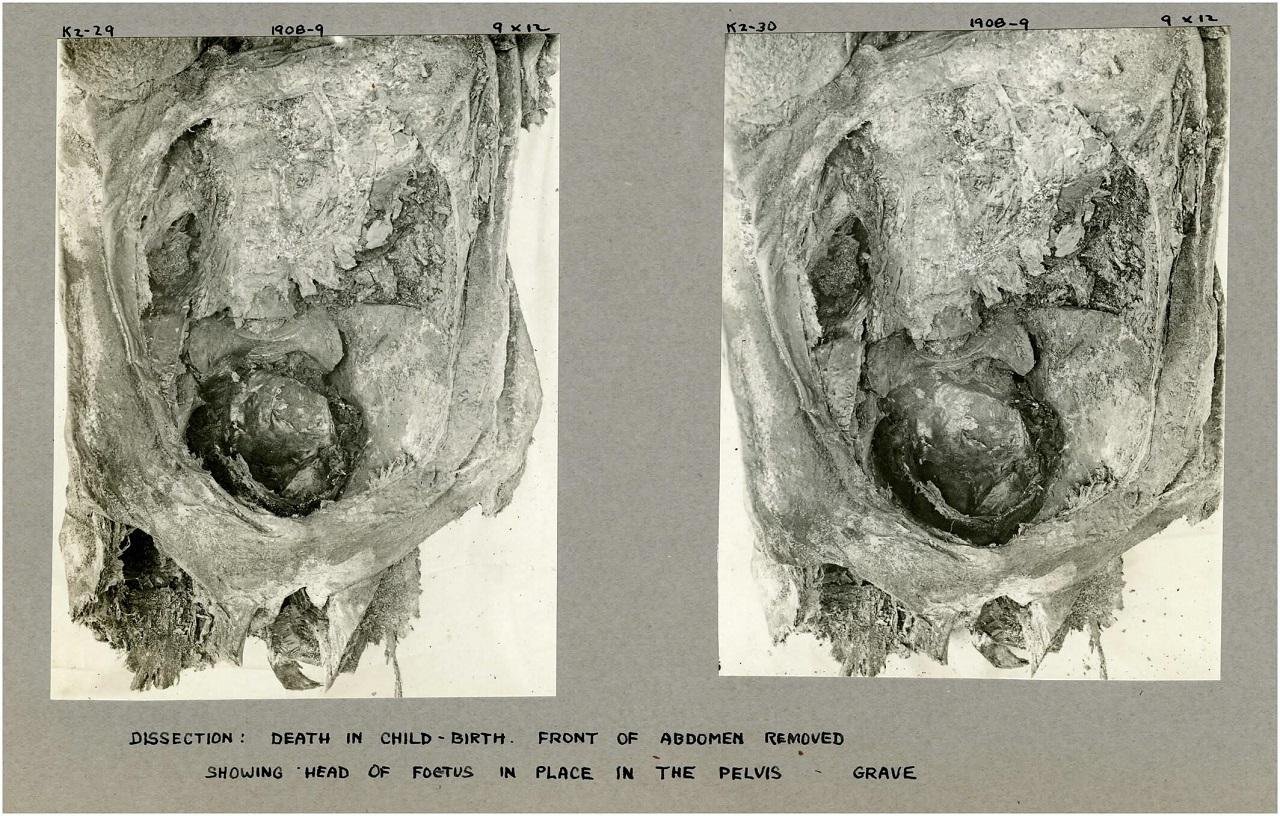 Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
Credit: wileyonlinelibrary.com / International Journal of Osteoarchaeology
The team also revisited field notes from the 1908 excavation, revealing the extensive measures taken during the analysis of the mummy, including the removal of arms and an incision on the abdomen.
In a separate research project conducted in 2019, the mummy’s measurements were examined to determine if pelvic shape played a role in her unsuccessful delivery. The teen mummy displayed smaller measurements compared to other Egyptian females from the same region, indicating a possible contributing factor to the tragic outcome.
The story of this young Egyptian mother and her unborn twins stands as a poignant testament to the challenges and dangers of childbirth in a bygone era.
More information: Margolis, F., & Hunt, D. R. (2023). Twins found in a Late Dynastic/Coptic Egyptian mummy. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 1–6.





