Archaeologists have unearthed a Second Intermediate Period royal tomb (c. 1640–1540 BCE) in the Mount Anubis necropolis of Abydos in Egypt. The discovery, by an Egyptian-American team directed by Professor Josef Wegner of the University of Pennsylvania, is an advancement in studies on the so-called Abydos Dynasty. However, though the design and inscriptions of the tomb indicate that it must have belonged to a king from this period, the king’s name is unknown because of damage inflicted by ancient robbers.
 The 3,600-year-old tomb of the unknown Egyptian king. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
The 3,600-year-old tomb of the unknown Egyptian king. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
The tomb, buried about 23 feet (7 meters) beneath the earth, is a limestone burial chamber with mudbrick vault linings. The structure originally stood about 16 feet (5 meters) high and is larger than other tombs from this period. The entrance inscriptions depict the goddesses Isis and Nephthys, who were normally ᴀssociated with funerary rites, but the hieroglyphic inscriptions that originally bore the king’s name have been damaged, and identification is difficult.
One of the less documented periods of Egyptian history is the Abydos Dynasty, the ruling power of Upper Egypt when the Hyksos controlled the north. The style and location of the tomb resemble that of King Senebkay’s, whose tomb was discovered in Abydos in 2014. Mohamed Abdel Badie, head of the Egyptian Antiquities Sector at the Supreme Council of Antiquities, thinks that the newly discovered tomb might have belonged to one of Senebkay’s predecessors. The candidates are kings Senaiib and Paentjeni, who are known to have erected monuments in Abydos.
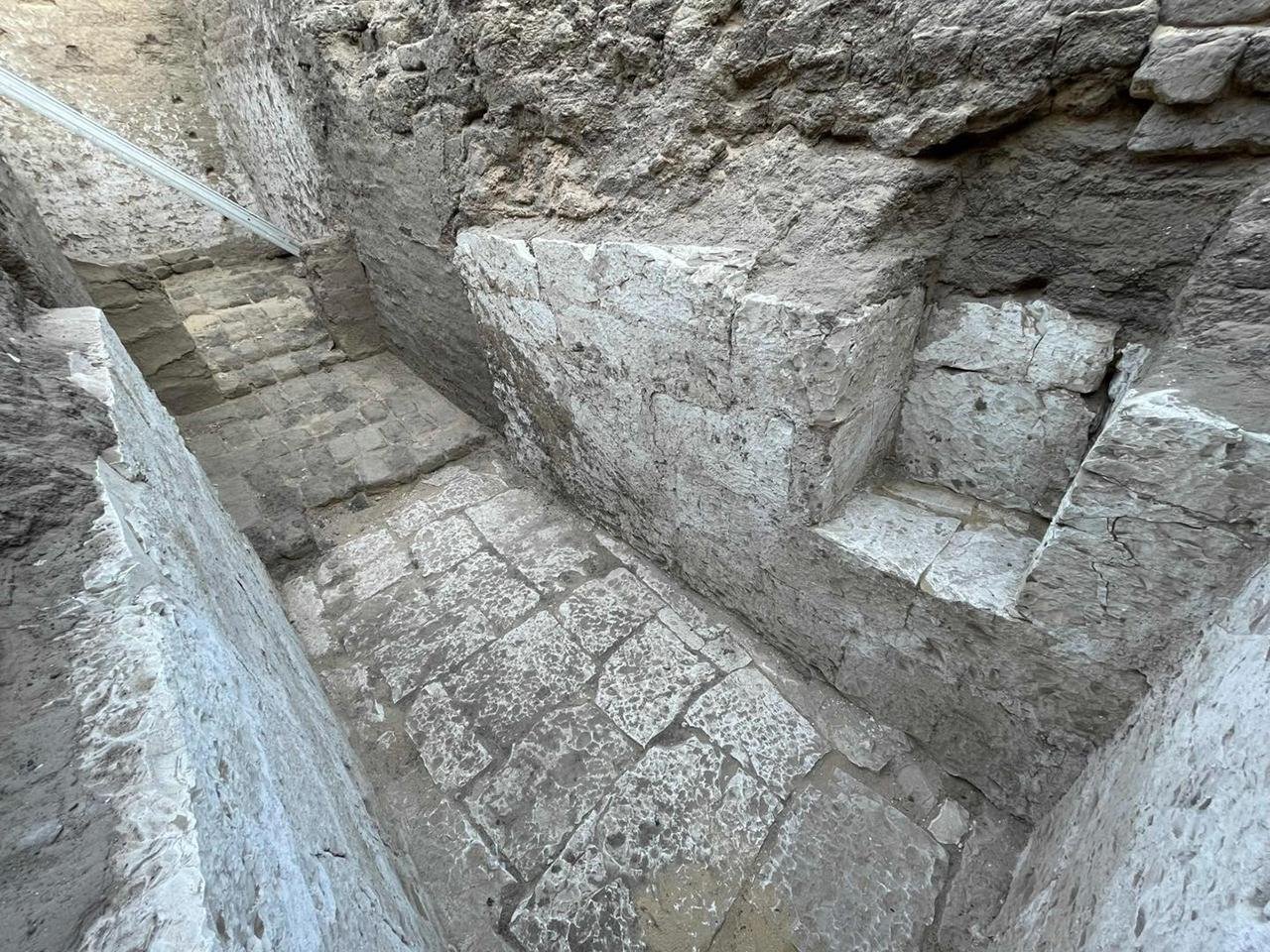 The tomb is a limestone burial chamber with mudbrick vault linings. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
The tomb is a limestone burial chamber with mudbrick vault linings. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Unfortunately, the tomb was heavily looted during ancient times. Robbers took away all the treasures, including the mummy and sarcophagus of the king, leaving little for archaeologists to discover about his idenтιтy. The recess where canopic jars were meant to be placed was also empty. Tomb looting in the region has been documented as far back as the Roman period, when people invaded burial sites to extract valuable limestone, granite, and quartzite.
