A groundbreaking archaeological discovery in Vanguard Cave, part of the Gorham’s Cave complex in Gibraltar, has unveiled a 65,000-year-old tar-making site built by Neanderthals.
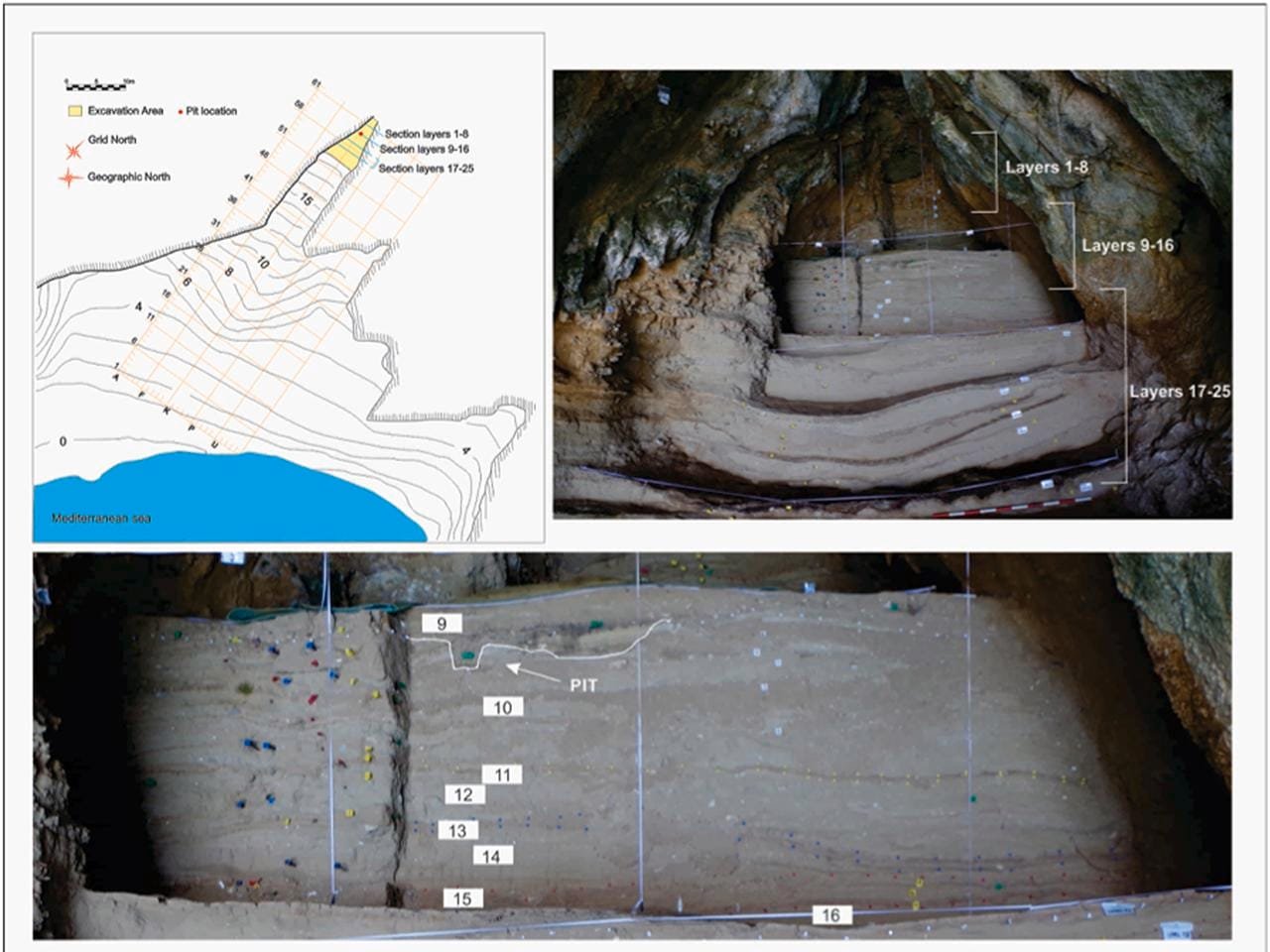 Plan view map of Vanguard Cave site and pictures showing the section profiles excavated and the section of the pit. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
Plan view map of Vanguard Cave site and pictures showing the section profiles excavated and the section of the pit. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
Archaeologists discovered a carefully engineered combustion structure, or hearth, used to produce tar from resinous plants such as rockrose (Cistus genus). Tar served as a critical adhesive, enabling Neanderthals to attach stone tools to wooden handles—an innovation that predates similar techniques by Homo sapiens by over 20,000 years.
