A recent study published in Science Advances has unveiled that the Menga Dolmen, a 6,000-year-old megalithic burial mound in southern Spain, was constructed using “advanced engineering” techniques.
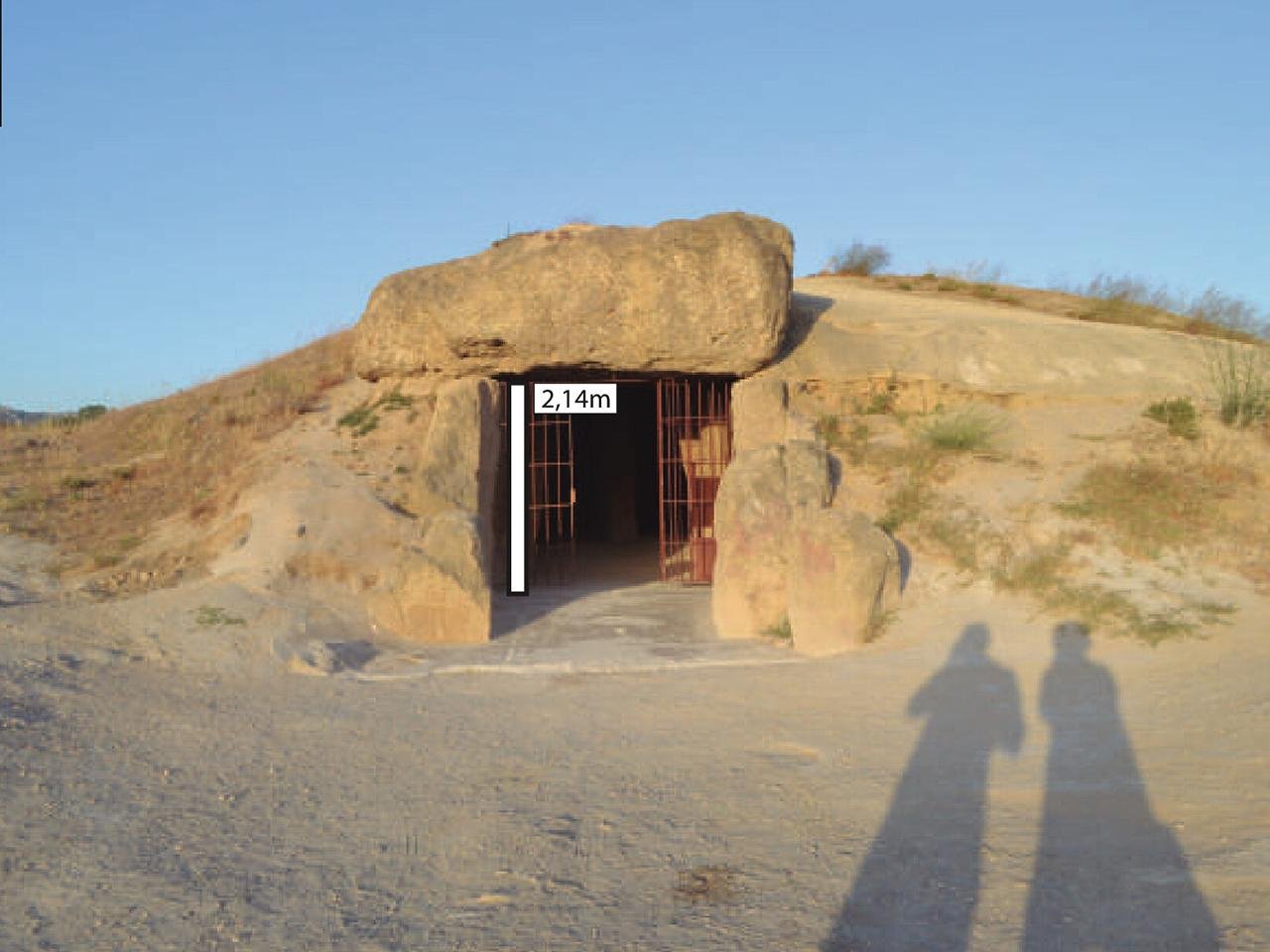 Entrance to the Menga dolmen. Credit: José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
Entrance to the Menga dolmen. Credit: José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
Built between 3800 and 3600 BCE, this Neolithic monument is a single-chamber tomb, or dolmen, consisting of 32 mᴀssive stones that collectively weigh about 1,140 metric tons. These stones are significantly larger than those used to build Stonehenge, with some weighing as much as 150 metric tons, equivalent to the weight of a blue whale.
