In a fascinating intersection of Egyptology and astronomy, Dr. Or Graur, ᴀssociate Professor of Astrophysics at the University of Portsmouth, has uncovered compelling evidence that suggests that ancient Egyptians may have visually represented the Milky Way in artwork on funerary coffins and tomb ceilings. His study, which was recently published in the Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage, goes against prevailing theories about how the sky goddess Nut was depicted and how her image may have incorporated elements of the night sky, including the galaxy that arcs across it.
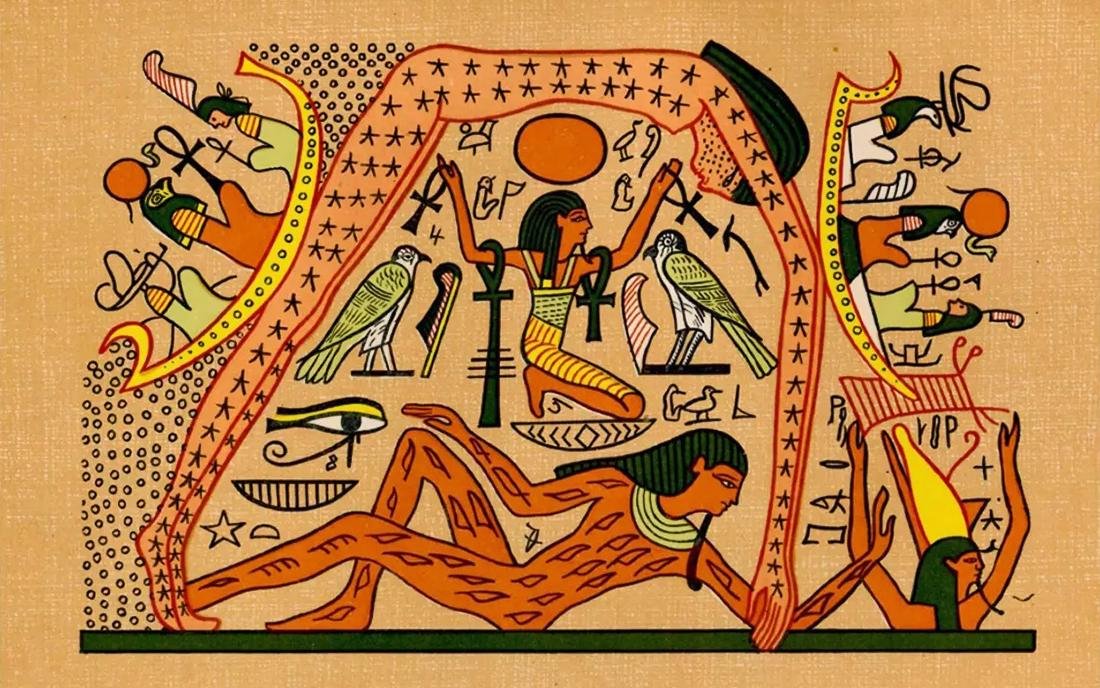 The sky goddess Nut, covered in stars, is held aloft by her father, Shu, and is arched over Geb, her brother the Earth god. On the left, the rising sun (the falcon-headed god Re) sails up Nut’s legs. On the right, the setting sun sails down her arms towards the outstretched arms of Osiris, who will regenerate the sun in the netherworld during the night. Credit: E. A. Wallis Budge, The Gods of the Egyptians, Vol. 2 (Methuen & Co., 1904).
The sky goddess Nut, covered in stars, is held aloft by her father, Shu, and is arched over Geb, her brother the Earth god. On the left, the rising sun (the falcon-headed god Re) sails up Nut’s legs. On the right, the setting sun sails down her arms towards the outstretched arms of Osiris, who will regenerate the sun in the netherworld during the night. Credit: E. A. Wallis Budge, The Gods of the Egyptians, Vol. 2 (Methuen & Co., 1904).
Nut, one of the major characters in Egyptian mythology, was often shown as a naked, star-covered woman protectively arching over the earth god Geb. Her image, often used on the lids of coffins, symbolized the heavens and the cycle of life and death. She was believed to devour the Sun each evening and give birth to it at dawn, underscoring her cosmic function.
Dr. Graur analyzed 125 images of Nut from a list of 555 ancient Egyptian coffins, many dating back nearly 5,000 years. Most show her in the usual way, but a fascinating exception is found on the outer coffin of Nesitaudjatakhet, a chantress to Amun-Re who died about 3,000 years ago. There, a thick, wavy black curve runs across Nut’s star-covered body from her feet to her fingertips—an unusual feature not usually found in Egyptian art on coffins.
“I think that the undulating curve represents the Milky Way and could be a representation of the Great Rift—the dark band of dust that cuts through the Milky Way’s bright band of diffused light,” Dr. Graur said. “Comparing this depiction with a pH๏τograph of the Milky Way shows the stark similarity.”
 The sky goddess Nut and human figures representing stars and constellations from the star chart in the tomb of Ramses VI. Credit: Hans Bernhard, GFDL-CC-BY-SA
The sky goddess Nut and human figures representing stars and constellations from the star chart in the tomb of Ramses VI. Credit: Hans Bernhard, GFDL-CC-BY-SA
Similar curved motifs have also been found in tombs in the Valley of the Kings, including those of Ramesses IV, VI, and IX, as well as on the ceiling of the tomb of Seti I. These curves divide cosmological scenes, especially in the Books of the Day and Night, where arched figures of Nut are depicted back-to-back. As Dr. Graur contends, these visual characteristics further reinforce his theory that the ancient Egyptians might have linked such curves with the Milky Way.
Interestingly, these wavy features occur in the cosmological artwork of Indigenous American cultures, such as the Navajo, Hopi, and Zuni, where they represent the Milky Way.
 A representation of the Egyptian Goddess Nut as a naked woman with stars on her body forming an arc, as she was depicted in The Tomb of Ramesses VI. Credit: Eternal Space, CC BY-SA 4.0
A representation of the Egyptian Goddess Nut as a naked woman with stars on her body forming an arc, as she was depicted in The Tomb of Ramesses VI. Credit: Eternal Space, CC BY-SA 4.0
Dr. Graur’s previous research, published in April 2024, focused on written records like the Pyramid Texts, Coffin Texts, and Book of Nut. In that research, the Milky Way was suggested to have helped ancient observers locate Nut in the night sky visually—highlighting her extended arms in winter and tracing her backbone in summer. This current research, based on visual observation of funerary art, refines the view.
Despite the visual connections, Dr. Graur cautions against equating Nut with the Milky Way itself. Nut’s body is represented as covered with stars in perhaps a quarter of the cosmological vignettes under study, implying that Egyptians during the 21st and 22nd Dynasties had a preference for illustrating the day sky rather than the night sky. This preference further complicates how the ancient Egyptians conceptualized the cosmos.
Dr. Graur’s study is part of a broader investigation into the mythological perceptions of the Milky Way across cultures.
More information: Graur, O. (2025). The ancient Egyptian cosmological vignette: First visual evidence of the milky way and trends in coffin depictions of the sky goddess nut. Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage, 28(1), 97–124. doi:10.3724/sp.j.140-2807.2025.01.06