The hearth, described as a “round pit” nearly 22 centimeters wide and 9 centimeters deep, featured sharply cut vertical walls and two short trenches extending outward. Researchers believe this design allowed Neanderthals to control airflow and temperature, a vital requirement for low-oxygen tar production.
Geochemical and microscopic analyses of sediment from the hearth revealed compounds like levoglucosan and retene, formed during the combustion of resinous plants. Charcoal analysis showed that most of the material burned came from rockrose plants, with minimal use of conifer wood. This controlled burning process aligns with experimental archaeology results, proving that Neanderthals achieved effective tar production.
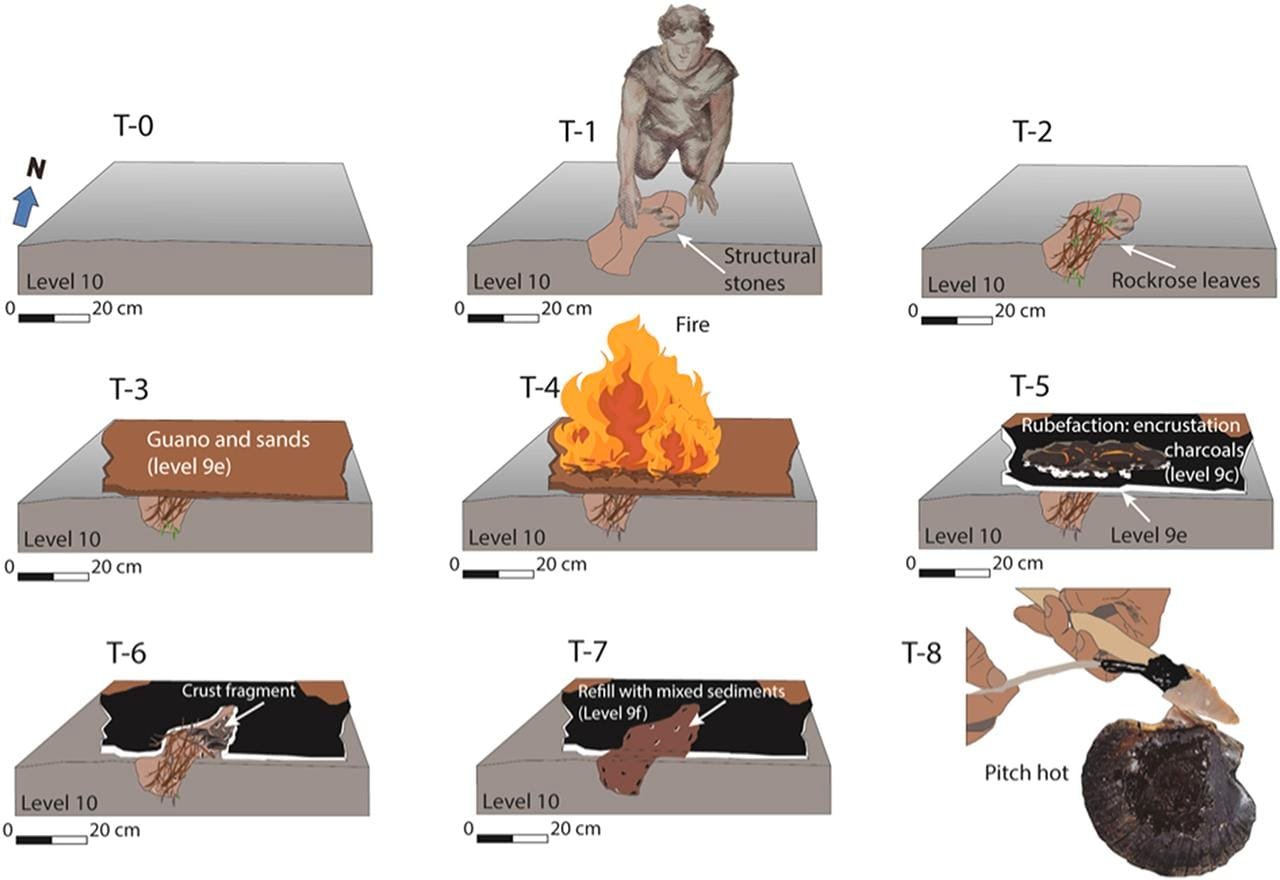 The anthropogenic structure could have been made following these steps. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
The anthropogenic structure could have been made following these steps. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
To verify their findings, researchers replicated the tar-making process using tools and materials available to Neanderthals. By heating rockrose leaves under a sealed, low-oxygen environment, they successfully produced tar. The process required precise temperature control—about 300°F (150°C)—and careful management of fire using thin twigs.