The Menga Dolmen, located in the Antequera municipality, stands out as one of the largest and most significant megalithic structures from the Neolithic period. According to José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez, a geologist at the Canary Islands Oceanographic Center and the study’s lead author, the dolmen is “a unique example of creative genius and early science among Neolithic societies.” His team’s decade-long research project combined archaeological, sedimentological, and paleontological evidence to shed light on the advanced engineering knowledge of the dolmen’s builders.
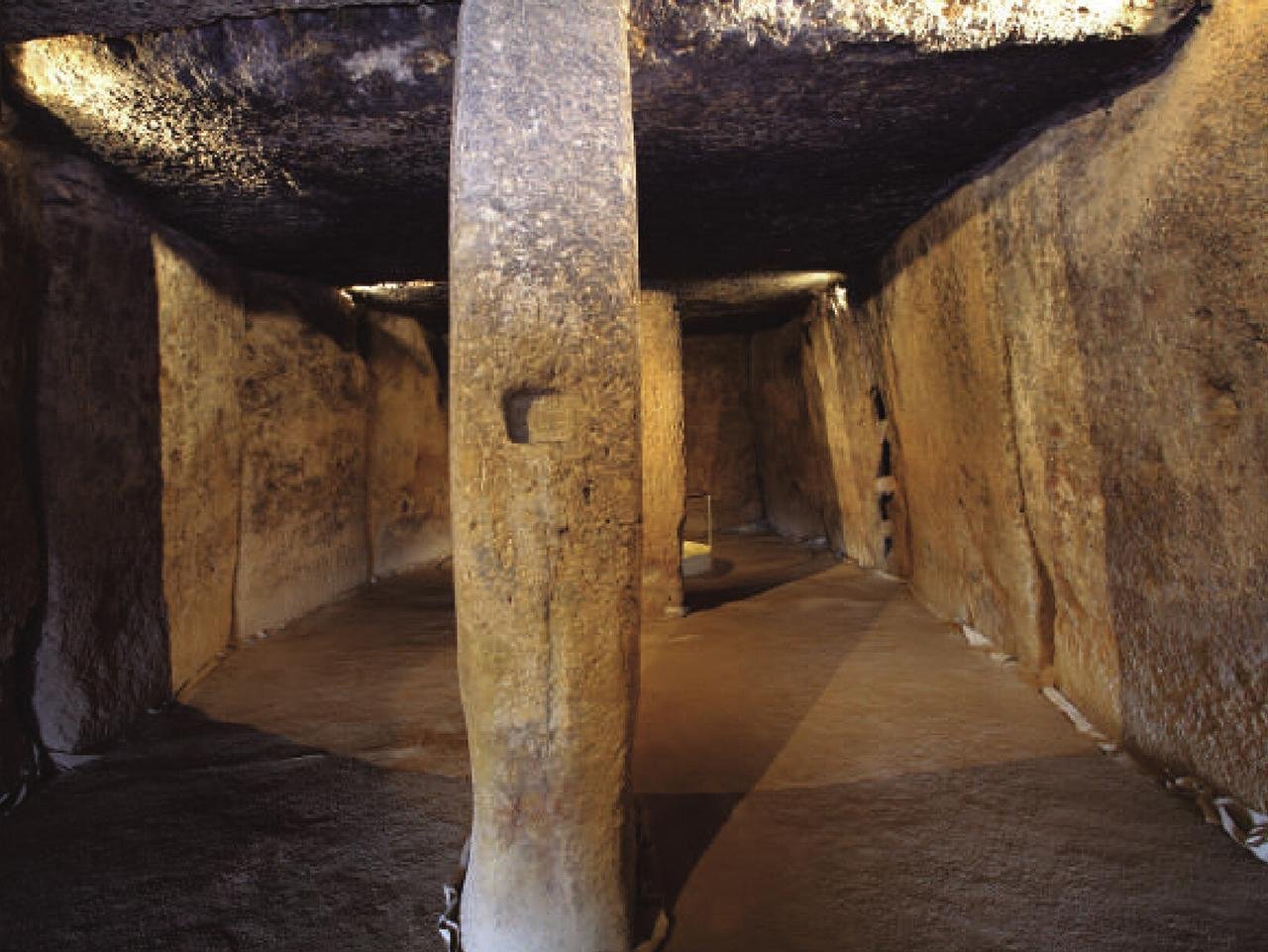 Interior of the dolmen from the second pillar. Credit: Antequera Dolmens Archaeological Site / José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
Interior of the dolmen from the second pillar. Credit: Antequera Dolmens Archaeological Site / José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
The study challenges the traditional view that construction techniques in the Neolithic era were primitive. Instead, the findings suggest that the builders possessed a sophisticated understanding of