A recent study published in PLOS ONE reveals that early humans living in the Ethiopian Highlands between 1.6 and 1 million years ago displayed remarkable cognitive and technological capabilities. By strategically selecting specific types of stone for toolmaking, these early hominins showcased an advanced understanding of their natural environment and its resources.
 An artistic representation of Homo erectus holding an Acheulean hand axe. Archaeology News Online Magazine
An artistic representation of Homo erectus holding an Acheulean hand axe. Archaeology News Online Magazine
The research, conducted at the Melka Wakena site in the Ethiopian Highlands, highlights the significance of material properties in the development and use of early Acheulean tools. Using advanced imaging and robotic experiments, researchers demonstrated that early humans were not randomly choosing stones but were carefully evaluating factors like durability, efficiency, and suitability for specific tasks.
Findings show that early hominins had a deep understanding of the properties of different stones, enabling them to make informed decisions about their tools.
The research team used technologies from the TraCEr Laboratory of MONREPOS Archaeological Research Center and Museum for Human Behavioral Evolution in Germany, such as sophisticated imaging methods, including 3D scanning and pH๏τogrammetry, to analyze wear patterns on stone tools. The data revealed that within the same utilization conditions, the physical properties of different materials significantly influenced the tools’ durability and performance.
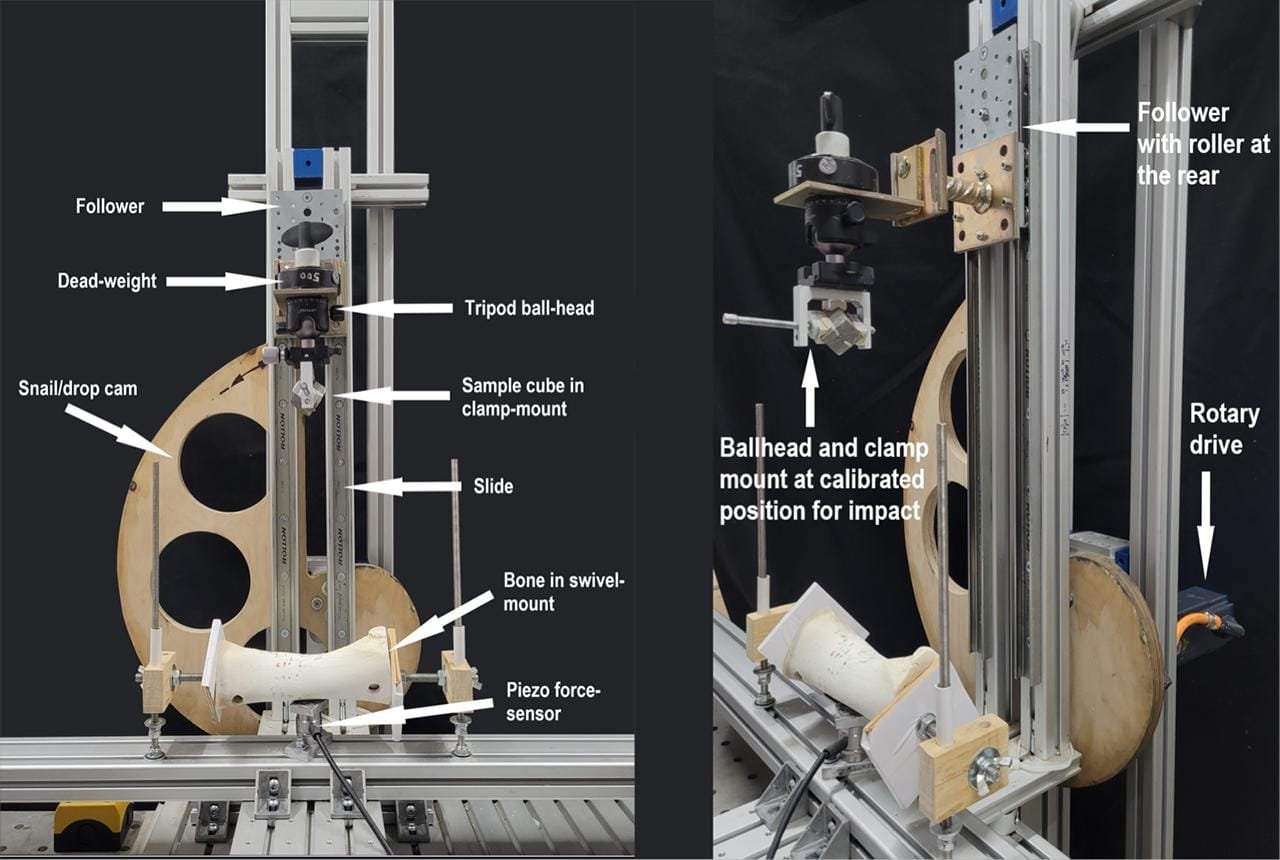 Experimental mechanical setup (SMARTTESTER, manufactured by Inotec AP GmbH, with adaptations made by Walter Gneisinger) at TraCEr laboratory in Monrepos. Credit: Eduardo Paixão, Walter Gneisinger
Experimental mechanical setup (SMARTTESTER, manufactured by Inotec AP GmbH, with adaptations made by Walter Gneisinger) at TraCEr laboratory in Monrepos. Credit: Eduardo Paixão, Walter Gneisinger
Prof. Erella Hovers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, who co-led excavations at the site with Dr. Tegenu Gossa, said: “Early humans were making complex decisions about which stones to use based on their intended purposes.” This reflects an advanced level of technological foresight and adaptability.
