Archaeologists have made a fascinating discovery in a Roman-era cemetery in Pommerœul, Belgium, revealing a skeleton composed of bones from at least five individuals, representing a span of over 2,500 years.
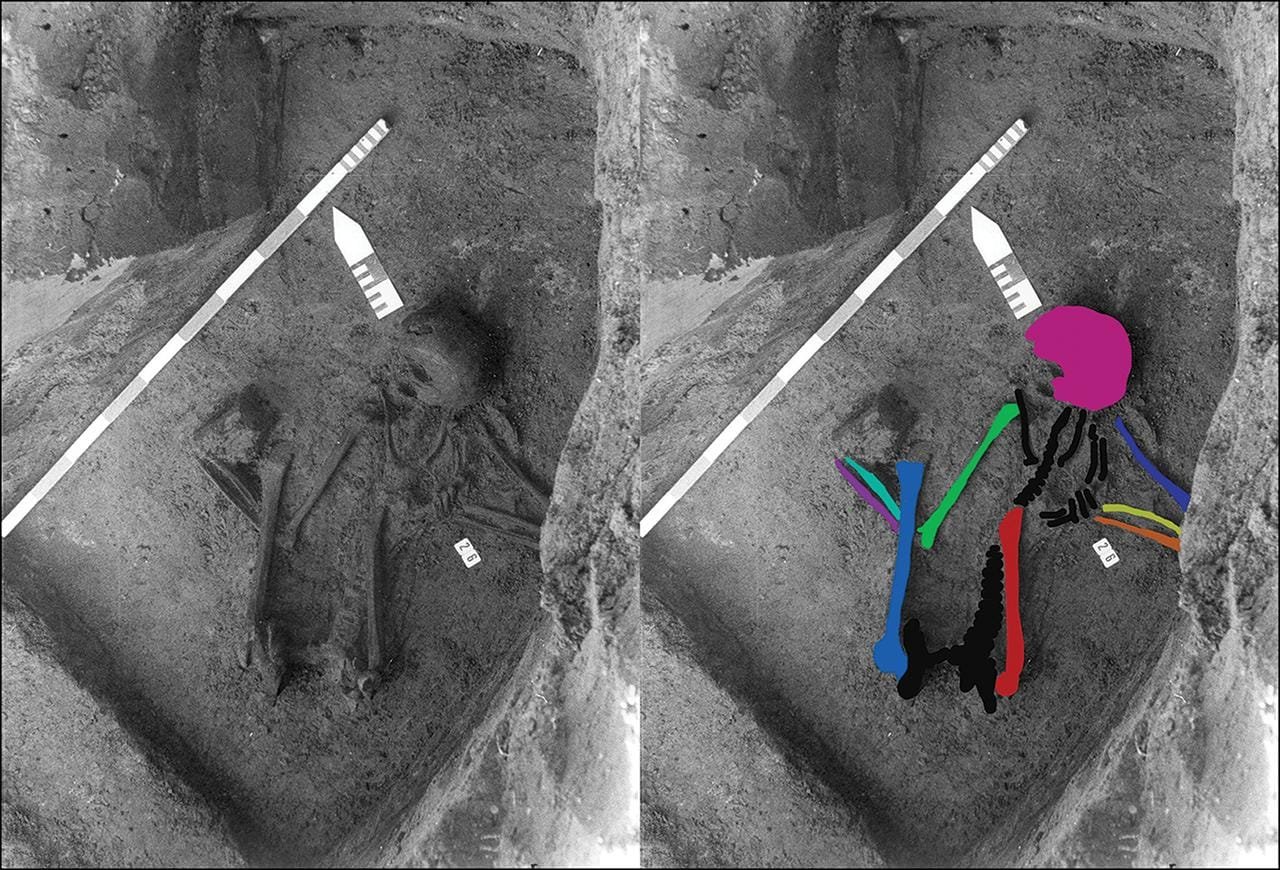 A Neolithic grave in Pommerœul, Belgium, contains the remains of at least five individuals. The color indicates the bones that were sampled for aDNA analysis. Credit: Paumen, Wargnies and Demory, Fédération Wallonie-Bruxelles
A Neolithic grave in Pommerœul, Belgium, contains the remains of at least five individuals. The color indicates the bones that were sampled for aDNA analysis. Credit: Paumen, Wargnies and Demory, Fédération Wallonie-Bruxelles
Unearthed in the 1970s and first thought to date to the Gallo-Roman period of the second or third century CE, the skeleton has sparked widespread interest for its unusual composition and meticulously arranged structure, according to a recent study published in Antiquity.
The site in Pommerœul contained 76 Roman-era cremation burials and one inhumation in a fetal position—a style more common in prehistoric contexts than Roman ones. The archaeologists initially concluded that the skeleton belonged to a woman from the Roman period due to the presence of a Roman-style bone pin found near the skull. However, radiocarbon dating in 2019 revealed that, while the skull and pin dated to around the third century CE, other bones belonged to the Neolithic period (7000–3000 BCE), indicating that this was not a single individual but a composite skeleton ᴀssembled from parts of multiple people.
Barbara Veselka, an archaeologist at Vrije Universiteit Brussel who led the study, explained that the skeleton likely originated from a mix of ancient remains rather than representing a typical burial. “It is likely that more than five individuals contributed to the ‘individual,’ but five were confirmed by DNA,” Veselka told Live Science. The bones, she noted, appeared carefully selected and arranged to mimic a complete person, suggesting a deliberate and ritualistic intention behind their placement. This precision, Veselka highlighted, implies not only familiarity with human anatomy but also respect for the deceased.
