Archaeologists have uncovered the remains of a post-medieval township known as Brunell in Glen Brittle Forest on the Isle of Skye. This discovery was made during an environmental survey conducted before the harvest of a mature conifer plantation.
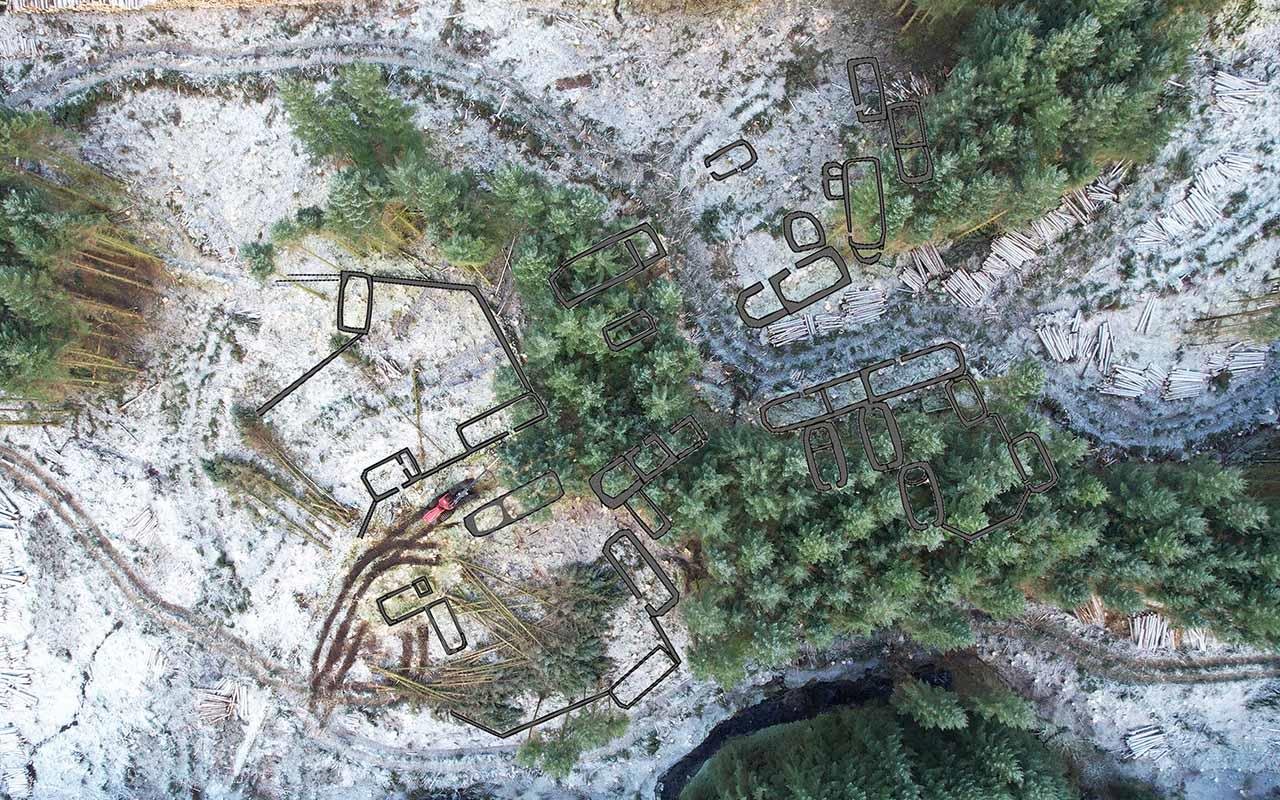 This vertical aerial view of the harvesting operation in and around the township has been annotated to show the location of the buildings. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
This vertical aerial view of the harvesting operation in and around the township has been annotated to show the location of the buildings. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
The findings include traces of 28 buildings, comprising houses, byres, barns, and corn-drying kilns, surrounded by fields and stock enclosures typical of a small clachan or township. Historical records indicate that Brunell dates back to the 17th and 18th centuries, as depicted in an early 19th-century map surveyed by John Thomson in 1832.
The decline of Brunell began in the late 18th century due to land consolidation for sheep-grazing, which led to the displacement of small tenants and ultimately resulted in the abandonment of the township. By the Ordnance Survey of 1881, Brunell had dwindled to only two roofless buildings and several fields, indicating the complete departure of its population by that time.
