A new interdisciplinary research project will investigate the organization of ancient building material production in the Roman city of Trier, an important city in the northern provinces of the empire. The German Research Foundation (DFG) has funded €340,000 for two years to a team of scientists from the Rheinisches Landesmuseum Trier, Goethe University Frankfurt, and the Leibniz-Zentrum für Archäologie (LEIZA) to analyze thousands of Roman-era fired bricks.
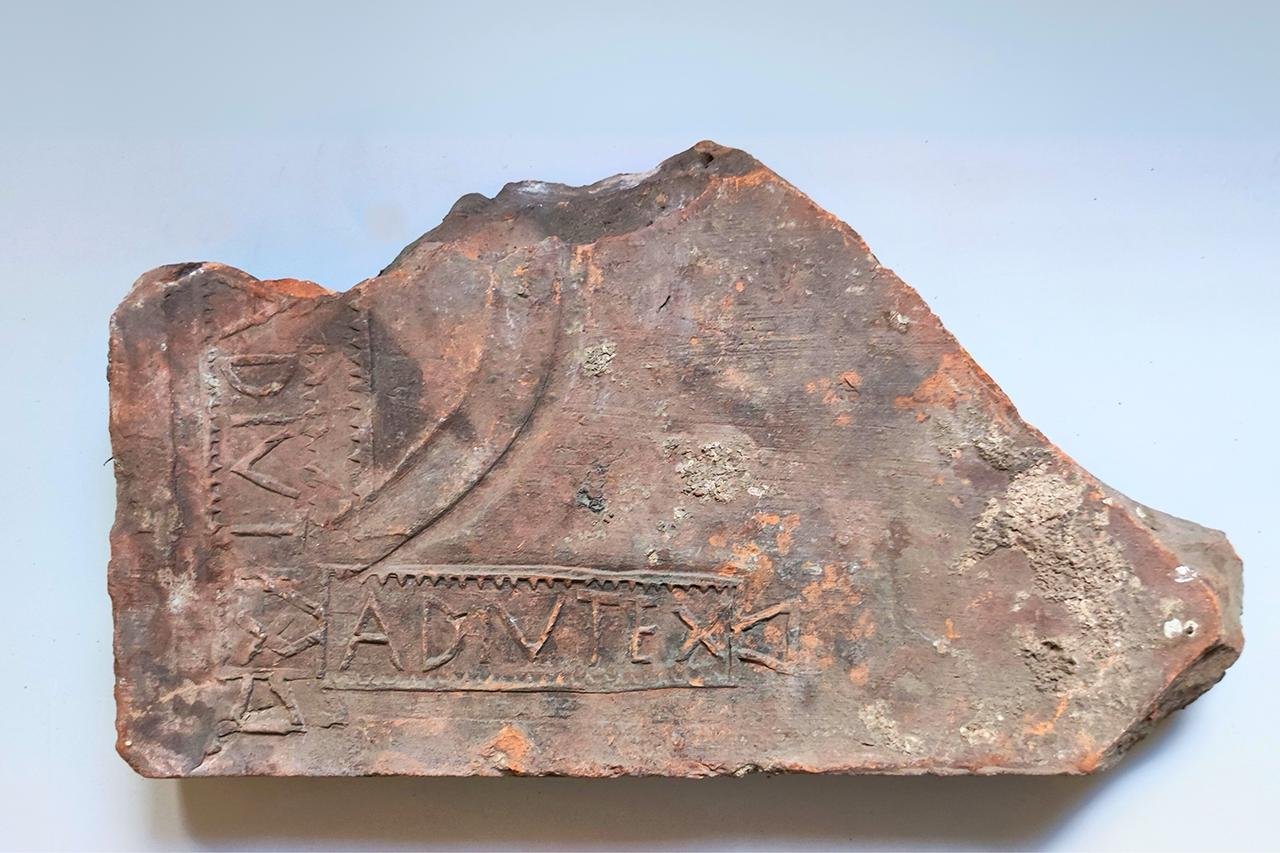 Fragment of a brick with two stamps, 4th century CE. Credit: Markus Helfert, Goethe University Frankfurt
Fragment of a brick with two stamps, 4th century CE. Credit: Markus Helfert, Goethe University Frankfurt
Trier, known as Augusta Treverorum in Roman times and then Treveris in Late Antiquity, flourished particularly in the 4th century CE when Roman emperors established residence there. The major structures like the Imperial Baths and the Basilica of Constantine stand today as a testament to the architectural legacy of the city. Many of these were constructed using fired bricks of many different forms and functions, such as for walls, roofs, and hypocaust heating systems.
Today, approximately 4,000 stamped Roman bricks are housed at the Rheinisches Landesmuseum Trier. While they have been unearthed since the early 20th century, the collection—one of the largest in the northern provinces—has been studied minimally. This project seeks to change that, providing new insight into the production and distribution of bricks during a pivotal period of urban expansion.
“We ᴀssume that most of the stamped bricks date from Late Antiquity,” said Dr. Thomas Schmidts, a private lecturer at Goethe University and conservator in Roman Archaeology at LEIZA. “Brick stamps are also key to understanding the economic and social structures of Late Antiquity,” he added. The research will do more than catalog the stamps, and will also include spatial analysis of the distribution of bricks with the potential for unveiling evidence of previously unknown state and public building initiatives.