Dr. João Marreiros, director of the TraCEr Laboratory, said: “The deliberate selection of materials influenced the surface changes of the tools. This demonstrates that differences in archaeological finds are not random.”
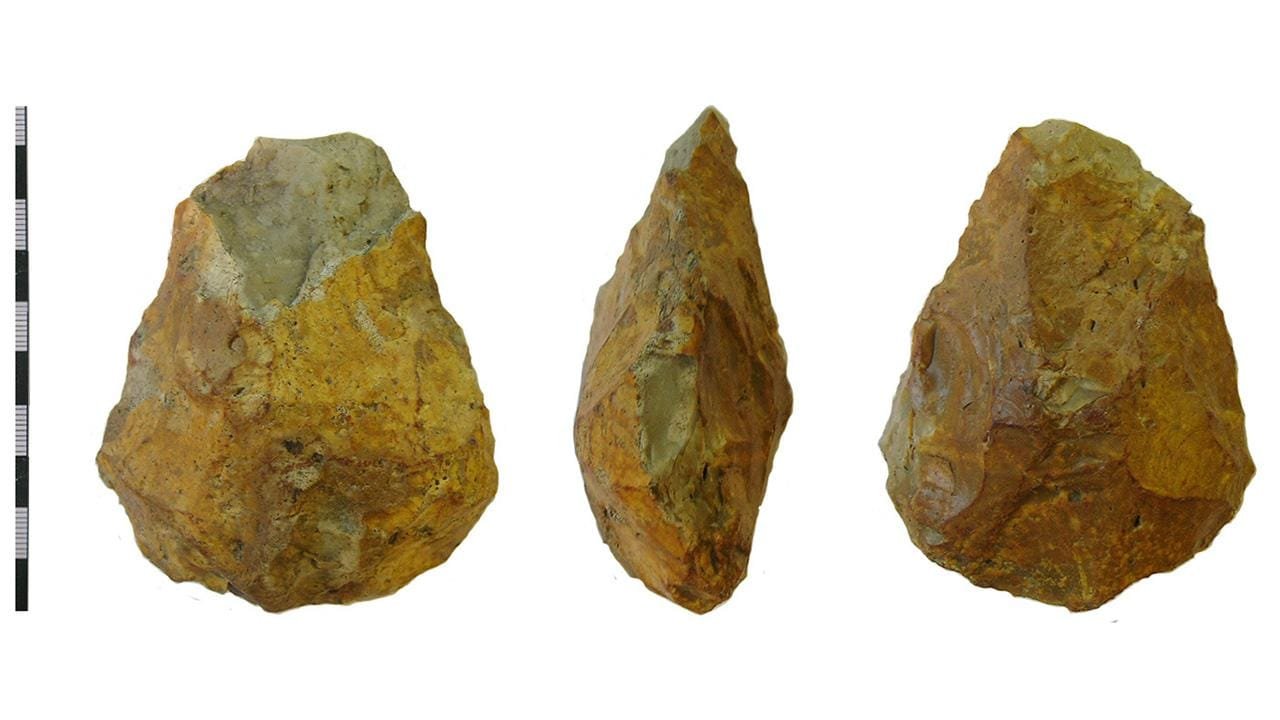 Acheulean hand axe. Credit: Julian Watters, CC BY-SA 2.0
Acheulean hand axe. Credit: Julian Watters, CC BY-SA 2.0
The study was a collaborative effort between different insтιтutions worldwide, including the Interdisciplinary Center for Archaeology and Evolution of Human Behavior (ICArEHB) at the University of Algarve, the TraCEr Laboratory, and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. This interdisciplinary approach allowed researchers to establish a quantifiable baseline for understanding the technological behaviors of early Pleistocene toolmakers.
More research will be done on other conditions that determine raw material choice, including tool use activities like stone flaking, bone breaking, and meat processing.
More information: Paixão E, Gossa T, Gneisinger W, Marreiros J, Tholen S, Calandra I, et al. (2025) Exploring early Acheulian technological decision-making: A controlled experimental approach to raw material selection for percussive artifacts in Melka Wakena, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 20(1): e0314039. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0314039





