
Ramses II
Ramses II, known as ‘the Great,’ was born about 1303 BC and died in the year 1213 BC, son of Seti I and Queen Tuya, the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. He is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the Egyptian Empire. He ruled Egypt from 1279 BC to 1213 BC. He took the throne in his early twenties, around 1279 BC, and ruled for 66 years until his death. He was the third ruler of the 19th Dynasty, and had the second longest reign of the ancient Egyptian pharaohs. He focused on building up Egypt with temples,and public buildings, including his own memorial temple called Ramessuem. He helped to improve Egypt’s wealth from collecting supplies from other empires during his reign.
Mummification
The brain was removed using a long hook that was inserted through his nasal cavity. After the brain was completely removed, they filled his nasal cavity with peppercorns, seeds, and small animal bones to retain the unique structure of Ramses II’s nose (2011).

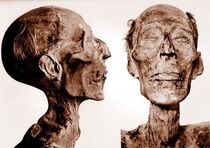
Mummy of Ramesses II
The embalmers then individually wrapped his toes, fingers, arms and legs which shows fine attention to detail and precision. Once every part of his body was wrapped, they placed the Book of the ᴅᴇᴀᴅ between his hands (Fitzgerald, 2009).
Finally, the body was draped in a white cloth and the embalmers carefully painted an image of Osiris (the Egyptian God of the underworld) on the outside of the wrappings as a finishing touch (Fitzgerald, 2009).
Ramesses II was originally buried in the tomb KV7 in the Valley of the Kings, Egypt but, because of looting, priests later transferred the body to a holding area, re-wrapped it, and placed it inside the tomb of queen Inhapy. Seventy-two hours later it was again moved, to the tomb of the high priest Pinudjem II. All of this is recorded in hieroglyphics on the linen covering the body. Today his mummy is in Cairo’s Egyptian Museum.


