A discovery made by scientists at the Olomouc Archaeological Center has provided the first physical evidence of a long-suspected military practice from the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
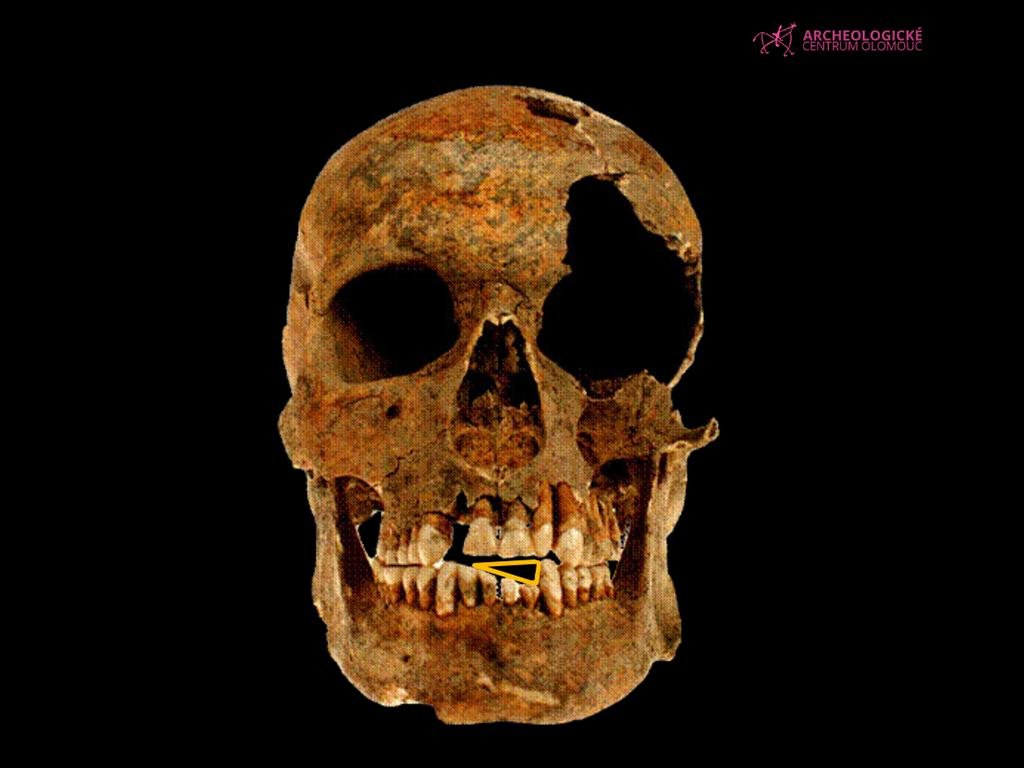 PH๏τograph of a damaged denтιтion of a soldier from the 19th century. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
PH๏τograph of a damaged denтιтion of a soldier from the 19th century. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
Analysis of the skeleton of a soldier found in the town of Majetín, in the Olomouc region, indicates that he habitually opened gunpowder cartridges with his teeth, leaving permanent damage to his incisors. Chemical testing further corroborated remnants of gunpowder in his dental tartar, providing an unusual insight into the daily life and physical stresses experienced by soldiers at the time.
The remains were first excavated in 2012, though it took nearly a decade of research to uncover the full extent of the find. Anthropologist Lukáš Šín, who led the study, stated that the skeleton belonged to a man aged between 30 and 50 years and who stood about 174 cm tall. His lower three incisors, however, showed definite signs of repeated mechanical stress that experts believe stemmed from the use of his teeth to tear open powder cartridges. “The soldier’s teeth were weakened through repeated activity, and this stress could have resulted in the crowns of the teeth breaking,” said Šín.
