A new study recently published in the journal Antiquity revealed the ancient Pueblo culture’s communication methods, and the significant role conch-shell trumpets played in community cohesion and social organization.
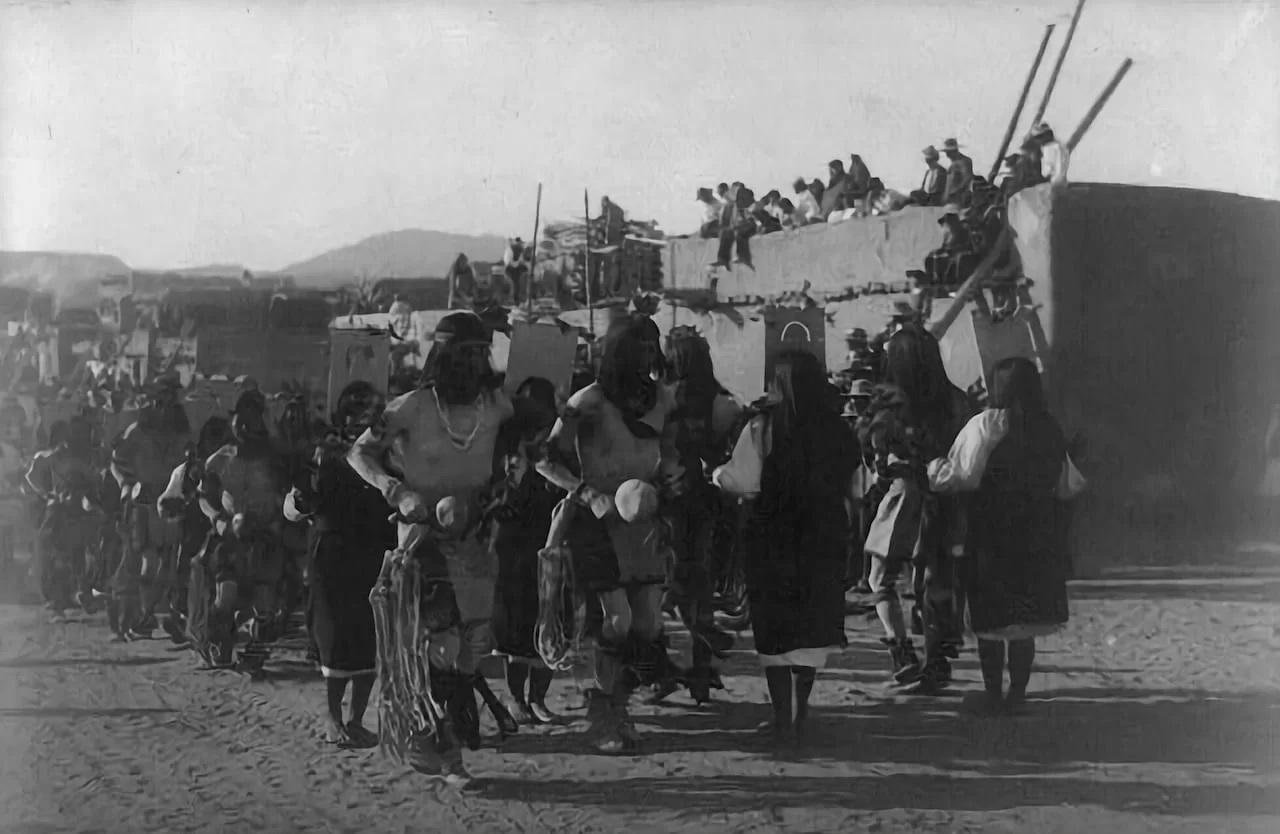 Pueblo Indians in a ceremonial dance, New Mexico, 1908. Credit: Simeon Schwemberger
Pueblo Indians in a ceremonial dance, New Mexico, 1908. Credit: Simeon Schwemberger
Led by Professor Ruth Van Dyke from Binghamton University, the interdisciplinary research team utilized Geographic Information Systems (GIS)-based modeling techniques to investigate the acoustic landscapes of the Chaco region in northwest New Mexico.
The focal point of the study was the Chaco Canyon, a site within the Chaco Culture National Historic Park, renowned for its numerous small dwellings and multi-story buildings known as great houses. Archaeologists estimate that during its peak from CE 1050 to 1130, Chaco Canyon was home to approximately 2,300 people, suggesting it was a bustling metropolis of the ancient world.
