During recent excavations in Pompeii, archaeologists have uncovered ancient graffiti believed to have been made by children, depicting scenes of gladiator battles and other imagery.
 Graffiti uncovered at Pompeii appear to depict gladiators. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Graffiti uncovered at Pompeii appear to depict gladiators. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The drawings were found in various locations within the ruins of Pompeii. One of the significant findings comes from the Casa del Cenacolo Colonnato enclosure, where archaeologists found charcoal drawings made by children, likely just before the volcanic eruption of Mount Vesuvius. These drawings depict scenes of Roman gladiators, reflecting the impact of the violent spectacles witnessed by the children at the nearby amphitheater.
Gabriel Zuchtriegel, Director of the Pompeii Archaeological Park, said: “Together with psychologists from the Federico II [university of Naples], we have come to the conclusion that the drawings of gladiators and hunters were made based on a direct vision, and not of pictorial models. They had probably witnessed battles in the amphitheater, thus coming into contact with an extreme form of spectacularised violence.” Zuchtriegel emphasized that the graphic violence depicted in the graffiti may have had a lasting effect on the mental well-being and development of the young residents.
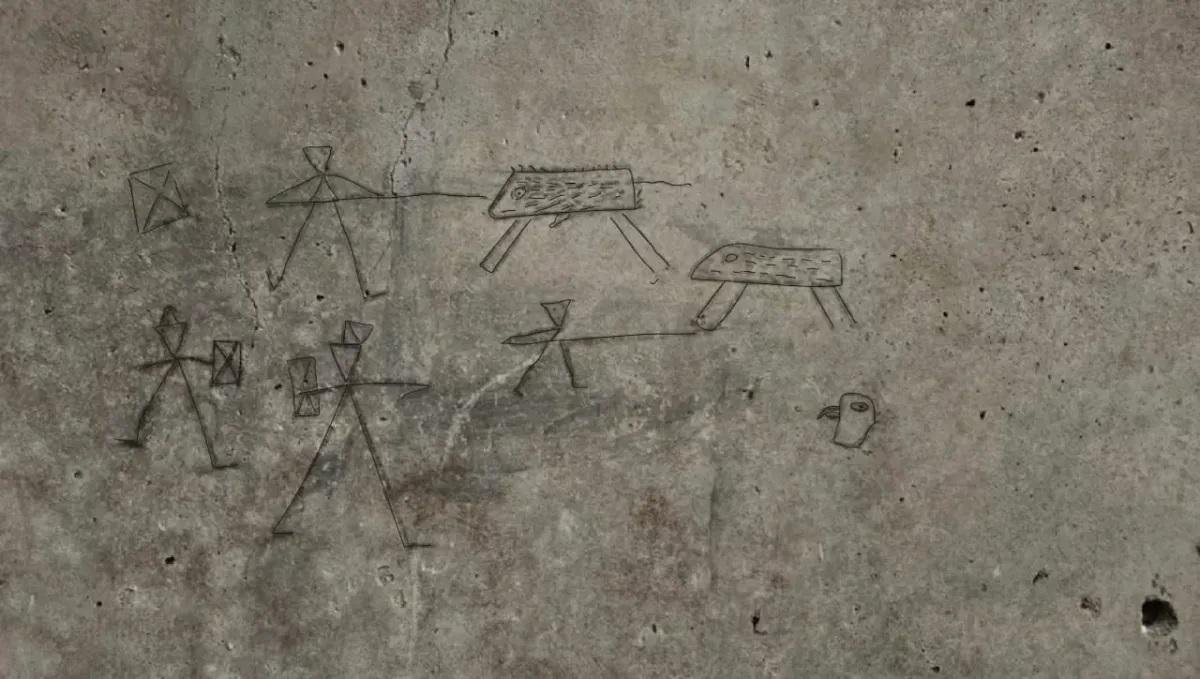
 Another graffiti found at Pompeii. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Another graffiti found at Pompeii. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Further discoveries at the Insula dei Casti Amanti, another cluster of homes in Pompeii, revealed additional drawings, including outlines of small hands, figures playing with a ball, hunting scenes, and depictions of gladiators. These primitive sketches, believed to be around 2,000 years old, depict men with spears and shields engaged in battles with wild animals and each other.
