Spanish Levantine rock art has provided remarkable visual evidence of the expertise developed by ancient societies in eastern Spain concerning climbing and the use of specialized equipment to minimize risks ᴀssociated with this activity.
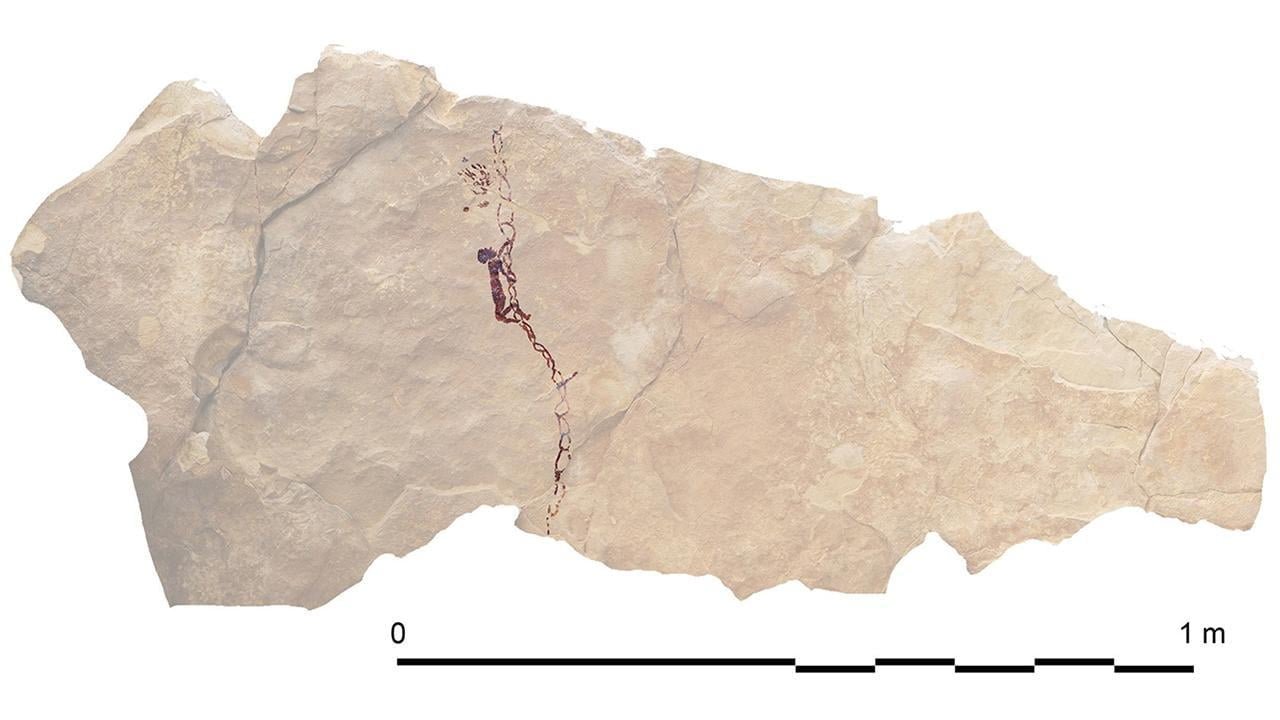 A honey gathering scene was recently discovered at the Barranco Gómez site, featuring an image of a honey gatherer climbing a ladder. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
A honey gathering scene was recently discovered at the Barranco Gómez site, featuring an image of a honey gatherer climbing a ladder. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
The analysis of existing depictions found in Albacete, Castelló, Huesca, Teruel, and Valencia reveals that Spanish Levantine societies possessed the technological know-how to craft high-quality ropes, tailored specifically for climbing purposes.
A recently discovered depiction at the Barranco Gómez site in Teruel showcases intricate rope use in Spanish Levantine art, particularly focusing on a rope ladder used to access a beehive.
The representation of this rope ladder measuring approximately 25 meters in length indicates the significant effort invested in rope production and its use for climbing, particularly in activities like collecting honey and wax from beehives. Bee-related products held significant importance in prehistoric times, serving various economic, technological, and cultural purposes.
