Analysis of over 1,200 vessels from hunter-gatherer sites revealed that pottery-making processes spread vast distances in a short period of time due to the transfer of social traditions.
 Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain
Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain
The team, which included researchers from the University of York and the British Museum, examined the remains of 1,226 pottery vessels from 156 hunter-gatherer sites in nine Northern and Eastern European countries. They combined radiocarbon dating with information on the production and decorating of ceramic vessels, as well as analyses of food remains found inside the pots.
Their findings, published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour, show that pottery-making moved rapidly westwards from around 5,900 BCE and took only 300-400 years to advance over 3,000 km, or 250 km in a single generation.
Professor Oliver Craig of the Department of Archaeology at the University of York stated, “Our analysis of the ways pots were designed and decorated as well as new radiocarbon dates suggests that knowledge of pottery spread through a process of cultural transmission.
“By this we mean that the activity spread by the exchange of ideas between groups of hunter-gatherers living nearby, rather than through migration of people or an expanding population as we see for other key changes in human history such as the introduction of agriculture.”
“That methods of pottery-making spread so far and so fast through the pᴀssing on of ideas is quite surprising. Specific knowledge may have been shared through marriages or at centers of aggregation, specific points in the landscape where groups of hunter-gatherers came together perhaps at certain times of the year.”
The team demonstrated that the pottery was used for cooking by analyzing traces of organic materials left in the pots, implying that pottery-making ideas may have spread through shared culinary traditions.
Carl Heron, from the British Museum, said, “We found evidence that the vessels were used for cooking a wide range of animals, fish and plants, and this variety suggests that the drivers for making the pottery were not in response to a particular need, such as detoxifying plants or processing fish, as has previously been suggested.
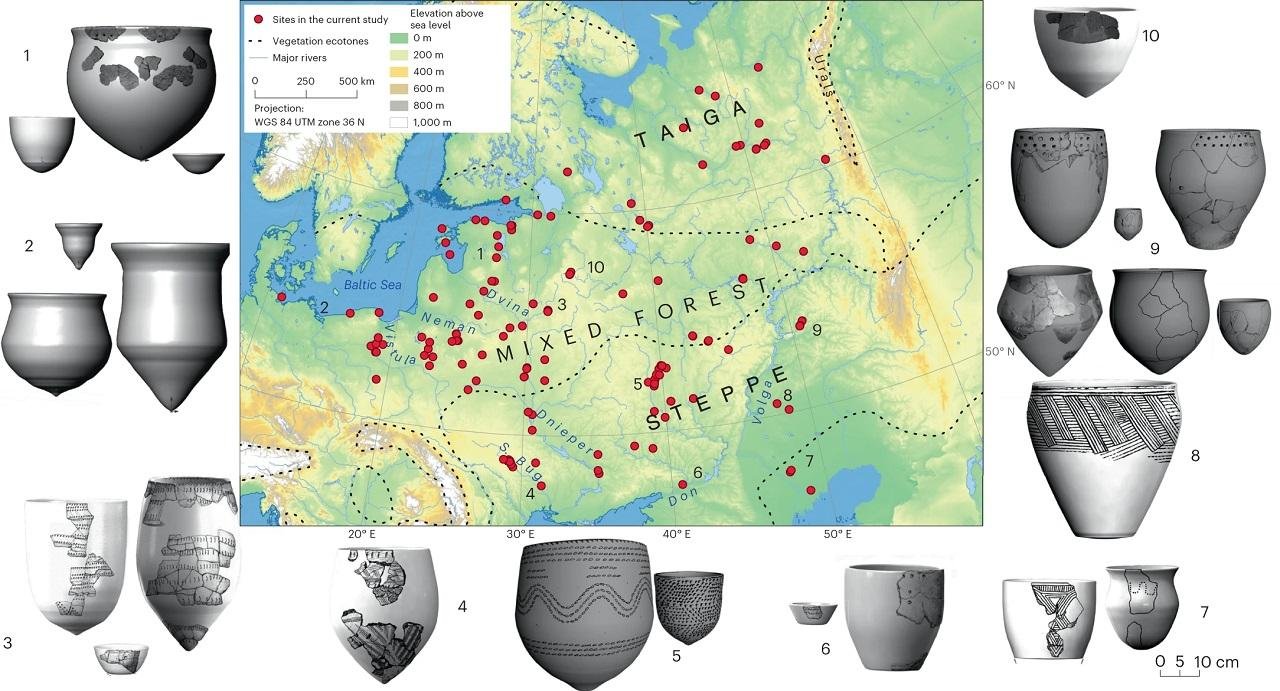 Study area, site locations and examples of reconstructed forms for the pottery styles included in this study. Credit: Rowan McLaughlin/Nature Human Behaviour
Study area, site locations and examples of reconstructed forms for the pottery styles included in this study. Credit: Rowan McLaughlin/Nature Human Behaviour
“We also found patterns suggesting that pottery use was transmitted along with knowledge of their manufacture and decoration. These can be seen as culinary traditions that were rapidly transmitted with the artifacts themselves.”
The world’s earliest pottery containers come from East Asia and spread rapidly eastward through Siberia before being adopted by hunter-gatherer societies across Northern Europe long before farming. —University of York
More information: Rowan McLaughlin, (2022). The transmission of pottery technology among prehistoric European hunter-gatherers, Nature Human Behaviour. DOI: 10.1038/s41562-022-01491-8.