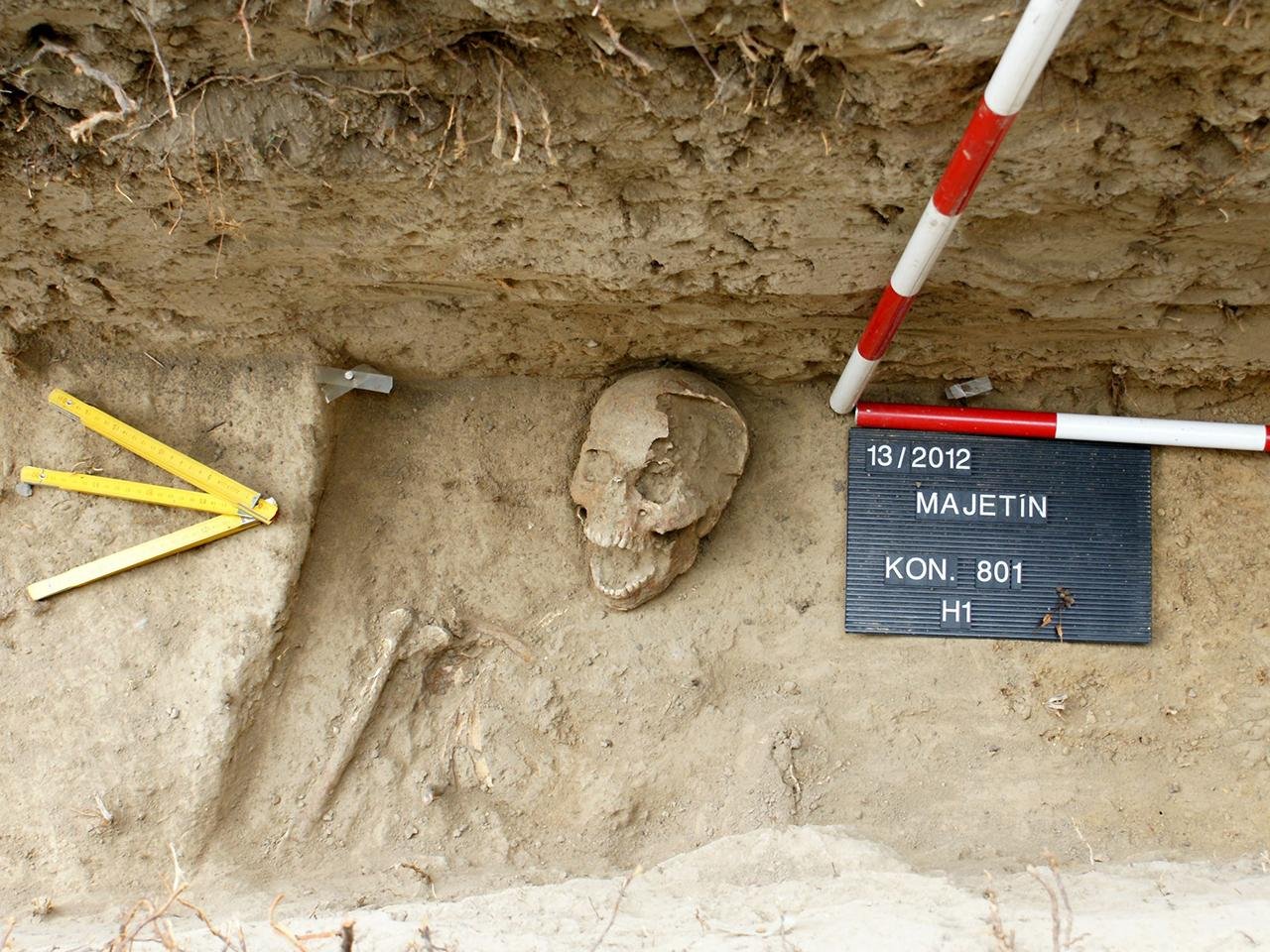 PH๏τograph of the Soldier Found in Majetín. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
PH๏τograph of the Soldier Found in Majetín. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
Historical records indicate that soldiers of this era loaded their firearms by biting into paper cartridges containing gunpowder and bullets, separating the powder before pouring it into the muzzle of their weapons. The practice has been documented in military manuals, although direct physical evidence had always been lacking—until now. The find in Majetín thus represents the first documented case where the recovery of skeletal remains confirms this method.
 An illustration of bullets. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
An illustration of bullets. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
Further evidence supporting this hypothesis emerged in 2017, when Dr. Dana Fialová from Masaryk University performed a chemical analysis of the dental tartar of the remains using X-ray spectroscopy. Her team detected significant concentrations of sulfur, which is an important component of gunpowder. “The sulfur from the gunpowder not only contaminated the dental cavity and the tartar, but also contributed to exposing the tooth bed and causing gingivitis,” Šín explained. This confirms that the soldier frequently handled gunpowder in his mouth, reinforcing the theory that he was involved in loading firearms using his teeth.
