Recent archaeological studies centered on the Viking era in Scandinavia have unearthed a plethora of permanent bodily modifications, illuminating the methods through which ancient societies communicated and expressed social idenтιтies.
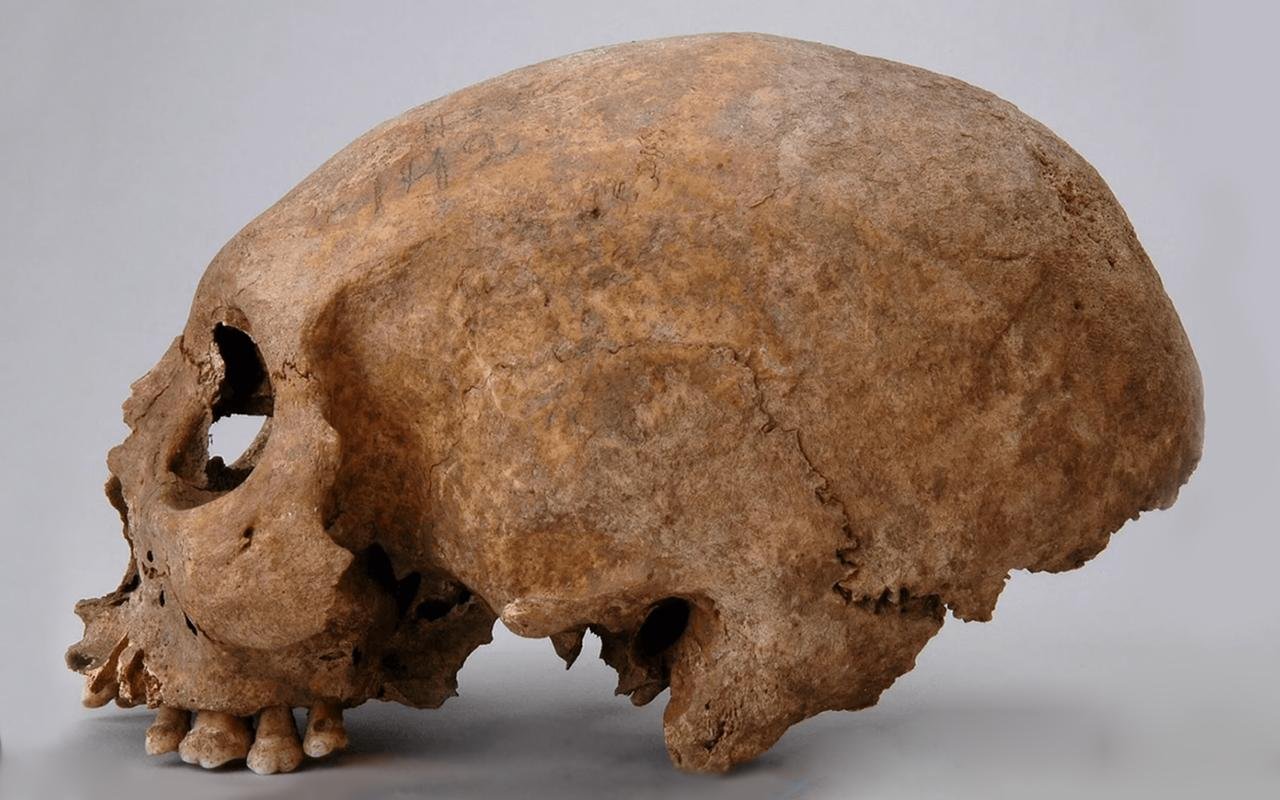 The skull of a female individual in grave 192 from Havor, located in Hablingbo parish, Gotland, shows signs of deliberate modification. Credit: SHM/Johnny Karlsson 2008-11-05 (CC BY 2.5 SE)
The skull of a female individual in grave 192 from Havor, located in Hablingbo parish, Gotland, shows signs of deliberate modification. Credit: SHM/Johnny Karlsson 2008-11-05 (CC BY 2.5 SE)
A study, conducted by Matthias Toplak and Lukas Kerk and published in Current Swedish Archaeology, has brought to attention various forms of bodily alterations prevalent among Vikings, particularly in Gotland, a Baltic island serving as a significant trading hub during that time.
Among the most intriguing discoveries are dental alterations, with approximately 130 individuals, predominantly adult men, found to have horizontal grooves carved into their teeth. Concentrated mainly on Gotland, these modifications have sparked debates ranging from interpretations as marks of slaves to symbols denoting elite warrior status.
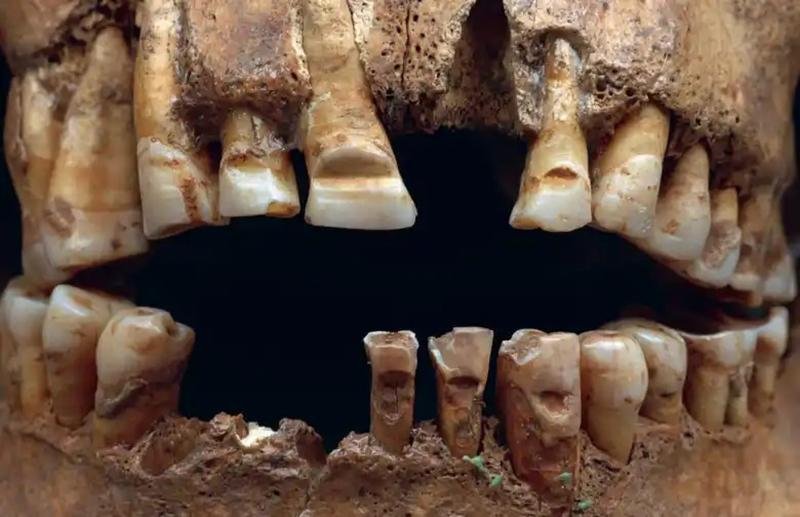 Detail of the filed teeth of the male individual from grave 25 at Slite, Othem parish, Gotland. Credit: Lisa Hartzell
Detail of the filed teeth of the male individual from grave 25 at Slite, Othem parish, Gotland. Credit: Lisa Hartzell
However, a closer examination suggests they may have functioned as signals of identification within a closed group of traders, akin to later medieval guilds. Variations in the patterns of notches indicate a possible regional signaling code, facilitating communication both within and outside the immediate community.
