Archaeologists have unearthed what may be some of the earliest evidence of wheel-like technology in human history at the Nahal-Ein Gev II site in northern Israel.
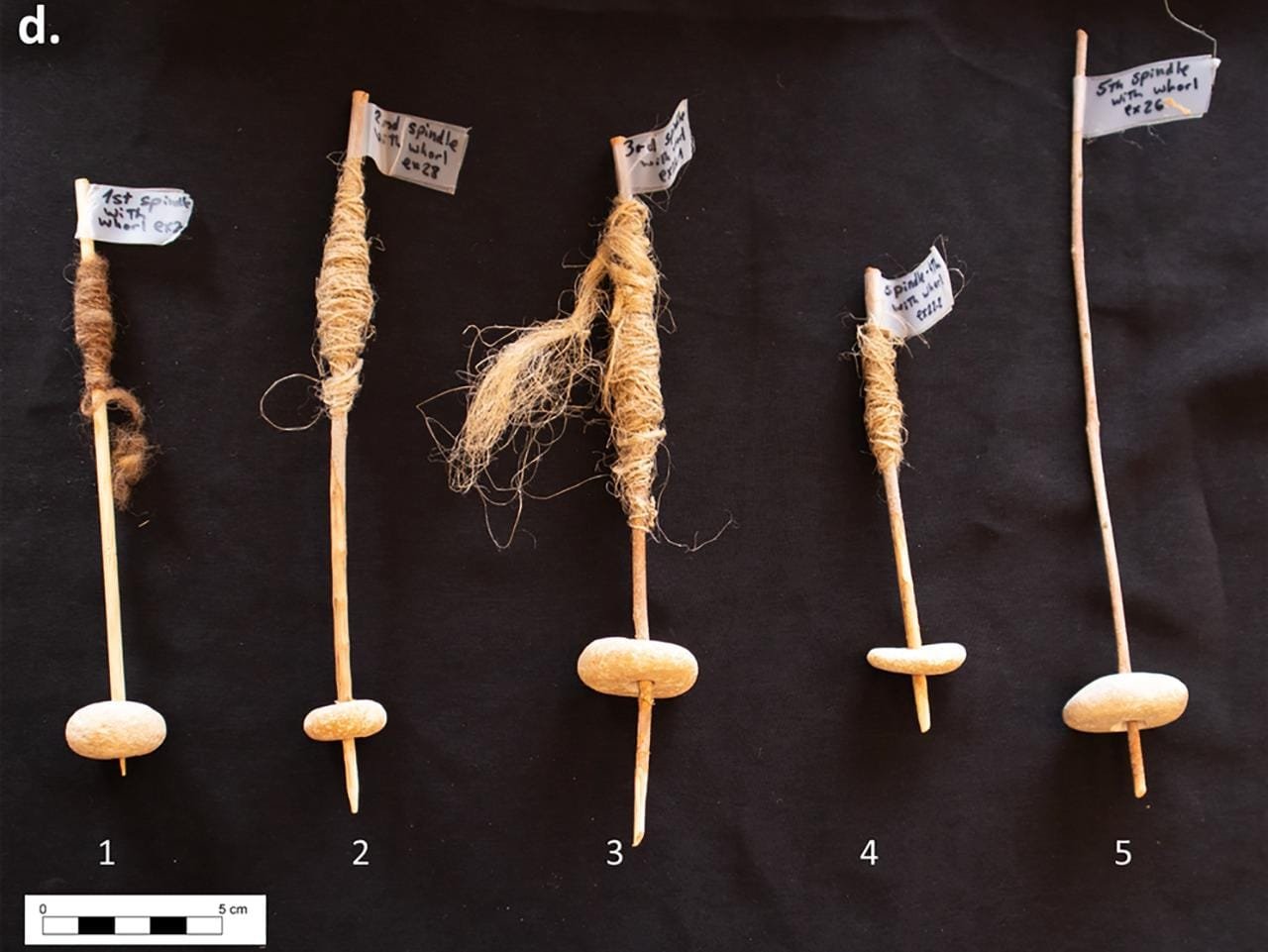 The experimental spindles and whorls, the 3D scans of the pebbles and their negative perforations. Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
The experimental spindles and whorls, the 3D scans of the pebbles and their negative perforations. Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
A recent study published on November 13, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Talia Yashuv and Leore Grosman of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem suggests that a collection of perforated, donut-shaped pebbles dating back approximately 12,000 years were likely spindle whorls. This discovery significantly predates the traditional invention of the wheel, which is generally dated to around 6,000 years ago.
Spindle whorls are small, weighted objects attached to a spindle stick to facilitate the spinning of fibers such as flax or wool into yarn. These tools operate on a wheel-and-axle principle, enabling prolonged and efficient rotation essential for textile production.
