Researchers have discovered the complete skeletal remains of a spider monkey ritually sacrificed 1,700 years ago, providing new evidence about the social-political ties between two ancient powerhouses: Teotihuacán and Maya Indigenous rulers.
 1,700 year-old skeletal remains of a female spider monkey found in Teotihuacán, Mexico. Credit: Nawa Sugiyama, UC Riverside
1,700 year-old skeletal remains of a female spider monkey found in Teotihuacán, Mexico. Credit: Nawa Sugiyama, UC Riverside
According to a new study published Monday in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the monkey was a gift from the Maya to Teotihuacán during a period of peace and diplomacy before the two groups clashed.
Spider monkeys aren’t indigenous to Teotihuacan. The female monkey, who was no more than five to eight years old when she died, was born in an unknown lowland region outside Teotihuacan and had spent at least two years in captivity in the arid highlands.
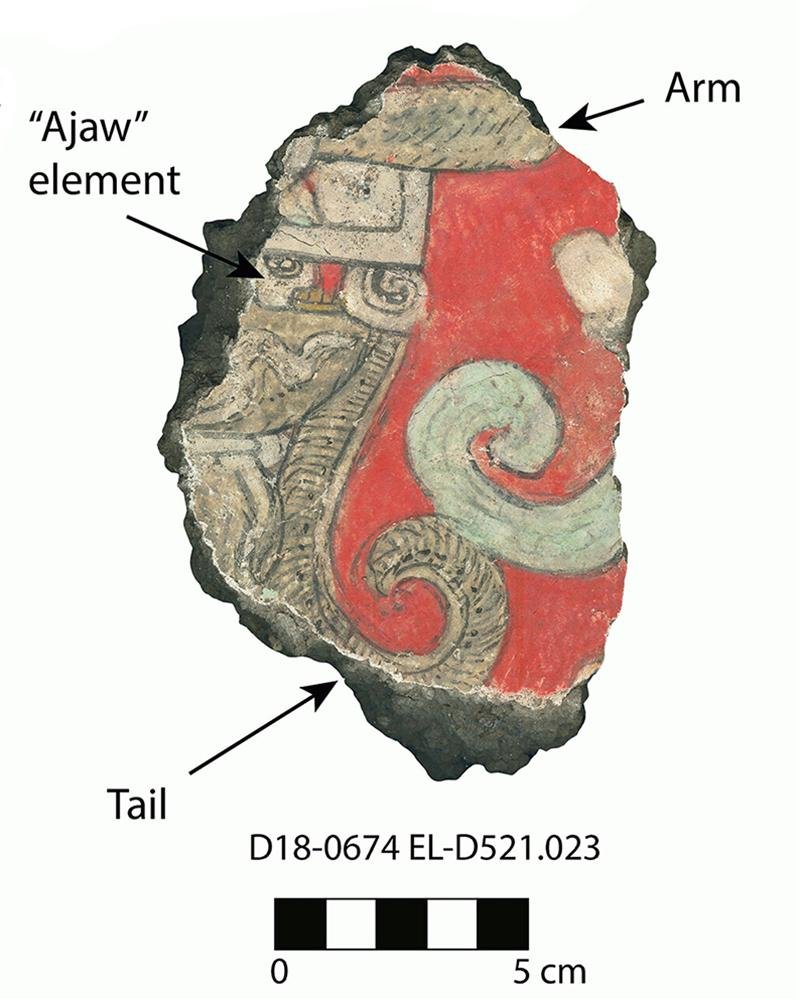 Scan of mural fragment of a spider monkey. Credit: Project Plaza of the Columns Complex / PNAS
Scan of mural fragment of a spider monkey. Credit: Project Plaza of the Columns Complex / PNAS
The discovery was made by Nawa Sugiyama, an anthropological archaeologist from UC Riverside, and a team of archaeologists and anthropologists who since 2015 have been excavating at Plaza of Columns Complex, in Teotihuacán, Mexico.
Other animal remains, as well as thousands of Maya-style mural fragments and over 14,000 ceramic sherds from a grand feast, were also uncovered. These pieces date back over 1,700 years.
Researchers used a multimethod archaeometric approach to detail the life of this female spider monkey.
Its skeleton remains were discovered with a golden eagle and many rattlesnakes, surrounded by unique artifacts like beautiful greenstone figurines made of jade from Guatemala’s Motagua Valley, shell/snail items, and lavish obsidian goods like blades and projectile points.
Evidence of animal sacrifices, including of predators like jaguars, has previously been discovered in the city. However, “up to that point, we did not have any instances of sacrificed primates in Teotihuacan,” says Nawa Sugiyama.
“This little story of one single spider monkey really brought out a lot of information about all sorts of inter-regional ties,” she says to National Geographic’s Kristin Romey.
According to the researchers, this is consistent with the evidence of the live sacrifice of symbolically potent animals participating in state rites observed in Moon and Sun Pyramid dedicatory caches.
“This helps us understand principles of diplomacy, to understand how urbanism developed … and how it failed. Teotihuacán was a successful system for over 500 years, and understanding past resilience, its strengths, and weaknesses are relevant in today’s society. There are many similarities then and now. Lessons can be seen and modeled from past societies; they provide us with cues as we go forward.” Sugiyama says to Sandra Baltazar Martinez (UC Riverside).
More information: Sugiyama, N, Sugiyama, S, et al. (2022). Earliest evidence of primate captivity and translocation supports gift diplomacy between Teotihuacan and the Maya. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 119 (47) e2212431119. Doi: 10.1073/pnas.2212431119





