Archaeologists have unearthed evidence of ancient ritual practices involving tobacco in Mesoamerica. The discovery, detailed in a study published in the journal Antiquity, provides insights into the ritual and therapeutic uses of tobacco among the ancient inhabitants of Cotzumalhuapa, Guatemala, during the Late Classic period (CE 650–950).
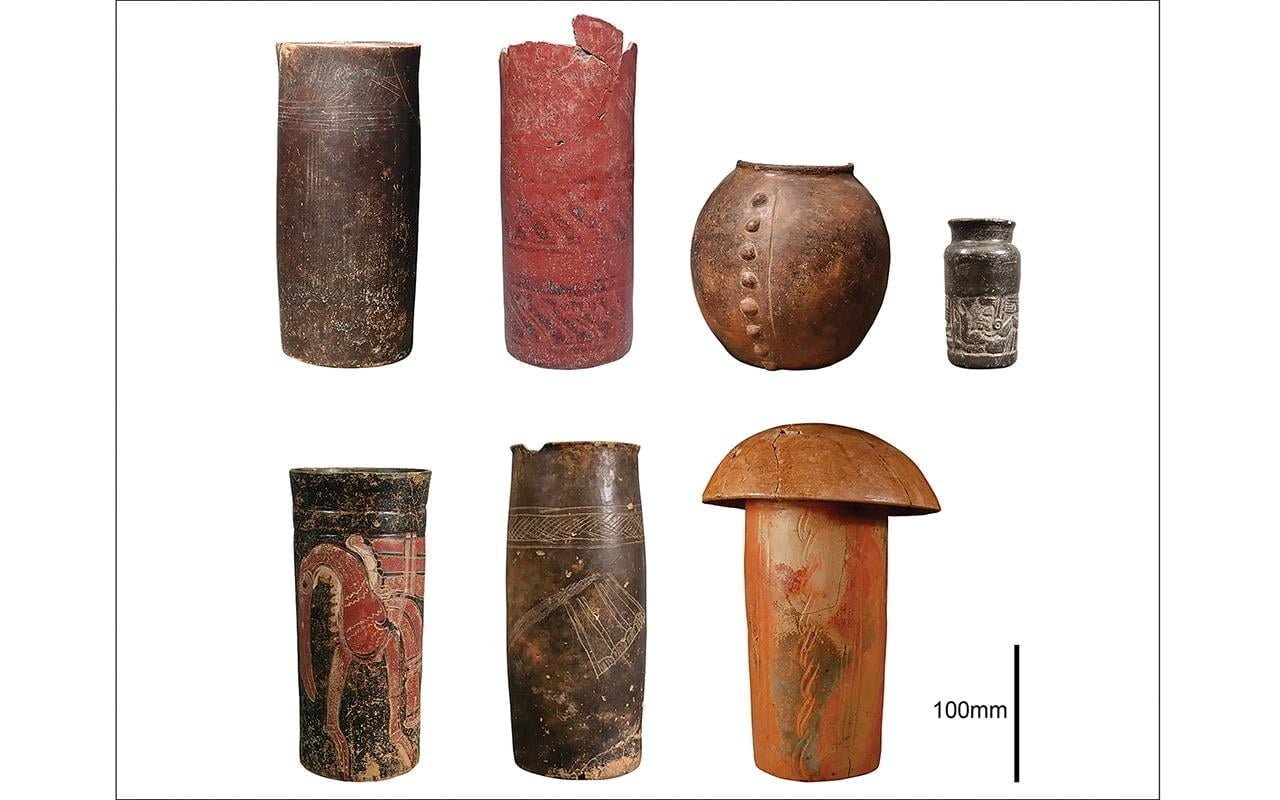 Archaeological vessels sampled for residue analysis from El Baúl, Cotzumalhuapa, Guatemala. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
Archaeological vessels sampled for residue analysis from El Baúl, Cotzumalhuapa, Guatemala. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
Cotzumalhuapa, situated near the town of Santa Lucía Cotzumalguapa in southern Guatemala, was a thriving Maya polity encompᴀssing over 10 square kilometers during its heyday. Recent archaeological excavations at the site have revealed a collection of ceramic vessels near the acropolis of El Baúl.
The findings indicate that these vessels, dating back to the Late Classic period, contain traces of nicotine, suggesting that tobacco was utilized for ritual and therapeutic purposes. Dr. Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos, co-author of the study from Yale University, notes, “We knew that tobacco was a very important substance employed for a variety of ritual and therapeutic purposes in ancient Mesoamerica and across the New World.”
While historical and ethnographic records have long attested to the significance of tobacco in Mesoamerican cultures, physical evidence of its use has been scarce. Previous studies have primarily focused on smaller artifacts, however, the identification of nicotine residue within larger ceramic vessels was an infrequent occurrence.
