In a bustling town square in Halmstad, Sweden, beneath the surface of Lilla Torg, an archaeological revelation has come to light. Recent excavations led by the Cultural Environment of Halland uncovered a total of 49 graves dating back to the medieval period, all concealed beneath a former convent that functioned from 1494 to 1531.
 Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland
Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland
Among these graves, one particularly stood out—a burial housing the remains of a towering elite man. Archaeologists meticulously unearthed a skeleton measuring an impressive 6 feet 2 inches, clad with a remarkably well-preserved longsword resting on his left side, measuring over 4 feet in length.
The sword, a rare find in medieval graves, holds significant historical weight. An X-ray examination unveiled an intricate inlaid decoration featuring two crosses, likely crafted from precious metal. This discovery prompted experts to ᴀssert that the presence of such a weapon indicated the deceased’s high social standing or elite status.
Upon uncovering this extraordinary grave, archaeologists promptly took measures to preserve and further study the sword. It was carefully wrapped and dispatched to a laboratory for detailed analysis, while ongoing excavations at Lilla Torg continue.
 Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland
Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland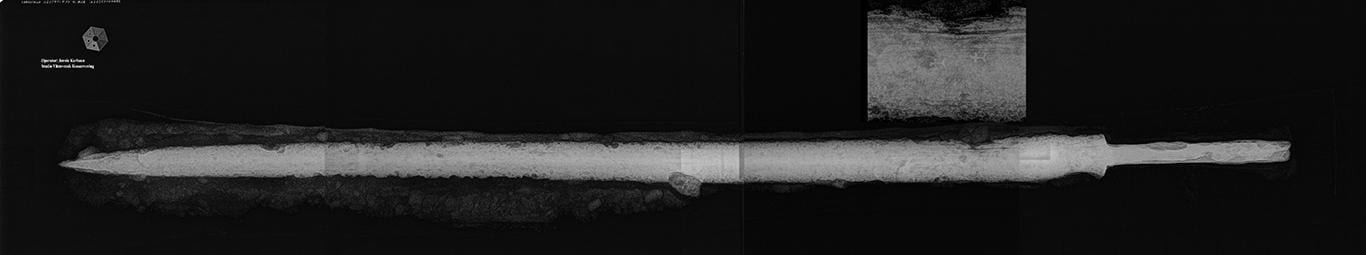 Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland
Credit: Cultural Environment of Halland
The burial site is situated in Lilla Torg, once part of the Franciscan monastery of Sankta Annas during the 15th century. Earlier excavations in 1932 had revealed remnants of the monastery kitchen and church, and this recent exploration brought to light additional sections of the monastery church.
The sword find at Lilla Torg confirms that Sankta Anna’s church was used as a burial place for people of noble birth during the 35 years of Franciscan operation on the site.
This conclusion aligns with the historical timeline of the Franciscan order’s presence, further corroborated by the discovery of two additional graves adjacent to the elite man’s, one belonging to an adult woman and the other to a man
The town of Halmstad, located approximately 270 miles southwest of Stockholm, played a pivotal role in the medieval era. Granted its first town charter in 1307, Halmstad’s historic center took shape in the 1320s as part of the Kingdom of Denmark.
The short-lived Sankta Annas monastery, constructed between 1494 and 1503, faced closure in 1531, leading to subsequent repurposing of its land for purposes such as an armory and hospital.