Yashuv and Grosman utilized innovative digital 3D scanning technology to create detailed models of over a hundred limestone pebbles recovered from the site. Their analysis revealed that these stones featured consistent circular shapes with central perforations, indicative of deliberate craftsmanship rather than natural formation. To test their hypothesis, the researchers replicated the spindle whorls and collaborated with Yonit Crystal, an expert in traditional craft making, who successfully used the replicas to spin flax and wool. The experiments confirmed that the pebbles functioned effectively as spindle whorls, supporting the study’s conclusion that these ancient tools represent an early form of rotational technology.
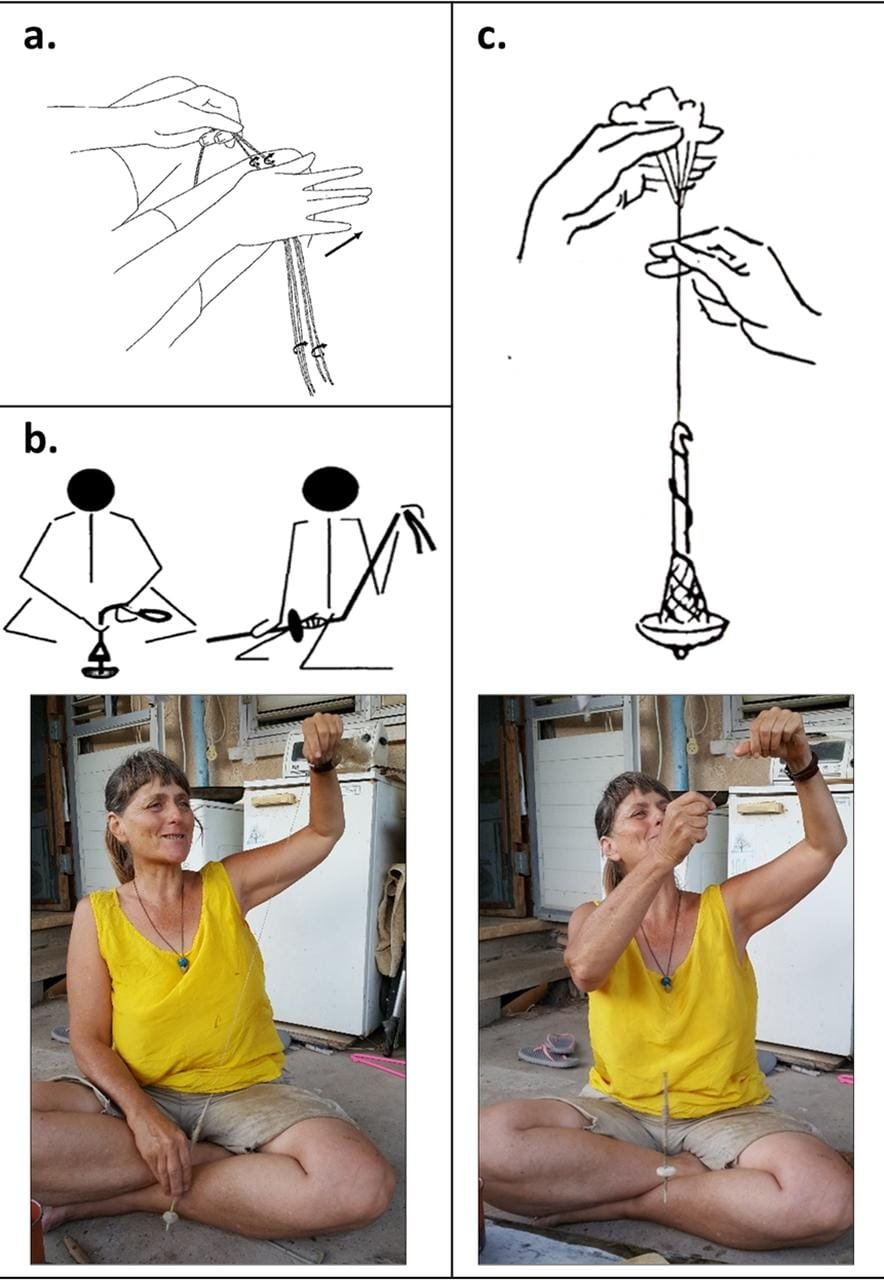 (a) Manual thigh-spinning; (b) Spindle-and-whorl “supported spinning”; (c) “drop spinning”; Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
(a) Manual thigh-spinning; (b) Spindle-and-whorl “supported spinning”; (c) “drop spinning”; Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
“This collection of spindle whorls would represent a very early example of humans using rotation with a wheel-shaped tool,” Yashuv explained. “They might have paved the way for later rotational technologies, such as the potter’s wheel and the cart wheel, which were vital to the development of early human civilizations.”