physics, geology, architectural principles, and engineering techniques. “Our findings run entirely counter to the idea of ‘primitiveness’ or ‘rudeness’ that for a long time has underpinned both the popular and scientific understanding of Neolithic societies,” Rodríguez stated in a press release.
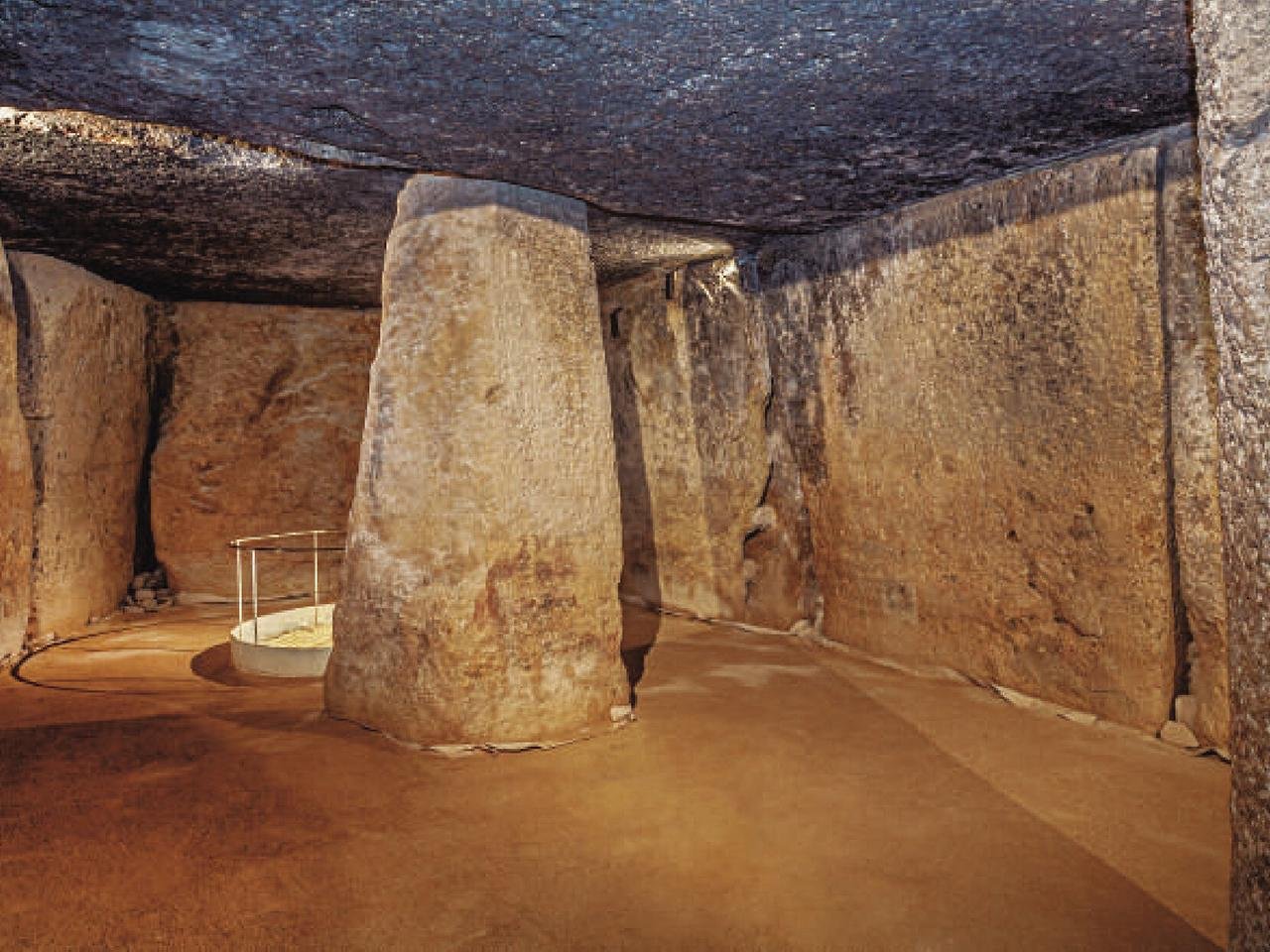 Dolmen chamber. Credit: Antequera Dolmens Archaeological Site / José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
Dolmen chamber. Credit: Antequera Dolmens Archaeological Site / José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
The construction of the Menga Dolmen involved a deep understanding of elementary physics, including friction and geometry, as well as an intricate knowledge of the properties and locations of rocks in the region. The upright stones that form the walls of the chamber were not perfectly vertical but instead tilted inward at a slight angle. This design made the building narrower at the roof than at the floor, creating a trapezoid-shaped chamber that enhanced the structure’s stability. The precision of these angles is millimetric, with each block fitting perfectly with the others, effectively locking them into place.
The stones used in the Menga Dolmen were quarried from a site about 850 meters away, which is about 50 meters higher in elevation than the monument’s location. This topographical advantage likely facilitated the transport of the mᴀssive stones downhill. Researchers believe the stones were transported on sledges over a specially designed wooden trackway to minimize friction. The largest stone, weighing 150 tons, required careful handling to avoid damage during transport. Rodríguez explained that the builders “designed the monument buried in the ground, thus avoiding the need to build large ascending ramps to place the gigantic stones that make up the capstone.”
The construction process was carefully planned and executed. The builders embedded the upright stones into foundation sockets so deep that up to one-third of the stones were below ground when first erected. Once the walls were in place, the builders added five huge capstones to form the roof. These capstones were slightly convex, distributing their weight to the sides and creating the earliest known example of a stress-relief arch.