The skeleton also bore signs of a tough military life. The wear on the lumbar vertebrae suggests the long and strenuous marches endured by infantrymen of this period.
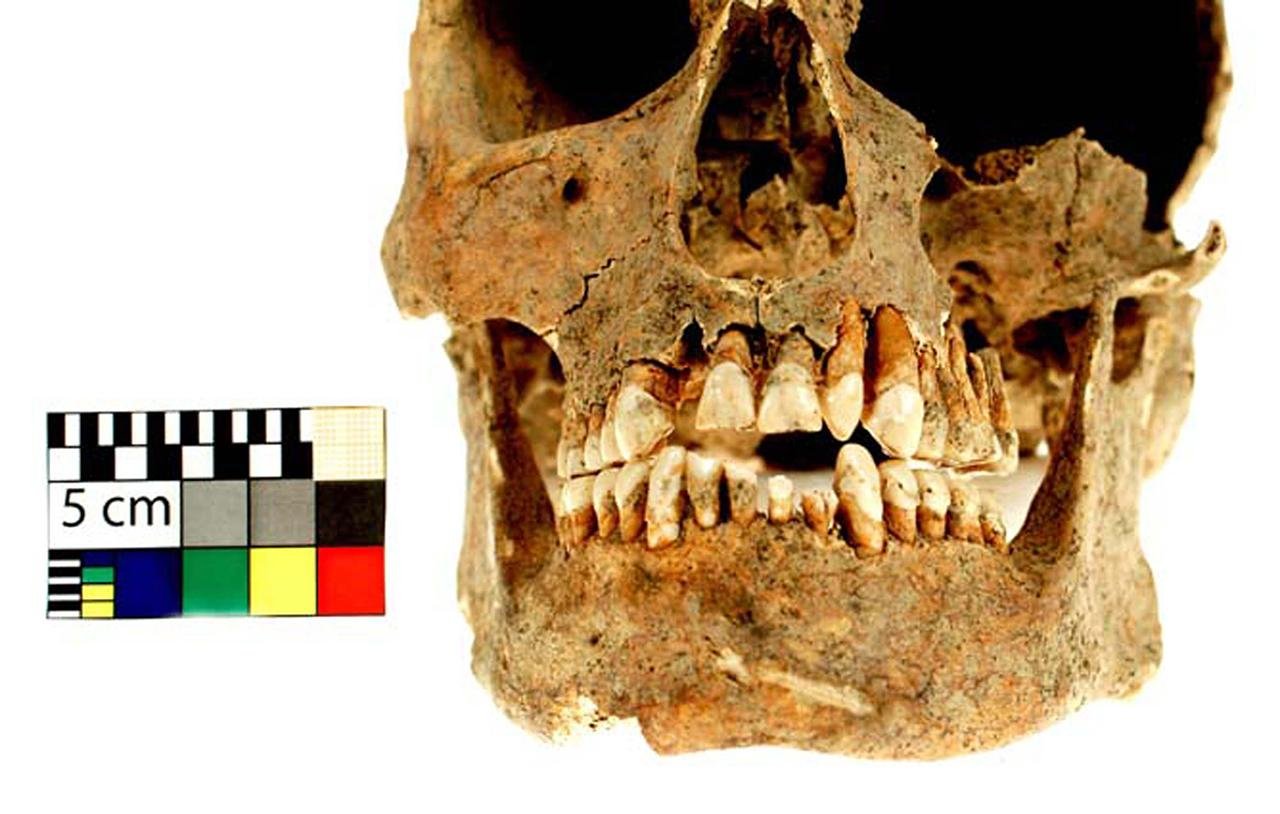 The Majetín soldier is the first globally recognized case of this phenomenon. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
The Majetín soldier is the first globally recognized case of this phenomenon. Credit: Archaeological Center Olomouc
Experts date the soldier to between the 18th and 19th centuries, coinciding with the period when front-loading firearms were used in military conflicts. Curiously enough, in June 2012, similar dental damage was observed by Belgian archaeologist Dominique Bosquet and her team on the battlefield of Waterloo. Yet their research has yet to be published, making the Majetín soldier the first case of its kind in the world to have been identified.
The skeletal remains are now preserved in the archives of the Olomouc Archaeological Center, and the results of this long-term study have been published in scientific journals.
More information: Archaeological Center Olomouc