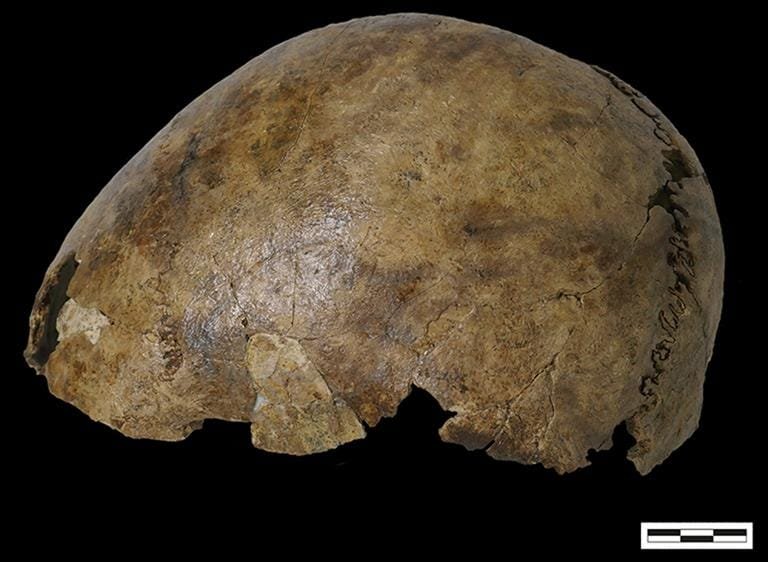 The cranium from the grave. Credit: B. Veselka et al. Antiquity (2024)
The cranium from the grave. Credit: B. Veselka et al. Antiquity (2024)
The creation of composite skeletons is rare in archaeological records, and even more so when the bones come from people separated by centuries or millennia. Archaeologists propose two primary theories to explain how this particular ᴀssemblage of bones came to be. One theory posits that the Romans, while burying their own ᴅᴇᴀᴅ, disturbed an ancient Neolithic burial by accident. In an attempt to “repair” or “complete” the site, they may have added a new skull, possibly to ensure the burial maintained spiritual integrity.
Another theory suggests that the Romans, “inspired by supersтιтion,” intentionally combined Neolithic bones with a Roman skull to forge a symbolic link with the land’s past inhabitants. The researchers speculate that such actions could have been a means to lay claim to the land or connect with the local ancestry of the region.
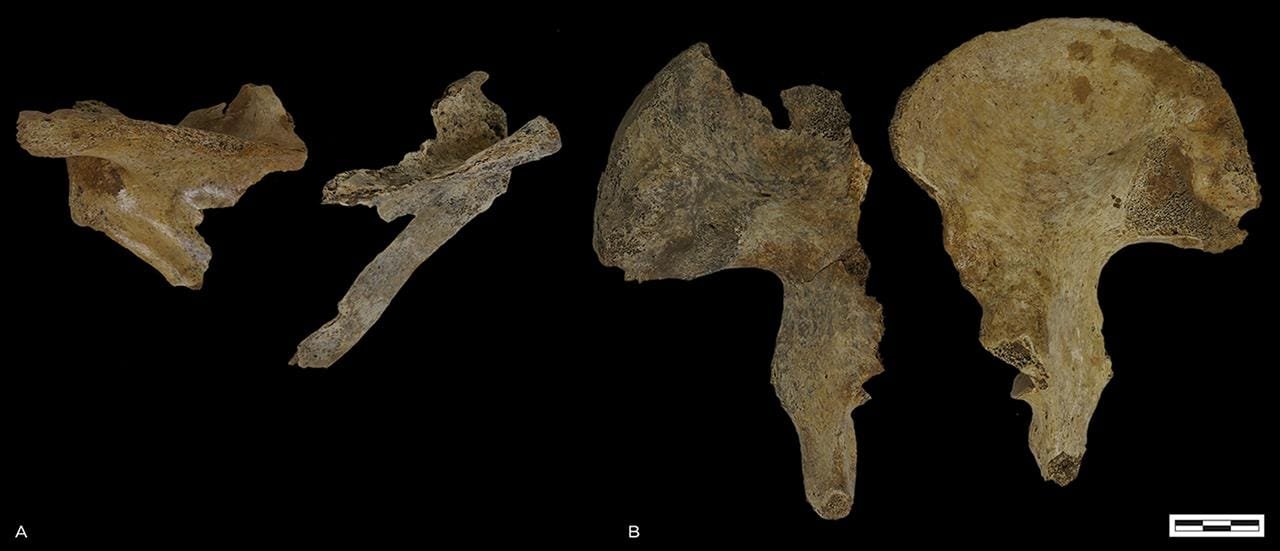 A) left and right scapulae; B) left and right os coxae. Credit: B. Veselka et al. Antiquity (2024)
A) left and right scapulae; B) left and right os coxae. Credit: B. Veselka et al. Antiquity (2024)
Adding to the mystery, the tomb’s proximity to a river may have also held spiritual significance. “Throughout the ages, rivers and other bodies of water were considered to be important, both geographically and spiritually,” Veselka explained to Live Science, noting that riversides often served as ritual sites across different cultures and time periods.
Although the original motivations remain unclear, the care with which the bones were arranged suggests a respect for ancient funerary practices. The researchers concluded that the presence of the ‘individual’ was clearly intentional.
More information: Veselka B, Reich D, Capuzzo G, et al. (2024). ᴀssembling ancestors: the manipulation of Neolithic and Gallo-Roman skeletal remains at Pommerœul, Belgium. Antiquity:1-16. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.158