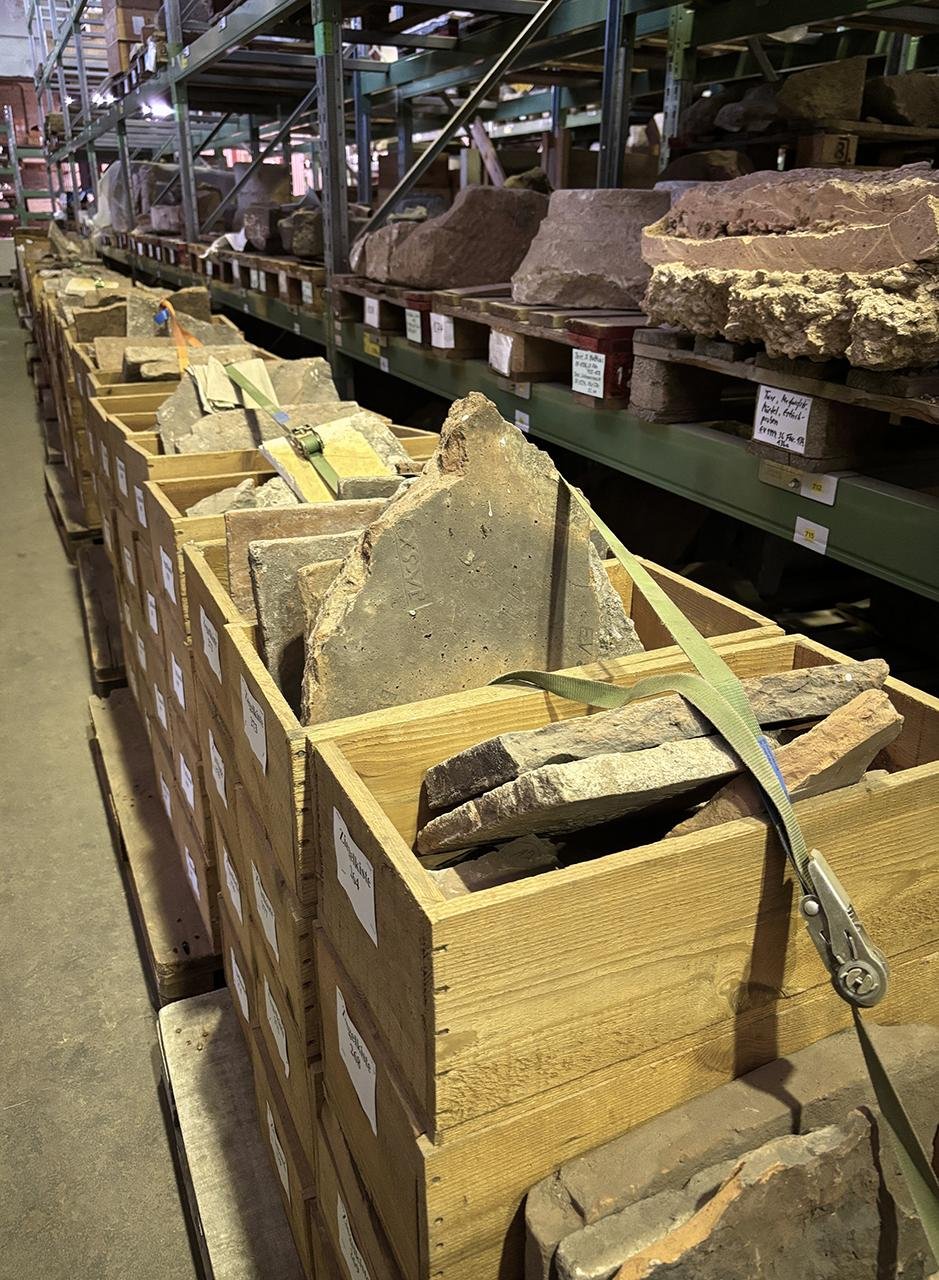 Boxes with stamped bricks from Trier in the depot of the Rhineland State Museum. Credit: Thomas Schmidts, LEIZA
Boxes with stamped bricks from Trier in the depot of the Rhineland State Museum. Credit: Thomas Schmidts, LEIZA
For the first time, archaeometric analyses will be conducted on the bricks, targeting the chemical composition of the clay. The findings will determine the sources of raw materials and perhaps confirm the locations of specific production workshops. Having these details could form a more comprehensive picture of Trier’s development as a Roman metropolis and the logistical systems that supported it.
Dr. Marcus Reuter, Director of the Rheinisches Landesmuseum Trier, and Prof. Dr. Markus Scholz from the Insтιтute of Archaeological Sciences at Goethe University are co-applicants for the project. The research also falls under the auspices of the “FoRuM” initiative—Forschungsschwerpunkt Römische Archäologie und Maritime Antike—a strategic alliance between LEIZA, the University of Trier, and GDKE to foster archaeological research in Rhineland-Palatinate.
Prof. Dr. Alexandra W. Busch, General Director of LEIZA, said, “A broad methodological spectrum is not just typical of LEIZA,” she said, “it is also increasingly important to gaining groundbreaking new insights.”
More information: LEIZA / DFG project site