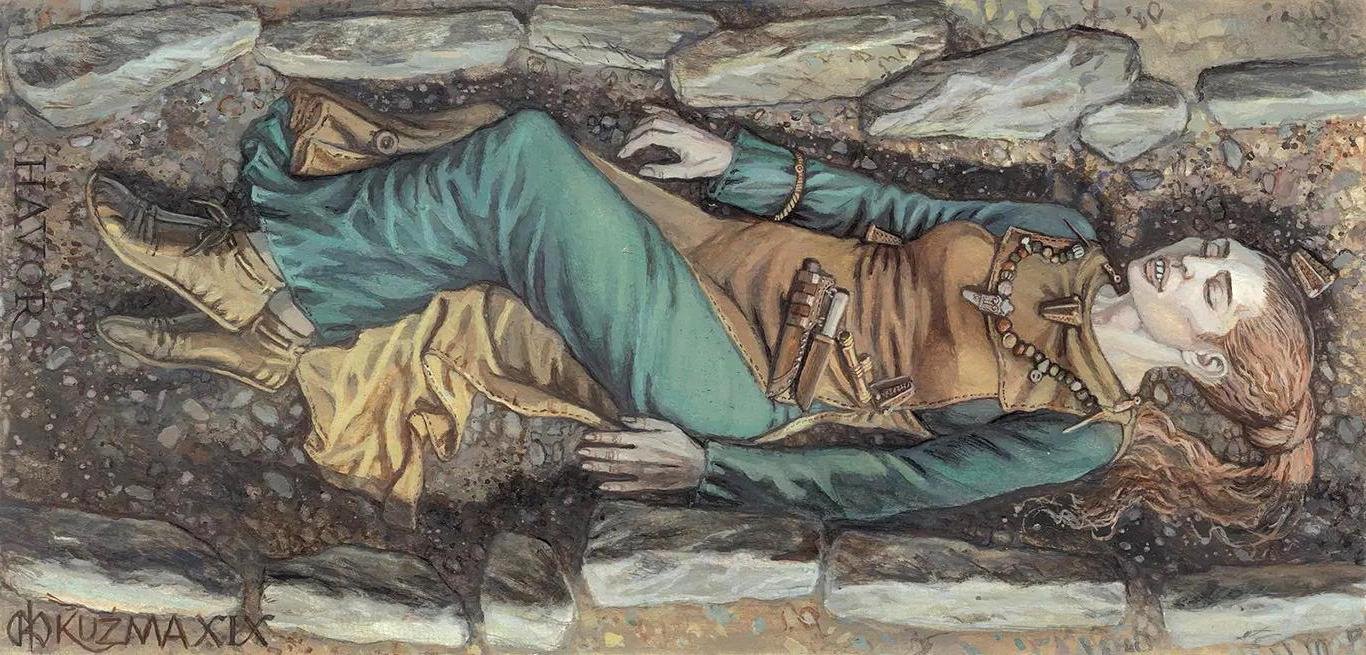 Drawing of the grave of the female individual with an artificially modified skull in Havor grave 192, Hablingbo parish, Gotland. Credit: Mirosław Kuźma / Matthias Toplak
Drawing of the grave of the female individual with an artificially modified skull in Havor grave 192, Hablingbo parish, Gotland. Credit: Mirosław Kuźma / Matthias Toplak
Moreover, the study unveils the presence of three Viking women with artificially elongated skulls, a practice seemingly foreign to Scandinavian Viking culture but prevalent in Eastern Europe during the same period. These women, buried with elaborate jewelry indicative of their acceptance and integration into the local community, raise questions about the adaptation and reinterpretation of foreign idenтιтy practices in Viking society.
The methodology behind these cranial modifications remains enigmatic. Whether these modifications were carried out before arrival in Scandinavia or on Gotland itself remains unclear, prompting researchers to explore possible cultural exchanges and societal interpretations of such alterations.
 The grave of the woman in grave 192 at Havor, Hablingbo parish, Gotland, contained exquisite accessories typical of Gotland attire, alongside her artificially modified skull. Credit: Bertha Amaya / Elisabet Pettersson
The grave of the woman in grave 192 at Havor, Hablingbo parish, Gotland, contained exquisite accessories typical of Gotland attire, alongside her artificially modified skull. Credit: Bertha Amaya / Elisabet Pettersson
Toplak and Kerk emphasize that these bodily modifications served not only as physical alterations but also as embodied signals conveying complex messages about an individual’s social status, group affiliation, and possibly cultural background. Through decoding these signals, researchers gain insights into the dynamic social dynamics and cultural practices of Viking communities.
More information: Matthias S. Toplak, Lukas Kerk, (2023). Body Modification on Viking Age Gotland. Filed Teeth and Artificially Modified Skulls as Embodiment of Social Idenтιтies. Current Swedish Archaeology, vol.31, doi:10.37718/CSA.2023.09