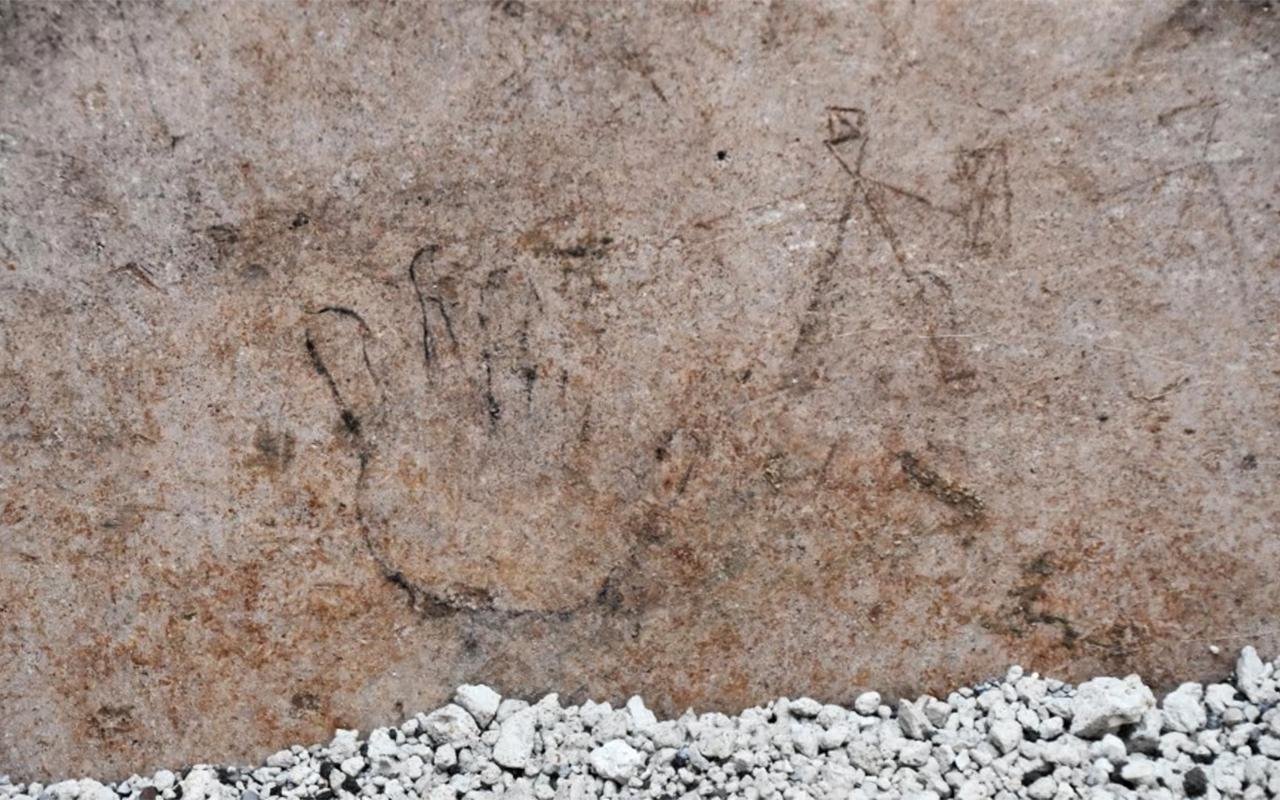 A drawing of a small hand was among the graffiti found. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
A drawing of a small hand was among the graffiti found. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The simplicity of execution and naivety of strokes in the graffiti indicate that they were likely made by children, possibly around five to six years old. Despite their primitive style, the drawings exhibit a remarkable sense of narrative and movement, portraying complete stories from the preparation for the fight to the victorious outcome. Zuchtriegel noted, “Evidently it is an anthropological constant that is independent of artistic and cultural fashions.”
The excavations also uncovered the remains of two victims of the eruption, highlighting the tragic fate of Pompeii’s residents in CE 79.