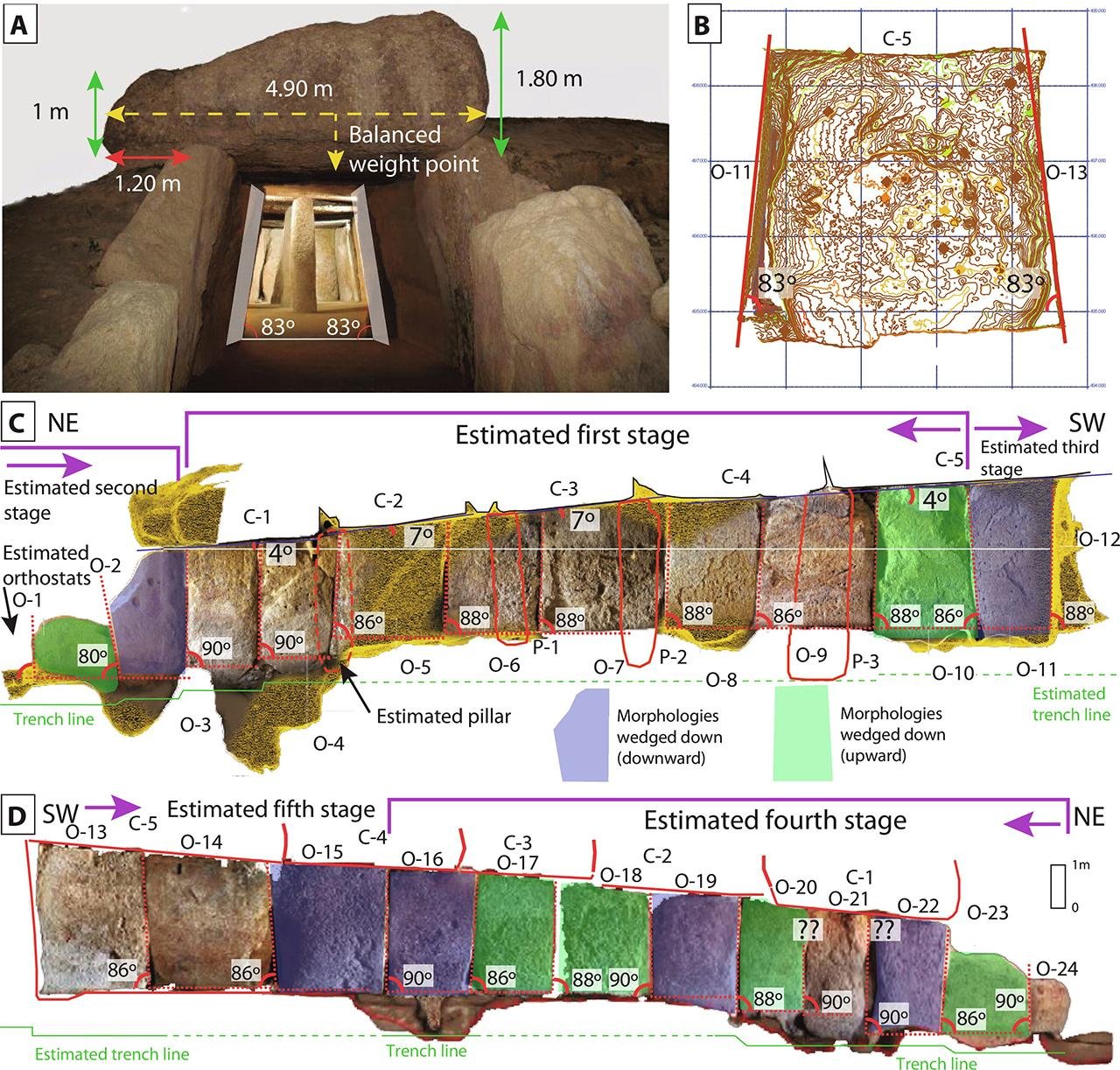 Architecture of the Menga dolmen. Credit: José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
Architecture of the Menga dolmen. Credit: José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al., Science Advances (2024)
The study reveals that these early builders employed what Rodríguez and his colleagues refer to as “early science” in their construction methods. This suggests a level of ingenuity and scientific understanding that was previously underestimated. The precision with which the stones were placed and the advanced techniques used to transport and erect them indicate a highly organized and knowledgeable society.
Leonardo García Sanjuán, a professor of prehistory at the University of Seville and co-author of the study described the Menga Dolmen as “one of the world’s greatest megalithic wonders” and noted that the builders’ intent was to create a structure that would stand the test of time. The monument was built to withstand the seismically active region’s challenges and to symbolize permanence, a feature shared by other prehistoric megalithic dolmens across western Europe.
More information: José Antonio Lozano Rodríguez et al. (2024). Early science and colossal stone engineering in Menga, a Neolithic dolmen (Antequera, Spain). Sci. Adv.10, eadp1295. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adp1295





