In the Cajamarca Basin of northern Peru, archaeologists from the University of Wyoming (UW) have unearthed a megalithic plaza dating back approximately 4,750 years.
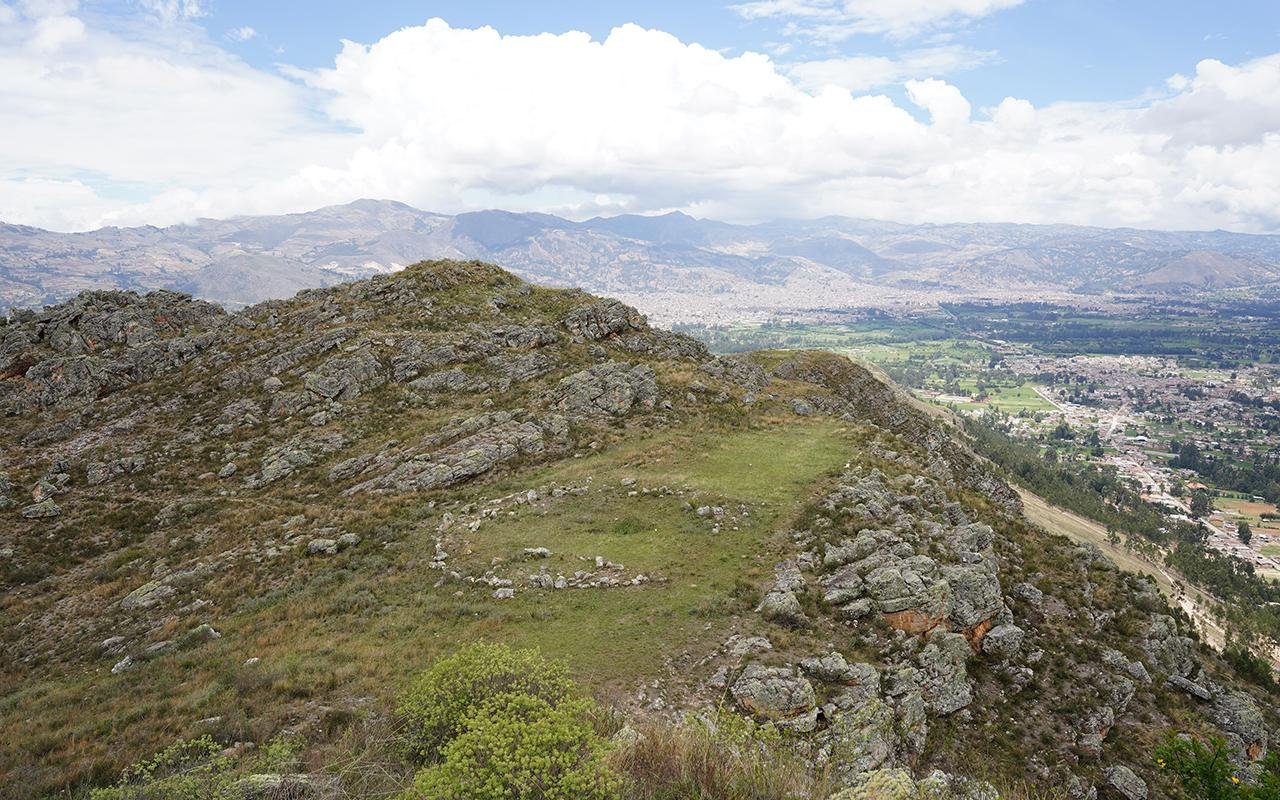 Overhead pH๏τo of the Callacpuma plaza, with the stone circle at the center. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
Overhead pH๏τo of the Callacpuma plaza, with the stone circle at the center. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
This circular plaza, unearthed at the Callacpuma archaeological site, represents one of the earliest examples of monumental construction in the Andean region. The structure, comprised of two concentric walls constructed from vertically placed megalithic stones, lacks evidence of domestic habitation, suggesting its primary function was ceremonial.
Under the leadership of ᴀssociate Professor Jason Toohey and Professor Melissa Murphy, the team of researchers began excavation work in 2018, expanding upon the systematic studies that were initiated in 2015.
Their findings, detailed in the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances, shed light on a crucial period of transition in South America, where coastal fishing communities began interacting with emerging agricultural societies in the mountains.