“This study not only highlights the innovativeness of prehistoric artisans but also bridges ancient technologies with our present-day capabilities,” Yashuv added. “By reconstructing and testing these tools, researchers are able to connect modern technology with the resourcefulness of our ancient ancestors, revealing a continuous link between early invention and current-day scientific methods.”
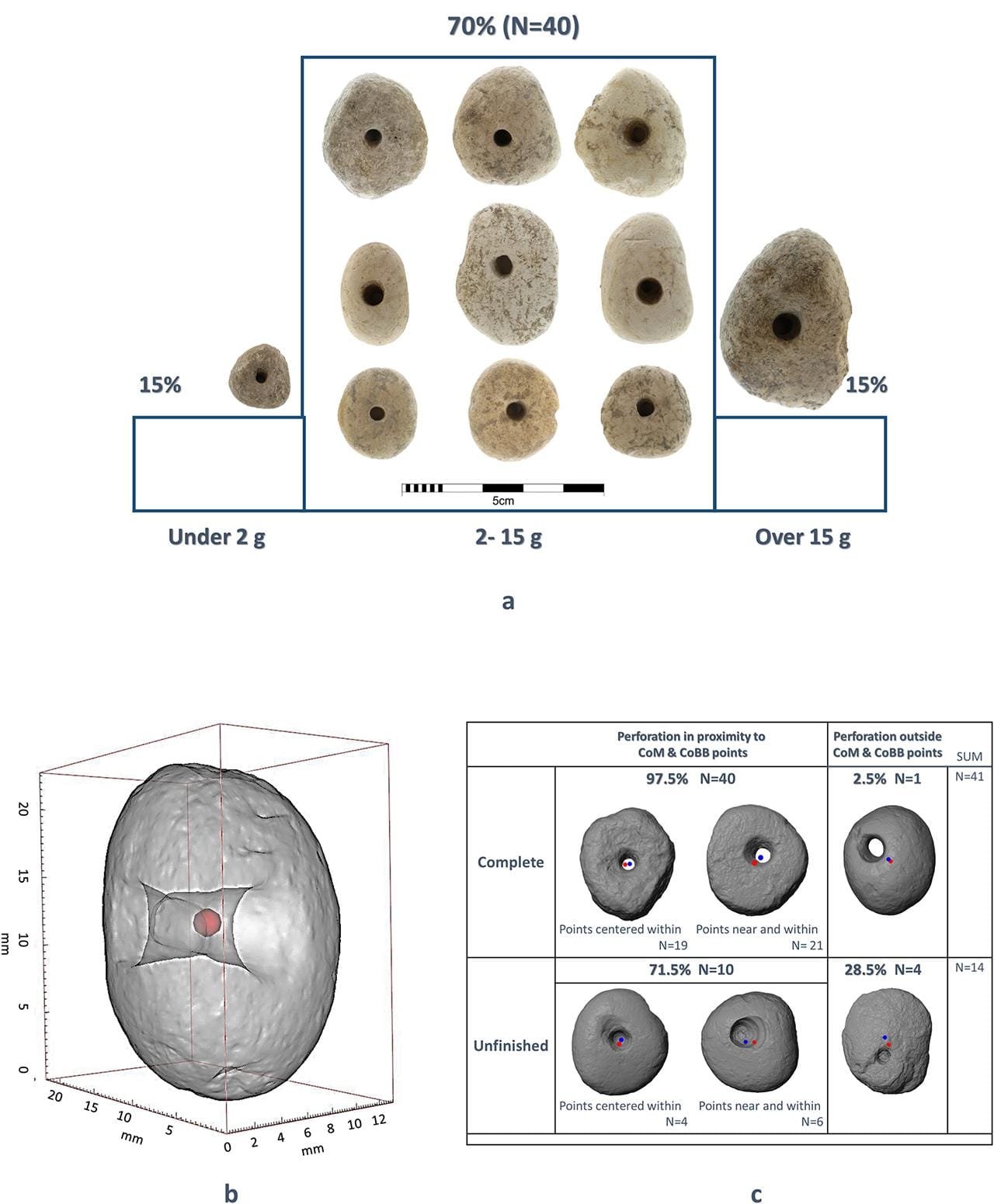 Complete shape 3D analysis of the perforated pebbles. Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
Complete shape 3D analysis of the perforated pebbles. Credit: Yashuv, Grosman, 2024, PLOS One, CC-BY 4.0
The findings encourage a reevaluation of the timeline and progression of rotational technologies in human history.
More information:Yashuv T, Grosman L (2024) 12,000-year-old spindle whorls and the innovation of wheeled rotational technologies. PLoS ONE 19(11): e0312007. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0312007