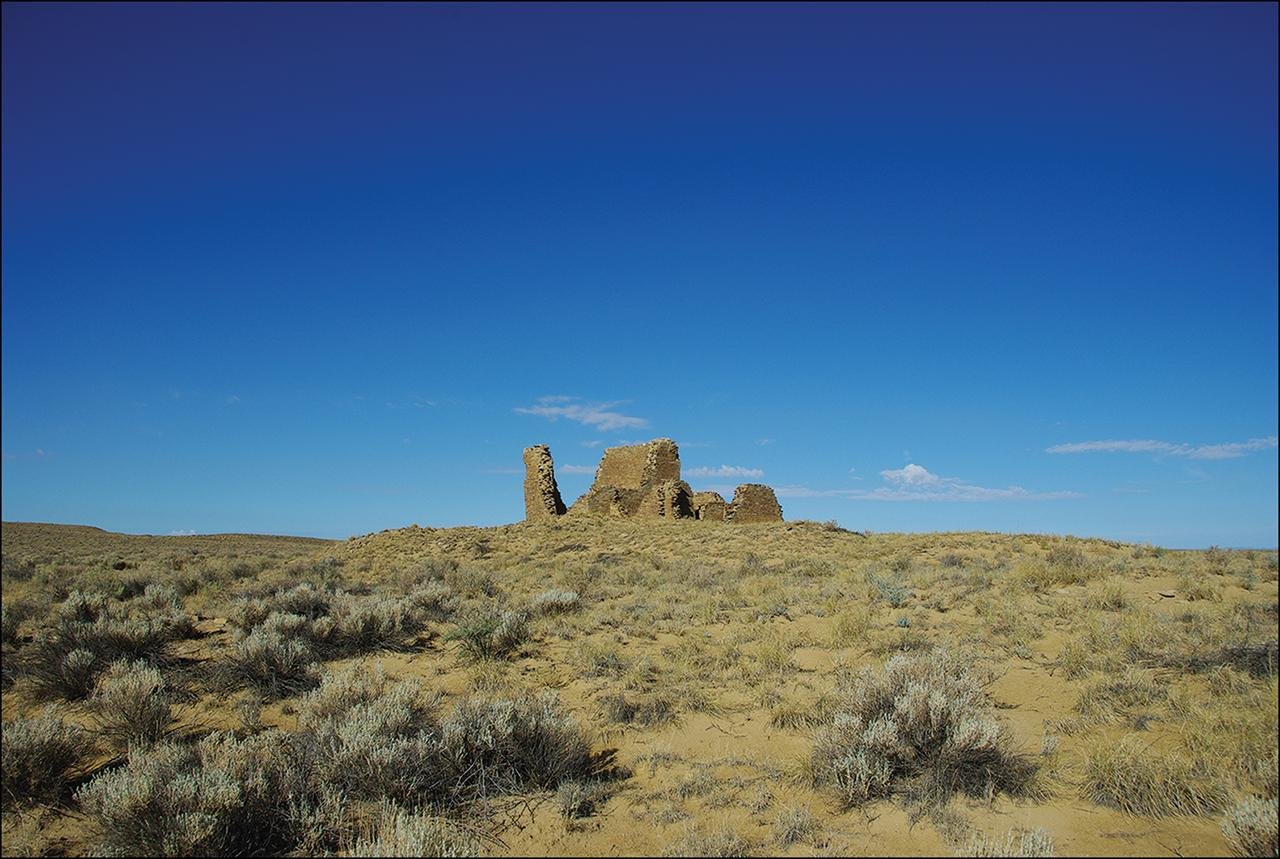 Kin Klizhin big house with kiva tower (LA 4935). Credit: Ruth M. Van Dyke / Antiquity 2024
Kin Klizhin big house with kiva tower (LA 4935). Credit: Ruth M. Van Dyke / Antiquity 2024
Conch-shell trumpets, integral to contemporary Pueblo ritual practices, were unearthed in burial contexts at Chaco Canyon. Through Soundshed Analysis modeling, the team digitally reconstructed the sound of conch-shell trumpets being sounded from great houses, considering factors such as elevation, ambient noise, and distance.