The township’s rediscovery was facilitated by Forestry and Land Scotland, which commissioned AOC Archaeology to conduct a comprehensive survey before tree harvesting. The survey revealed that the township was nestled within a mature conifer plantation primarily consisting of Sitka spruce trees, planted in 1977, with many sites partially concealed by windblown trees. The archaeological investigation uncovered 28 buildings clustered together with fields and stock enclosures, forming a small township situated on terraces on the north side of the Allt Dabhoch burn.
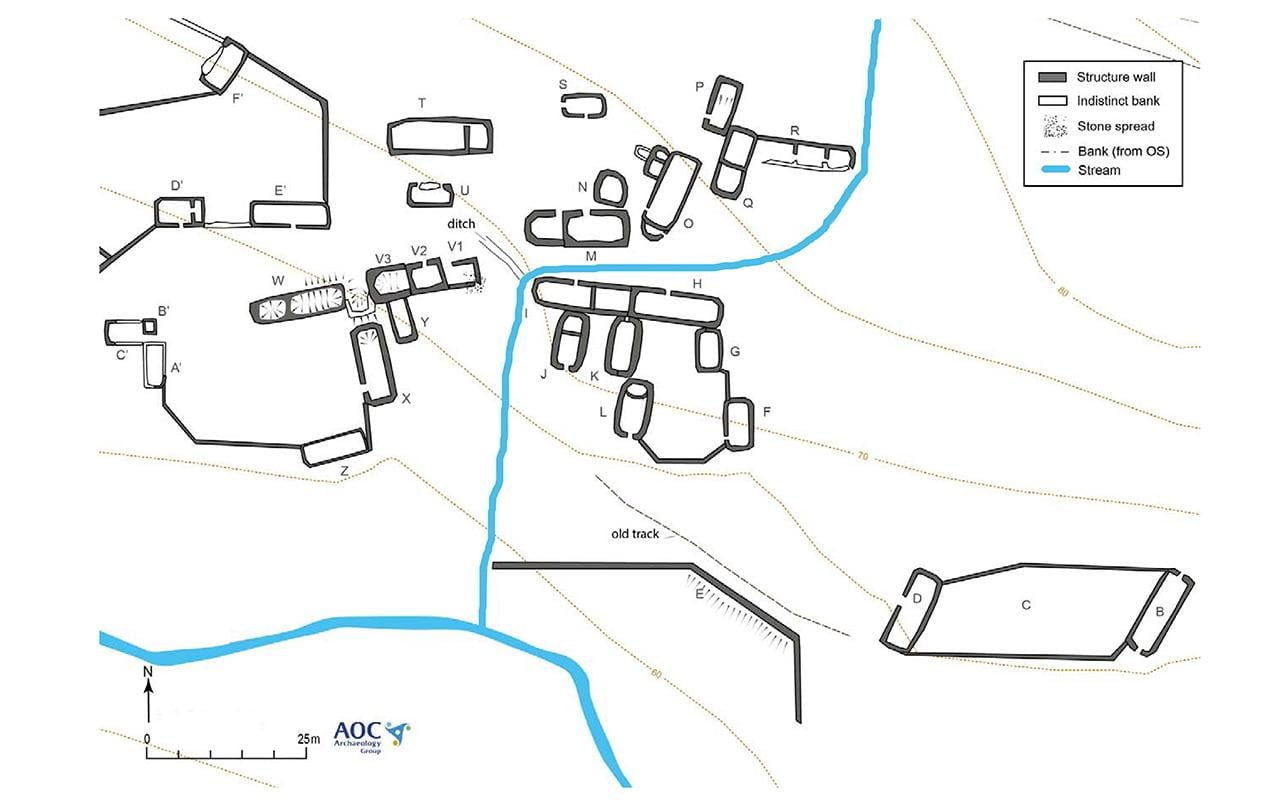 Twenty-eight buildings were recorded by the archaeological survey. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
Twenty-eight buildings were recorded by the archaeological survey. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
According to historical accounts consulted by the archaeologists, Brunell’s decline can be attributed to the Highland Clearances, during which landowners replaced small tenants with large sheep farms, leading to the desertion of settlements like Brunell. The Minister’s report from the Parish of Bracadale on Skye highlights the population decrease resulting from this farming system.