 Ostraca with Demotic script inscriptions. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Ostraca with Demotic script inscriptions. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Besides the royal tomb, another significant discovery was made in Banawit village, north of Abydos. Egyptians from the Supreme Council of Antiquities unearthed a workshop for Roman-era pottery and glᴀss, which shed light on Egypt’s industrial history during the Roman period (30 BCE–642 CE). The workshop contained a number of kilns and storage areas, and 32 ostraca—fragments of pottery inscribed with Greek and Demotic texts that documented commercial transactions and tax payments.
It was likely one of the biggest production centers that provided glᴀss and pottery for the Ninth District, said Mohamed Ismail Khaled, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities. The site appears to have been reused in the 14th century CE as a burial ground with graves. Among the burials were mudbrick tombs containing mummies and skeletons, including the remains of a child wearing a fabric cap and the skull of a woman who was approximately 30 years old. The presence of wheat roots, palm seeds, and barley indicates connections between agricultural practices and burial traditions in the Sohag region.
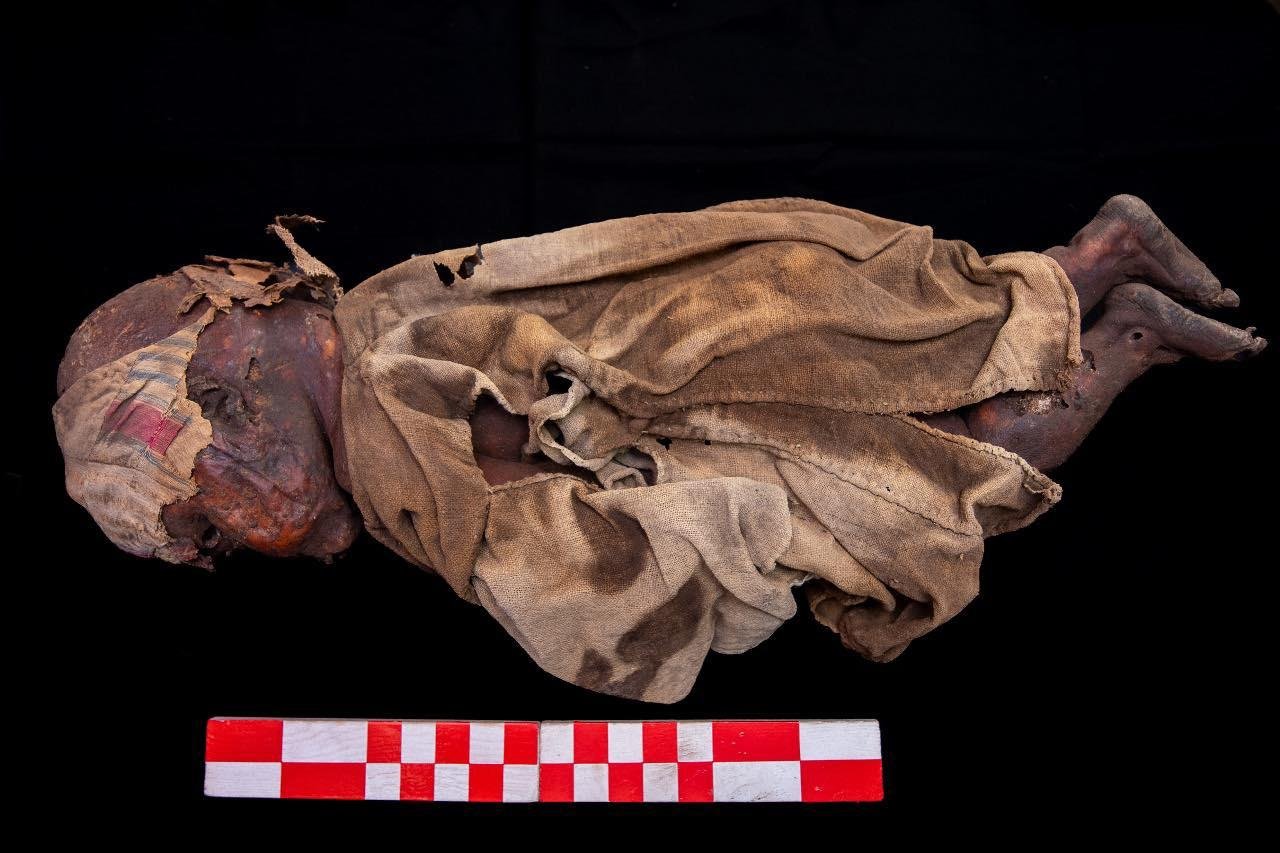 Among the burials were mudbrick tombs containing mummies and skeletons, including the remains of a child wearing a fabric cap. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Among the burials were mudbrick tombs containing mummies and skeletons, including the remains of a child wearing a fabric cap. Credit: Courtesy of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
The new find substantiates the idea that there are still many untold tales of ancient Egypt’s fragmented past. Even in the absence of a mummy, the architectural patterns and inscriptions in the newly found tomb are valuable for indicating the evolution of royal burials in Abydos.
The team plans to excavate deeper in hopes of unearthing additional tombs—perhaps even one that remains intact.
More information: Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities





