Researchers studying the teeth of an old woman who lived 2,000 years ago have charted her diet from infancy until shortly before her death.
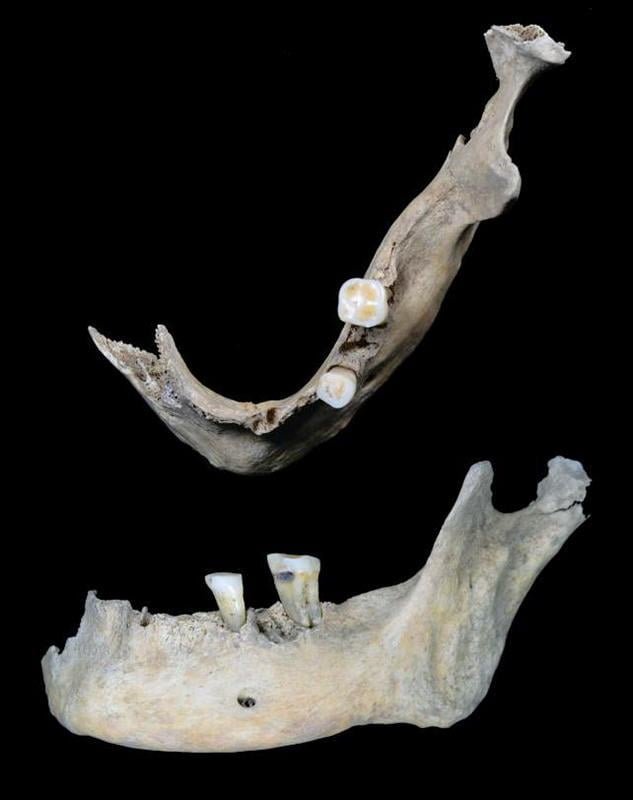 The teeth of the ‘Elder’. Credit: UHI Archaeology Insтιтute
The teeth of the ‘Elder’. Credit: UHI Archaeology Insтιтute
According to experts at the University of the Highlands and Islands, the woman’s unusually seafood-rich diet “flies in the face” of what we know about Iron Age Britain, because there is very little evidence of fish being ingested at that time (UHI).
It has been suggested that there may have been societal restrictions or taboos around the consumption of fish and seafood at the time, which is why the woman, called “The Elder” due to her age—estimated at around 50 or older—is considered a unique case.
The research, conducted at the British Geological Survey’s isotope facility by scientists from the University of York, has provided more insight into the lifestyle of Iron Age people, revealing evidence of a diet that included fish.
To gather the data, experts analyzed a tooth from the woman’s jawbone, using techniques that provided insight into her diet at ages three, seven, nine, eleven, thirteen, and fifteen – concluding that she had been eating seafood all her life, most likely out of necessity.
The bones were discovered in 2016 during excavations at The Cairns in South Ronaldsay, Orkney.
The woman’s lower jaw was placed in a whalebone vessel, along with three new-born lambs, at the Iron Age settlement of Cairns, South Ronaldsay, Orkney.
The study revealed that fish was consumed routinely throughout her life, implying that Iron Age people on Orkney did make use of the surrounding seas.
Researchers say the findings suggest that “The Elder” may have played a special role in society, or fish suppers were more popular in Iron Age Scotland than the rest of Britain
“It’s wonderful to be able to peer into the early, formative years of this older women’s life and actually establish something of her biographical details.” site Director of The Cairns excavations, Martin Carruthers, a Lecturer in Archaeology at the Archaeology Insтιтute at Orkney College, University of the Highlands and Islands.
“Now we can see that the marine foodstuffs that she ate were after all a normal part of Iron Age life, at least for her, and this allows us to move on with further investigation into the diets of Iron Age society.”