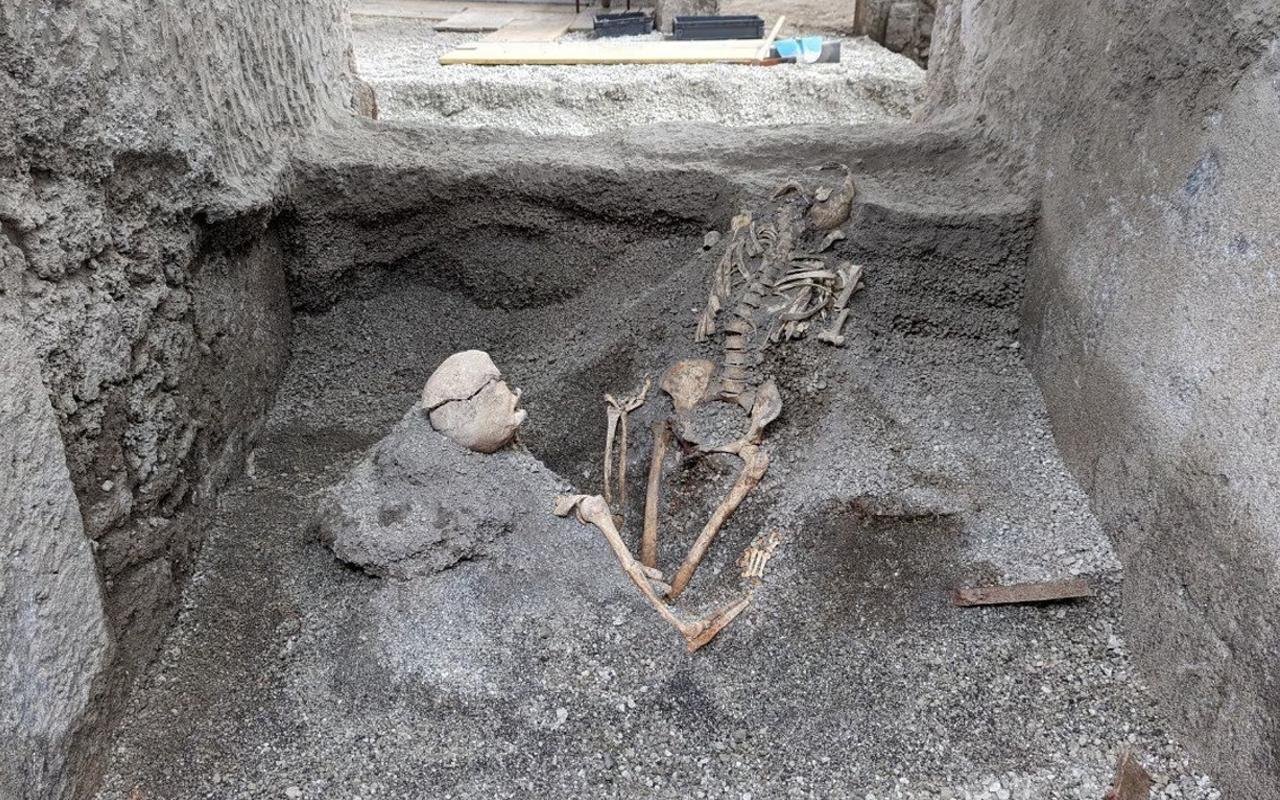 The remains of two bodies were also uncovered at the site. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The remains of two bodies were also uncovered at the site. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Last month an exquisite artwork was revealed depicting Helen of Troy, renowned for her beauty in Greek mythology, meeting Paris, the prince of Troy, for the first time.
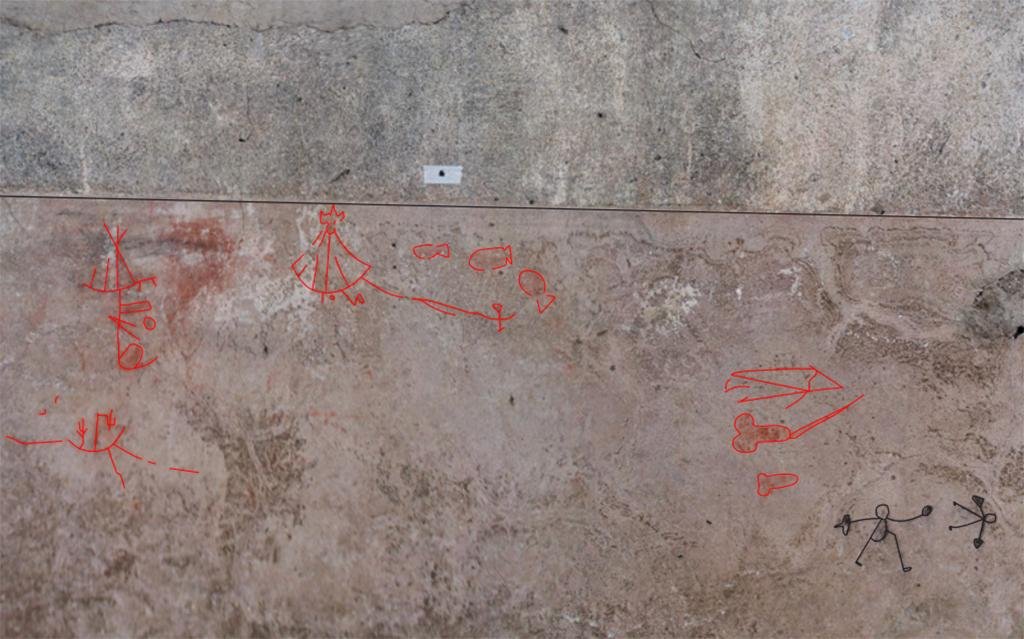 The graffiti also depicts ships. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
The graffiti also depicts ships. Courtesy of the Archaeological Park of Pompeii
With as much as a third of the city still buried under volcanic debris, archaeologists anticipate further revelations as they continue to explore this extraordinary archaeological site.
Archaeological Park of Pompeii





