Archaeologists have uncovered groundbreaking evidence of the earliest use of bows and arrows in Europe during excavations in a southern France cave. The researchers replicated spears that were made 54,000 years ago. Credit: Ludovic Slimak
The researchers replicated spears that were made 54,000 years ago. Credit: Ludovic Slimak
The discovery, which dates back approximately 54,000 years, reveals that Homo sapiens in the Rhône Valley may have used archery to hunt large animals such as bison, horses, and deer, challenging previous ᴀssumptions about prehistoric hunting techniques.
At the site, researchers unearthed over 300 small stone points, closely resembling arrowheads and crafted in the Neronian style. These findings suggest that the cave’s inhabitants, the region’s earliest Homo sapiens, shared the landscape with Neanderthals.
The arrowheads range in size from 10 to 60 millimeters, and around 200 show signs of impact and damage consistent with being propelled through the air, possibly through thrusting, throwing, or mechanical propulsion. To better understand how these points were used, archaeologist Laure Metz of Aix-Marseille Université and her team conducted experiments with replica weapons.
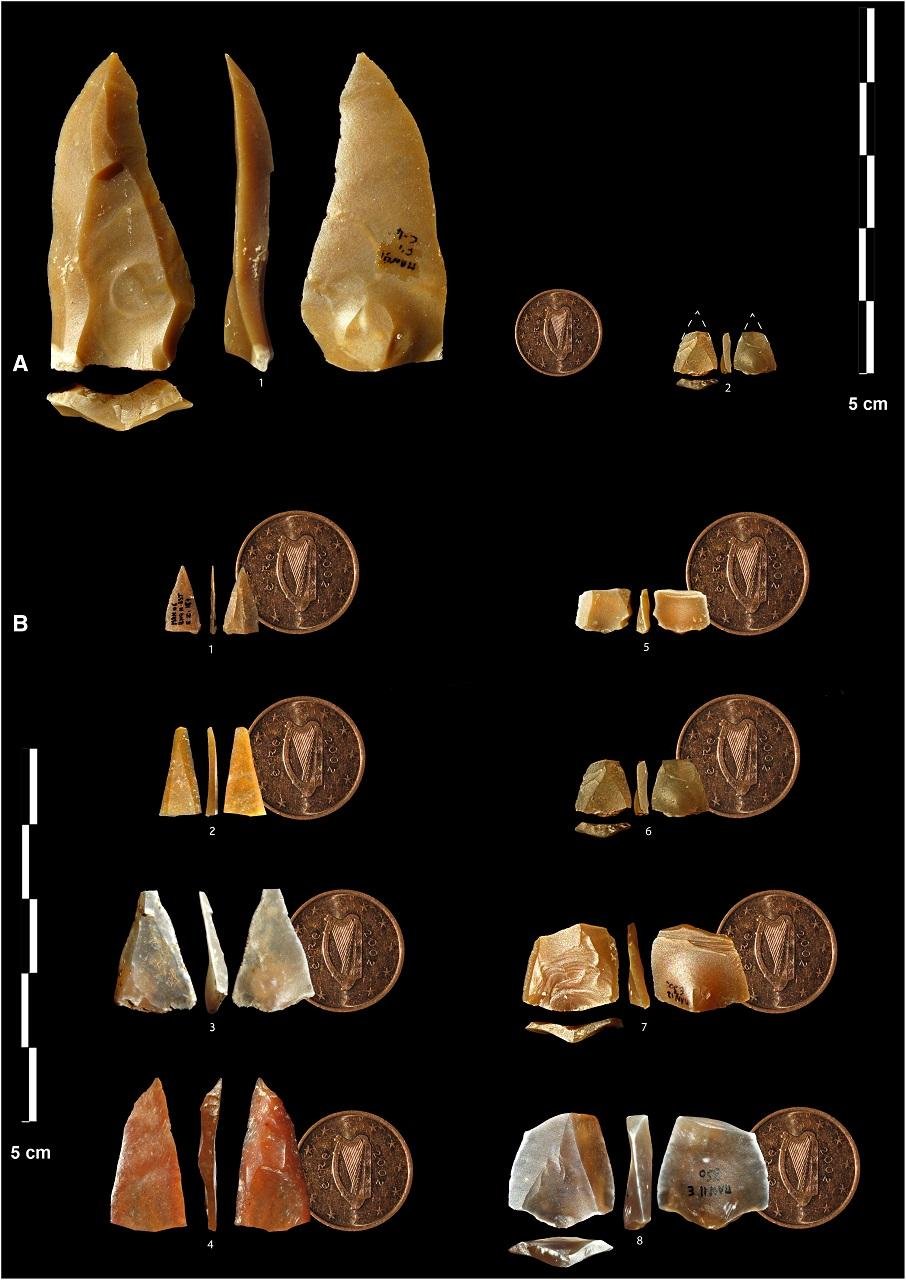 Mandrin E. Lithic points. Credit: Laure Metz et al. Science Advances (2023)
Mandrin E. Lithic points. Credit: Laure Metz et al. Science Advances (2023)
The findings propose that the bow and arrow could have provided a significant advantage to early Homo sapiens, particularly in their compeтιтion with Neanderthals, who disappeared around 40,000 years ago. While some of the larger points may have been suitable for spears or darts, the researchers believe only the bow and arrow could generate enough force to effectively use the smallest points for hunting.
Despite their small size, the researchers argue that these arrowheads were likely employed to hunt large prey, including bison, horses, and deer—animals whose remains were found in the cave. However, the possibility that these tiny points were used as weapons against other humans is also considered.
Marlize Lombard from the University of Johannesburg, who was not involved in the study, agrees with the interpretation that the Mandrin arrowheads were designed specifically for use in arrows.
This discovery pushes back the timeline of bow-and-arrow use in Europe, challenging the previously known earliest evidence from around 12,000 years ago, when wooden bows and arrow shafts were preserved in Northern Europe’s peat bogs.
The research behind this significant find was published in Science Advances.
More information: Laure Metz,Jason E. Lewis, Ludovic Slimak. (2023). Bow-and-arrow, technology of the first modern humans in Europe 54,000 years ago at Mandrin, France, Science Advances, 9, 8, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add4675