To preserve the historical ruins during the harvesting operation, Forestry and Land Scotland implemented careful planning and coordination. A spokesperson for the agency explained that forestry machinery operators utilized their skill to avoid causing damage to the ruins. This involved positioning the harvesters to fell trees away from the buildings into open space, ready for processing into logs.
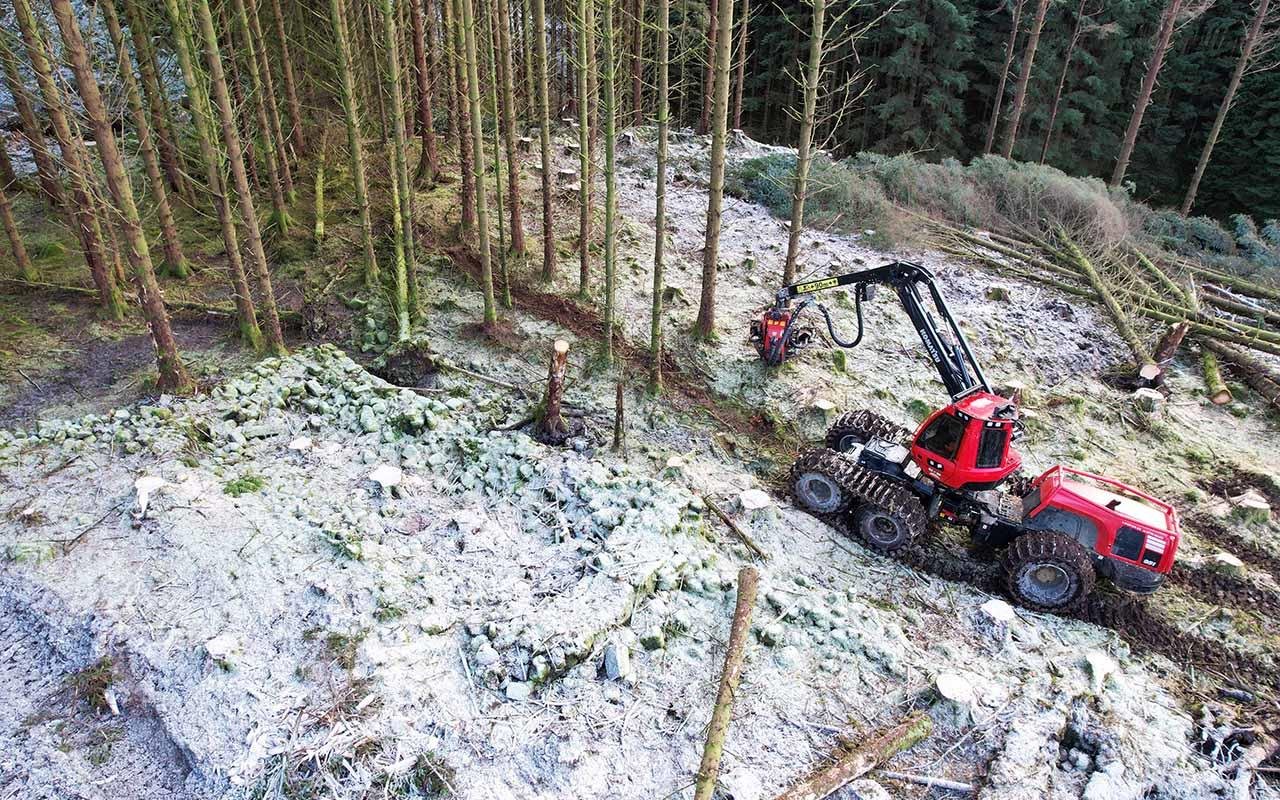 The buildings were first marked out on the ground. The machine operators then used their skill and experience to carefully plan the harvesting operation. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
The buildings were first marked out on the ground. The machine operators then used their skill and experience to carefully plan the harvesting operation. Credit: Forestry and Land Scotland
The meticulous approach taken by Highland Timber Harvesting, operating on behalf of Tilhill, involved marking out the individual buildings on the ground before planning the harvesting operation. Machine operators navigated short tracks around the township, ensuring trees were felled away from the buildings to prevent any harm.