Lead author Dr. Luis Ochando noted that their experiments demonstrated the collaborative effort likely involved in this task. “Our colleagues found that managing the fire and extracting the tar required two individuals working together,” he explained. This teamwork suggests that Neanderthals not only mastered engineering but also possessed advanced social and cooperative skills.
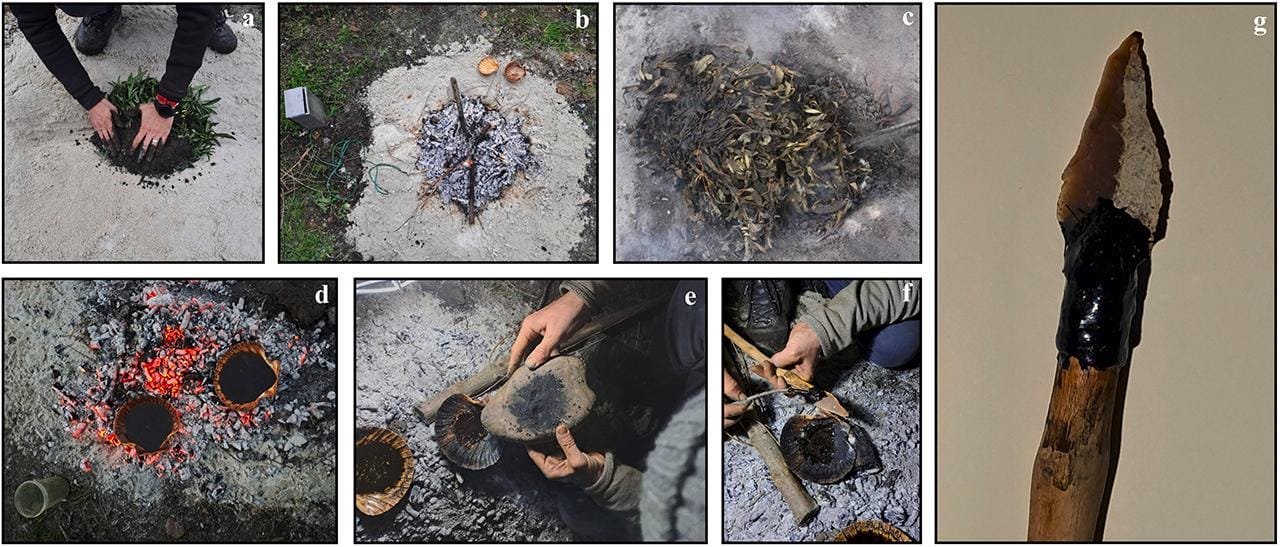 The pit structure was built by hand according to the morphology and dimensions defined by the archaeological excavations in Vanguard Cave. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
The pit structure was built by hand according to the morphology and dimensions defined by the archaeological excavations in Vanguard Cave. Credit: J. Ochando et al., Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
This discovery significantly enhances the perception of Neanderthals as innovative and resourceful. The presence of this tar-making structure in Vanguard Cave—a site forming part of the UNESCO-listed Gorham’s Cave complex—underscores their ability to adapt their environment to meet technological demands.
The study affirms that Neanderthals were capable of cognitive complexity and cultural sophistication far beyond previous ᴀssumptions. From precisely engineered structures to intricate fire management techniques, their achievements showcase a species that utilized innovation for survival and tool-making.
The findings, published in Quaternary Science Reviews, redefine our understanding of Neanderthal innovation.
More information: Ochando, J., Jiménez-Espejo, F. J., Giles-Guzmán, F., Neto de Carvalho, C., Carrión, J. S., Muñiz, F., … Finlayson, C. (2024). A Neanderthal’s specialised burning structure compatible with tar obtention. Quaternary Science Reviews, (109025), 109025. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2024.109025





