A child in Peru was sacrificed thousands of years ago as part of an ancient ritual, with the head chopped at the neck and made into a kind of trophy. A recent analysis of a single hair taken from the mummy’s skull reveals that the child consumed a psychoactive cactus before execution.
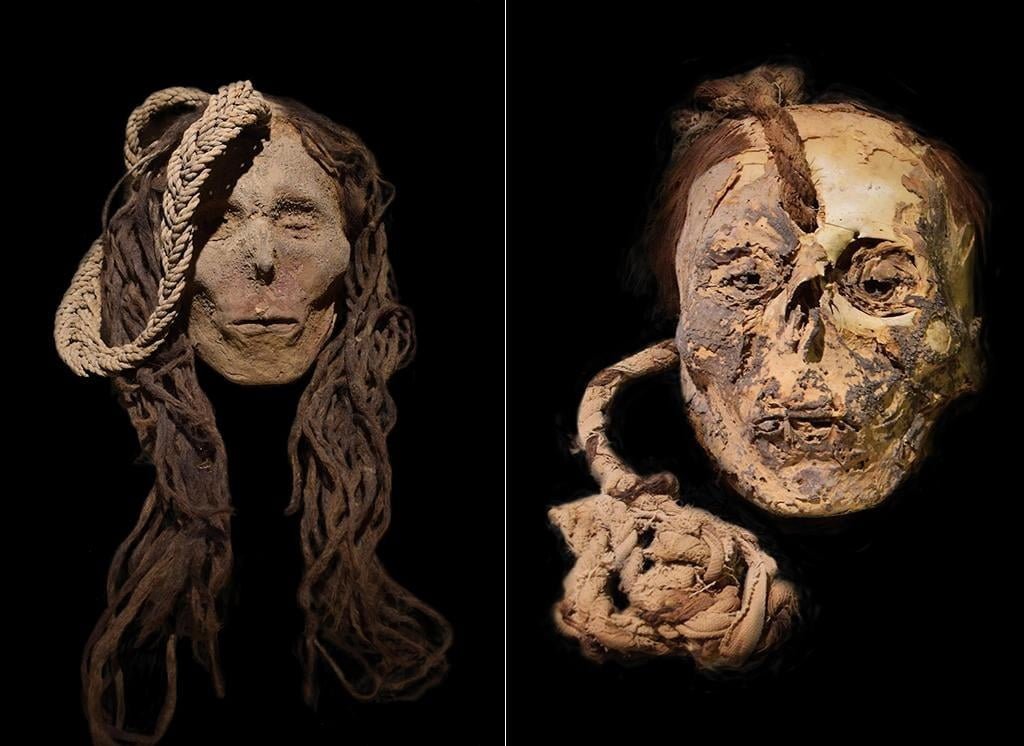 Two of the trophy heads, one of a woman and one of a child. Credit: D. Socha / Journal of Archaeological Science, CC BY-NC-ND
Two of the trophy heads, one of a woman and one of a child. Credit: D. Socha / Journal of Archaeological Science, CC BY-NC-ND
The child’s preserved head was one of 22 human remains -found in the Yauca Valley, Cahuachi, and Estaqueria in Peru- ᴀssociated with the ancient Nazca society examined in a new study; All of these people lived during the pre-Hispanic period (3500 BCE to 476 CE).
The child tested positive for a high amount of “mescaline,” a hallucinogen caused by excessive San Pedro Cactus use.
The same study discovered ayahuasca use among other mummified individuals from the Early Nazca Period (100 BCE to 450 CE), providing the first archaeological evidence for the consumption of these two psychedelic plants.
 Credit: D. Socha / Journal of Archaeological Science, CC BY-NC-ND
Credit: D. Socha / Journal of Archaeological Science, CC BY-NC-ND
“The trophy head is the first case of the consumption of San Pedro by an individual living on the southern Peruvian coast,” study lead author Dagmara Socha, a doctoral candidate in the Center for Andean Studies at the University of Warsaw in Poland, told Live Science.
“It’s also the first evidence that some of the victims who were made into trophy heads were given stimulants before they died.”
“The results of the study support the idea that some of the trophy heads dated to the Early Nazca Period could have been obtained from ritually sacrificed victims, rather than during warfare,” the study reads.
The study also examined the hair of two male trophy skulls, none containing any drug compounds. They believe this could be due to “different social origins of the victims” or other simple factors such as hair structure or preservation.
The finding has been published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
More information: Dagmara M. Socha, Marzena Sykutera, Giuseppe Orefici. (2022). Use of psychoactive and stimulant plants on the south coast of Peru from the Early Intermediate to Late Intermediate Period, Journal of Archaeological Science, 148, 105688,





