A recent excavation in ancient Megiddo, Israel, revealed the earliest example of cranial surgery in the Ancient Near East, and potentially one of the world’s oldest examples of leprosy.
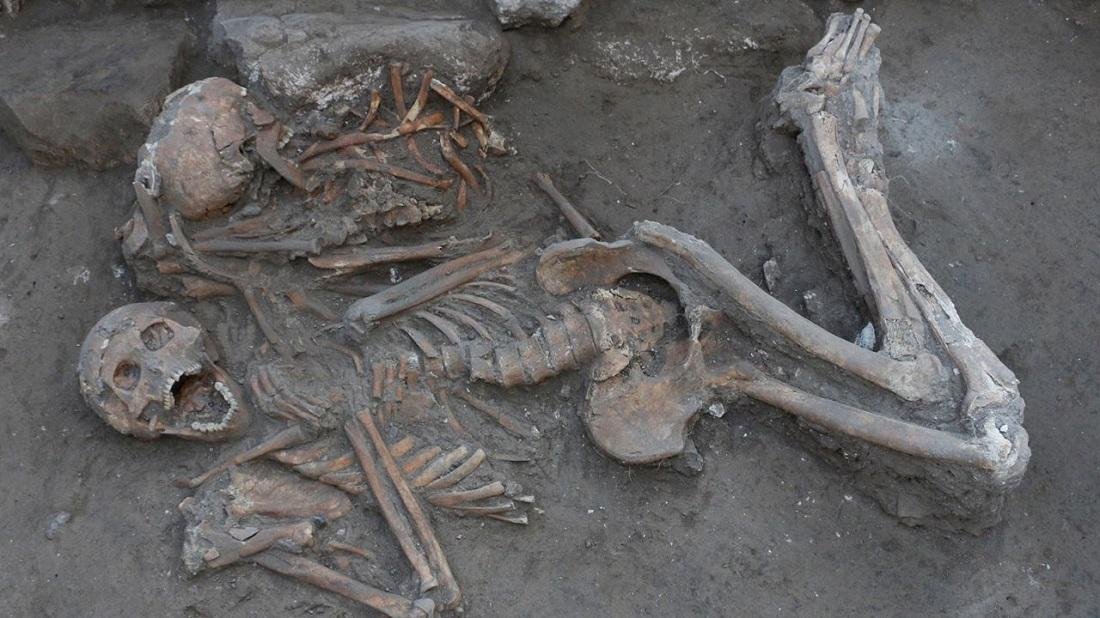 The remains of two elite brothers were found in the ancient city of Tel Megiddo, Israel. Credit: Megiddo Expedition
The remains of two elite brothers were found in the ancient city of Tel Megiddo, Israel. Credit: Megiddo Expedition
For thousands of years, people have practiced cranial trephination, a medical treatment that involves cutting a hole in the skull. Scientists discovered evidence that ancient civilizations from South America to Africa and beyond performed the surgery.
The recent discovery in Israel has revealed new evidence that one type of trephination dates back to at least the late Bronze Age. The remains of the brothers who lived between 1550 BCE and 1450 BCE, were found during an excavation of a tomb in the ancient city of Tel Megiddo.
Megiddo is an ancient city in northern Israel near Kibbutz Megiddo. It was an important Canaanite city-state during the Bronze Age, inhabited by a Semitic-speaking civilization with population centers in the region of the Southern Levant in the Ancient Near East.
 Credit: Kalisher et al., PLoS One, 2023
Credit: Kalisher et al., PLoS One, 2023
Rachel Kalisher, a Ph.D. candidate at Brown University‘s Joukowsky Insтιтute for Archaeology and the Ancient World, led an analysis of the unearthed remains of two upper-class brothers who lived in Megiddo around the 15th century BCE.
She found that not long before one of the brothers died, he had had angular notched trephination, a type of cranial surgery. The surgery involves cutting the scalp, cutting four intersecting lines in the skull with a sharp beveled edge, and making a square-shaped hole with leverage.
The discovery is the first example of trephination found in the ancient Near East.
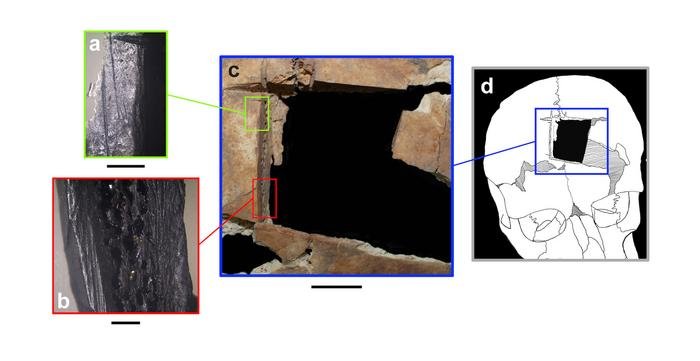 a-b: Magnified edges of the trephination, each with a 2 mm scale bar. c: All four edges of the trephination, scale bar is 1 cm. d: Reconstructed location of trephination on head. Credit: Kalisher et al., PLoS One, 2023
a-b: Magnified edges of the trephination, each with a 2 mm scale bar. c: All four edges of the trephination, scale bar is 1 cm. d: Reconstructed location of trephination on head. Credit: Kalisher et al., PLoS One, 2023
“We have evidence that trephination has been this universal, widespread type of surgery for thousands of years,” said Kalisher. “But in the Near East, we don’t see it so often. My hope is that adding more examples to the scholarly record will deepen our field’s understanding of medical care and cultural dynamics in ancient cities in this area.”
According to Kalisher, the two brothers whose bones she analyzed lived in a domestic area directly adjacent to Megiddo’s late Bronze Age palace, implying that they were elite members of society and possibly even royals themselves.
“In our study, we consider if the excised bone pieces were reinserted into the head because the pracтιтioner thought it would facilitate healing,” Kalisher explained. “But, I also come back to the medicinal/magical dicH๏τomy we impose on the past. It is possible that the excised bones also held some other, non-medical purpose, leading to its inclusion with the individual. It is simply unknowable to us. So for now, this mystery remains unsolved.”
More information: Kalisher R, Cradic MS, Adams MJ, Martin MAS, Finkelstein I. (2023). Cranial trephination and infectious disease in the Eastern Mediterranean: The evidence from two elite brothers from Late Bronze Megiddo, Israel. PLOS ONE 18(2): e0281020.