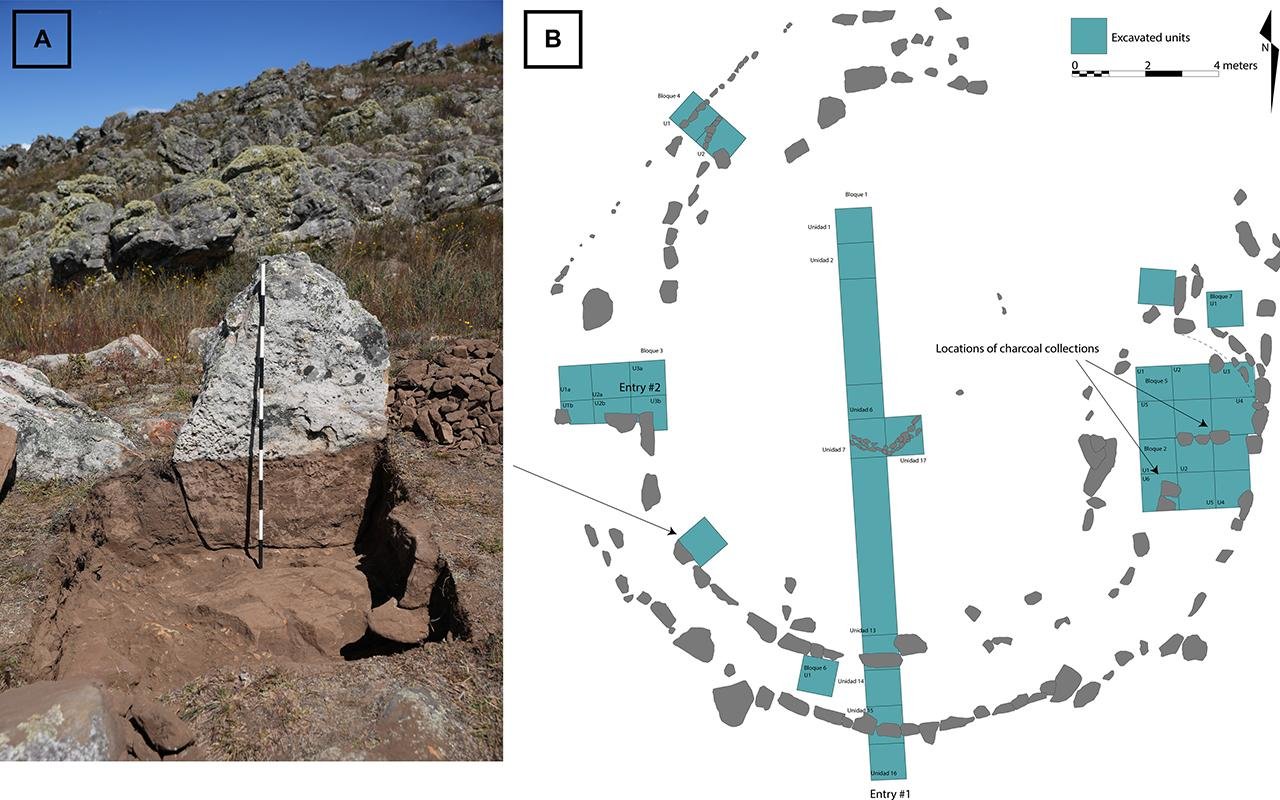 Plan of the circular plaza and its construction. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
Plan of the circular plaza and its construction. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
Carbon dating places the construction of the plaza around 4,750 years ago, predating iconic monuments like the Great Pyramids of Egypt and Stonehenge. Toohey emphasizes the plaza’s significance as a gathering place for early inhabitants of the Cajamarca Valley, who were primarily engaged in hunting and gathering activities while beginning to explore agriculture and animal domestication.
The plaza’s layout, featuring two entrances and an intricate foundation layer prepared with clay, soil, gravel, and charcoal, hints at controlled access and meticulous planning. Artifacts unearthed at the site include fragments of ceramic vessels, quartz crystals, and unworked lapis lazuli gems.
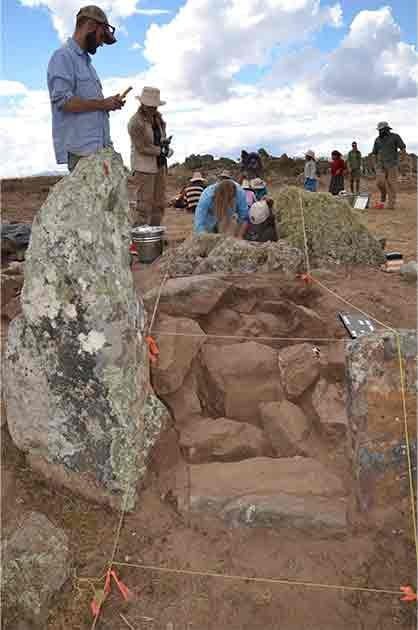 One of the entrances to the plaza. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
One of the entrances to the plaza. Credit: Toohey et al., Science Advances (2024)
Further analysis of the site suggests periodic visitation until its ceremonial closure during the Layzón period (500-200 BCE), signaling shifts in belief systems and societal organization. The construction of such monumental structures reflects a transition towards collective actions and regional cooperation among semi-nomadic groups.
The discovery challenges existing narratives of early Andean societies, highlighting the dynamic social landscape of the Late Preceramic period.
More information: Jason L. Toohey, Melissa S. Murphy, Patricia Chirinos Ogata, Sarah G. Stagg, Alex Garcia-Putnam. (2024). A monumental stone plaza at 4750 B.P. in the Cajamarca Valley of Peru. Science Advances; 10 (7) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adl0572