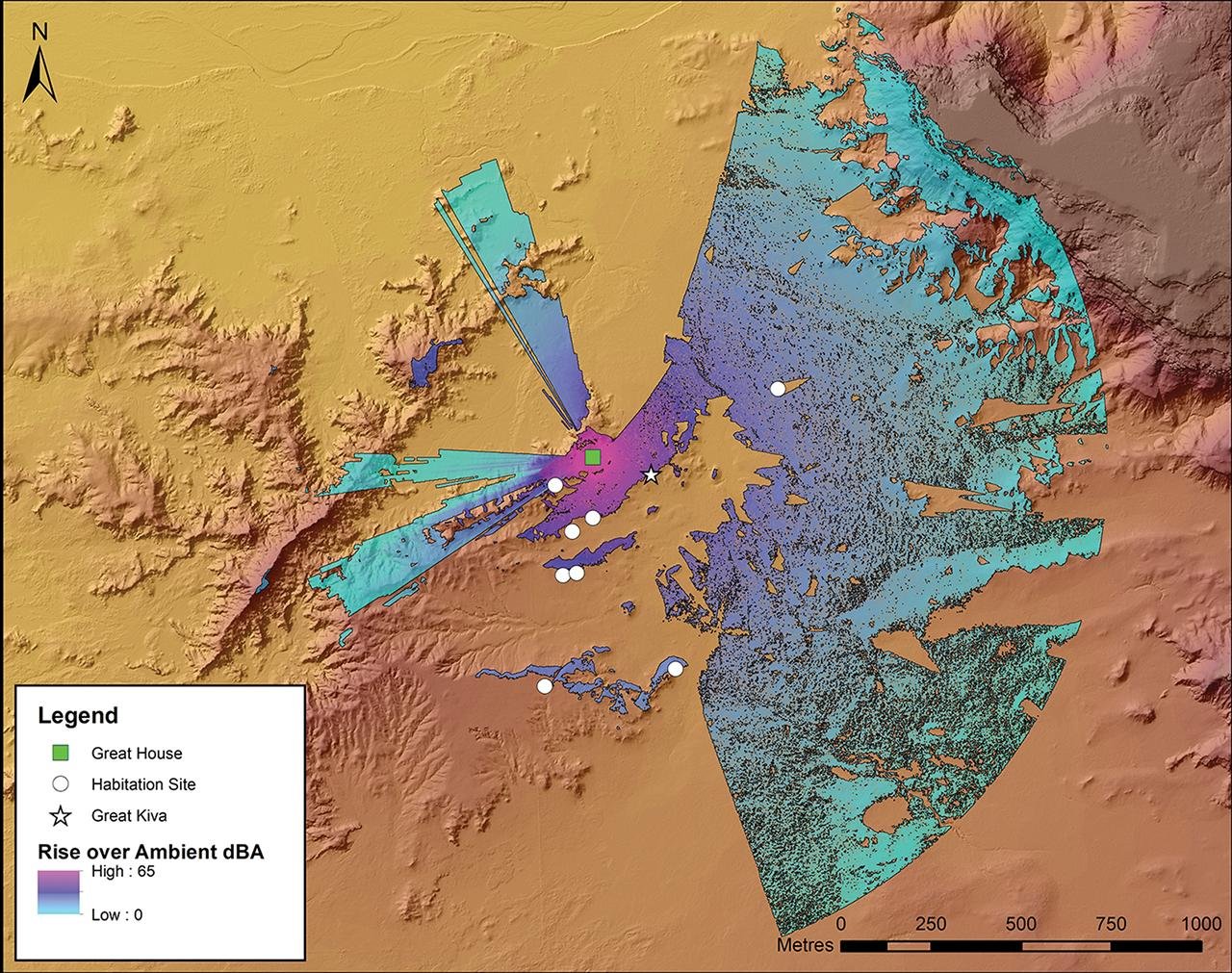 Modeled audible reach of a conch-shell blast from Padilla Wash great house (LA 40352). Credit: Van Dyke et al., Antiquity 2024
Modeled audible reach of a conch-shell blast from Padilla Wash great house (LA 40352). Credit: Van Dyke et al., Antiquity 2024
Their findings were remarkable. By modeling the sound of conch-shell trumpets from five Chacoan communities, the researchers determined that the sound would have reached almost all surrounding settlements, indicating a sophisticated system of communication and community organization.
The study’s lead author, Professor Van Dyke likened this to the medieval church bell, which called communities to mᴀss, suggesting that the sound of the conch-shell trumpet may have been used to signal communal activities, particularly religious ceremonies.
 Beyond the Chaco Canyon, about 200 additional great houses have been documented, each forming the nucleus of communities comprising multiple habitation sites. These great houses, scattered across the region, served as centers of community life. Professor Van Dyke explains that the aim was to ascertain if these extra-canyon great house communities exhibited similar relationships between landscape, community layout, and sound as observed in Chaco Canyon.
Beyond the Chaco Canyon, about 200 additional great houses have been documented, each forming the nucleus of communities comprising multiple habitation sites. These great houses, scattered across the region, served as centers of community life. Professor Van Dyke explains that the aim was to ascertain if these extra-canyon great house communities exhibited similar relationships between landscape, community layout, and sound as observed in Chaco Canyon.
The findings suggest that these wind instruments played a crucial role in inter-community communication. Moreover, the study underscores the significance of maintaining the social cohesion of ancient communities, a factor with implications for modern archaeological landscape management.
More information: Van Dyke RM, Primeau KE, Throgmorton K, Witt DE. (2024). Seashells and sound waves: modelling soundscapes in Chacoan great-house communities. Antiquity:1-18. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.54