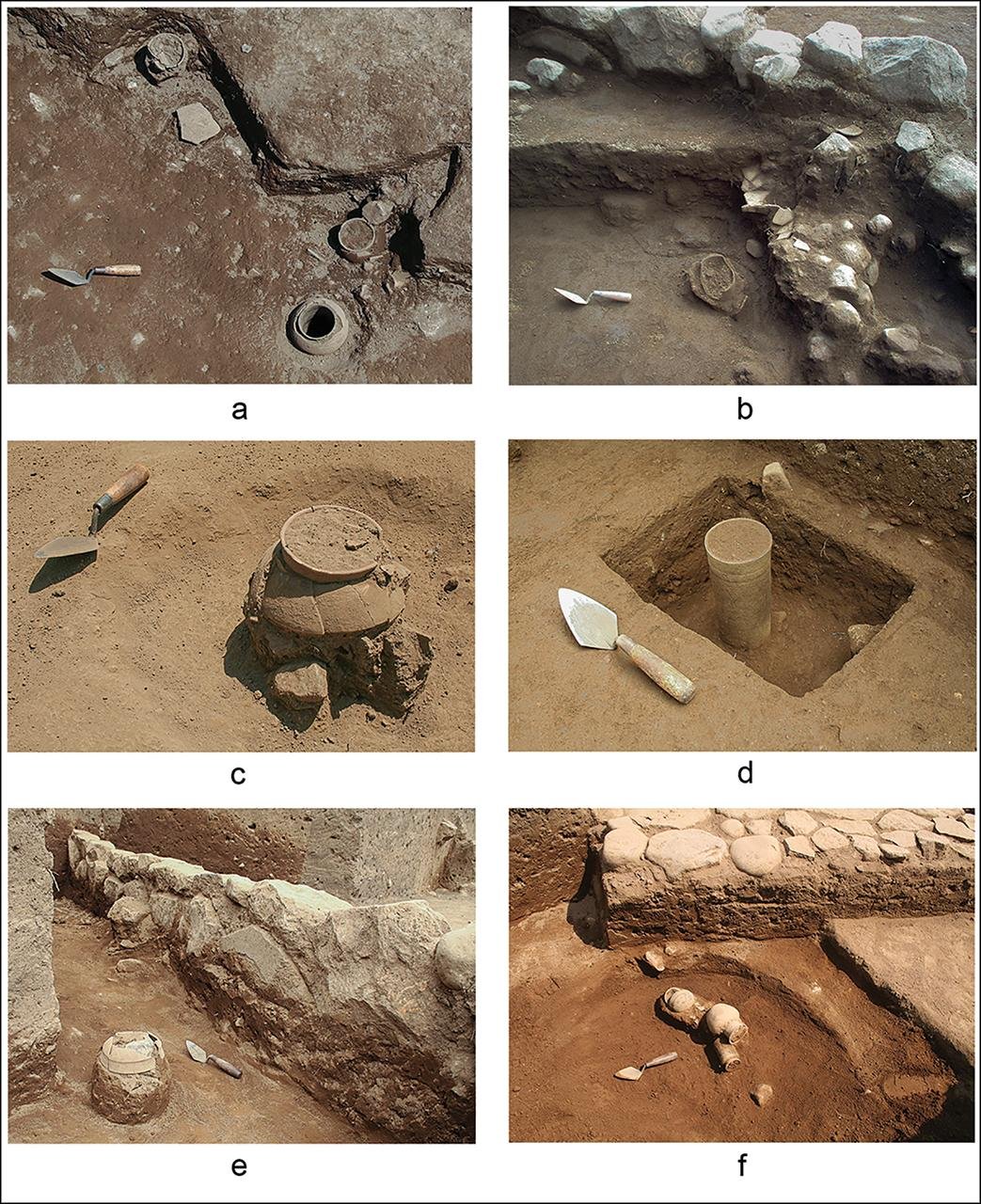 Cache vessels from Operation EB9 in situ, originally deposited below clay floors ᴀssociated with the stone foundations of buildings. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
Cache vessels from Operation EB9 in situ, originally deposited below clay floors ᴀssociated with the stone foundations of buildings. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
The vessels, resembling tall, narrow containers suitable for holding liquids, suggest that tobacco may have been consumed as a liquid infusion rather than smoked or sniffed in powder form. This discovery challenges previous ᴀssumptions about the methods of tobacco consumption in ancient Mesoamerica.
Moreover, the proximity of these vessels to sweat baths at Cotzumalhuapa suggests that tobacco infusions may have been used in purification rituals, highlighting the interconnectedness of ritual and therapeutic practices, including maternal care and childbirth.
 A royal portrait from Cotzumalhuapa (height 1.85m). The headdress features three ovate leaves whose shape, size, and venation are suggestive of tobacco. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
A royal portrait from Cotzumalhuapa (height 1.85m). The headdress features three ovate leaves whose shape, size, and venation are suggestive of tobacco. Credit: Oswaldo Chinchilla Mazariegos / Antiquity (2024)
The findings also challenge previous notions about the timeline of tobacco use in the Americas, suggesting that its ritualistic and therapeutic applications date back much earlier than previously believed.
Ingesting high concentrations of nicotine can be toxic and even lethal, indicating that tobacco may have been used during rituals as “narcotics to induce deep sleep, visions, and divinatory trances,” as suggested by the researchers.
More information: Negrin A, Chinchilla Mazariegos O, McNeil CL, Hurst WJ, Kennelly EJ. (2024). Residue analysis suggests ritual use of tobacco at the ancient Mesoamerican city of Cotzumalhuapa, Guatemala. Antiquity:1-17. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.13





