A team of researchers used geographical data systems with bio-geographical data inputs to find routes that Neanderthals would have likely taken.
 Credit: Yuliya S., Wikimedia Commons
Credit: Yuliya S., Wikimedia Commons
They looked for areas that experienced the most negligible climatic fluctuations and were most likely to provide stable environments for plants and animals.
The team suggested potential research locations in lesser-studied parts of Iran and Central Asia, where the modeling shows the ideal Paleolithic habitats.
Researchers focused on the Southern Caspian Sea corridor because it stood out as being more humid and mild compared to nearby areas, making it an ideal route for expansion and settlement. The weather conditions would likely help plants grow and give resources for wandering groups.
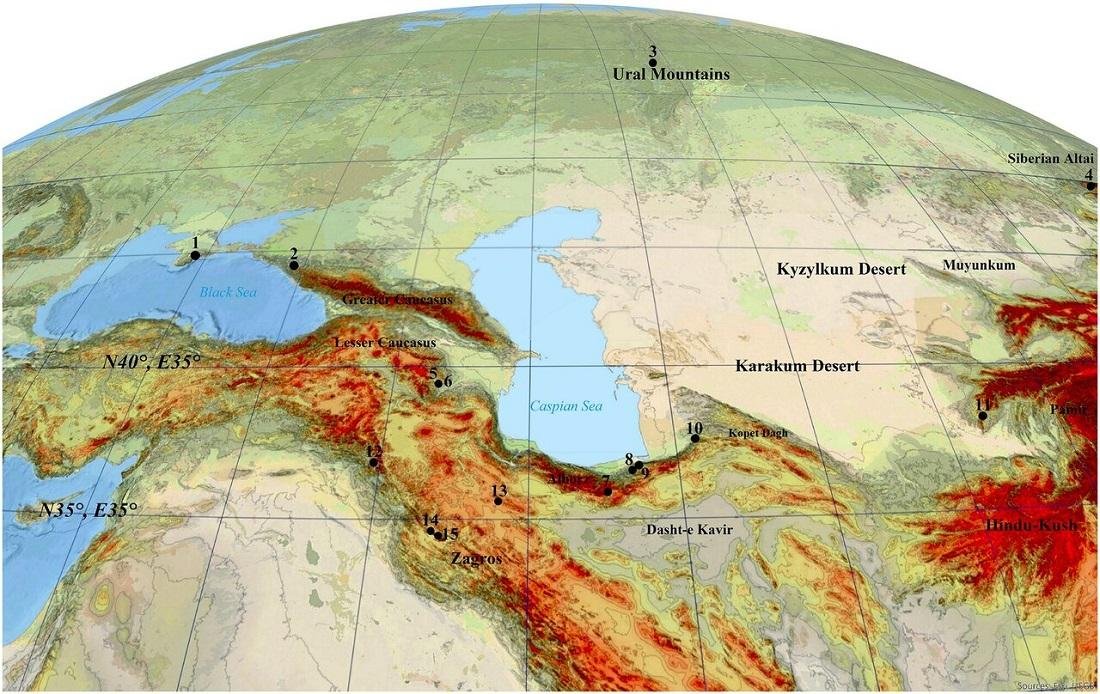 The study area and important Middle Paleolithic sites mentioned in the text: 1. Crimean sites, 2. Mezmaiskaya, 3. Trans Ural sites, 4. Siberian Altai sites (Chagyrskaya, Denisova, Okladnikov), 5. Azokh, 6. Taglar, 7. Liben, 8. Shoupari, 9. Wezwar, 10. Keyaram, 11. Teshik-Tash, 12. Shanidar, 13. Qale Kord, 14. Bawa Yawan, 15. Bisetun. Credit: PLOS ONE (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281978
The study area and important Middle Paleolithic sites mentioned in the text: 1. Crimean sites, 2. Mezmaiskaya, 3. Trans Ural sites, 4. Siberian Altai sites (Chagyrskaya, Denisova, Okladnikov), 5. Azokh, 6. Taglar, 7. Liben, 8. Shoupari, 9. Wezwar, 10. Keyaram, 11. Teshik-Tash, 12. Shanidar, 13. Qale Kord, 14. Bawa Yawan, 15. Bisetun. Credit: PLOS ONE (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281978
This route also provided a perfect entry and exit point for Europe, increasing the possibility of a significant cross-cultural meeting point between our two species.
Neanderthals were one of the earliest pre-human groups. They lived in some of the harshest environments ever inhabited by humans before and during the last ‘Pleistocene Ice Age.’
They created art, cared for the sick, and controlled fire. Furthermore, they were the most widespread species of people in their time, living as far away as Central Asia and Siberia from Europe’s western and northernmost regions.
In many ways, they are the first example of a ‘society’.
The study was published in the journal PLOS ONE.
More information: Ghasidian, E, et al, (2023). Modeling the Neanderthal migration routes from the Caucasus to the east, PLUS ONE. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281978