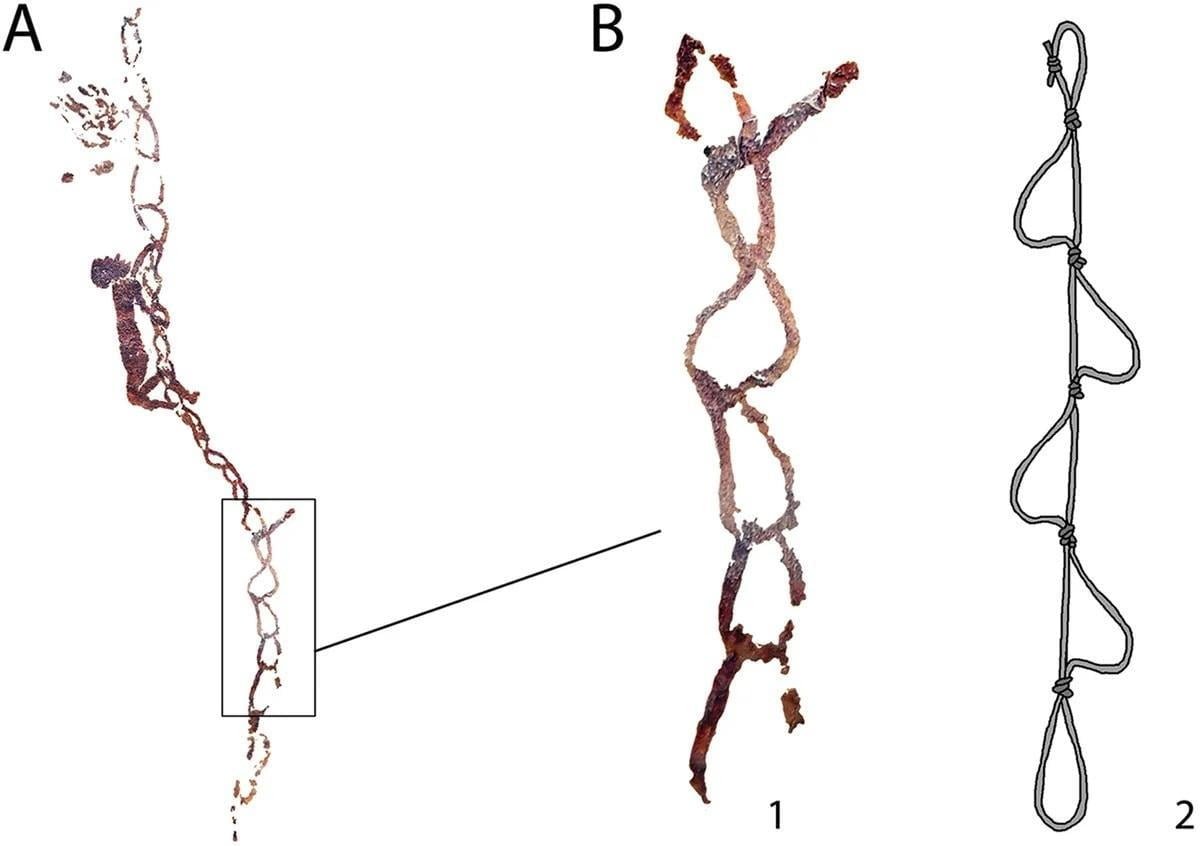 A close-up of the stirrup ladder compared with ladders still used in alpine climbing. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
A close-up of the stirrup ladder compared with ladders still used in alpine climbing. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
Spanish Levantine rock art, exclusive to the eastern Iberian Peninsula, consists of over a thousand recorded sites and offers a valuable glimpse into human life during that era. The artwork depicts dynamic scenes ranging from hunting and warfare to social activities and gatherings, providing a vivid depiction of prehistoric societies.
The comprehensive investigation of ropes and their technology presented challenges due to the imperceptibility of rope materials and manufacturing techniques in archaeological records. However, through analysis and on-site research, the research team led by Manuel Bea from the University of Zaragoza shed light on the structure, usage, and production of these ropes, emphasizing the adaptability of flexible climbing systems depicted in the art.
The rock art depictions of climbing systems are concentrated in two regions: the Maestrazgo in the north (Castelló and Teruel) and the Caroig Mᴀssif in the south (Alicante). This geographical concentration suggests that these representations may carry symbolic significance, indicate specific behaviors, or reflect territorial codes.
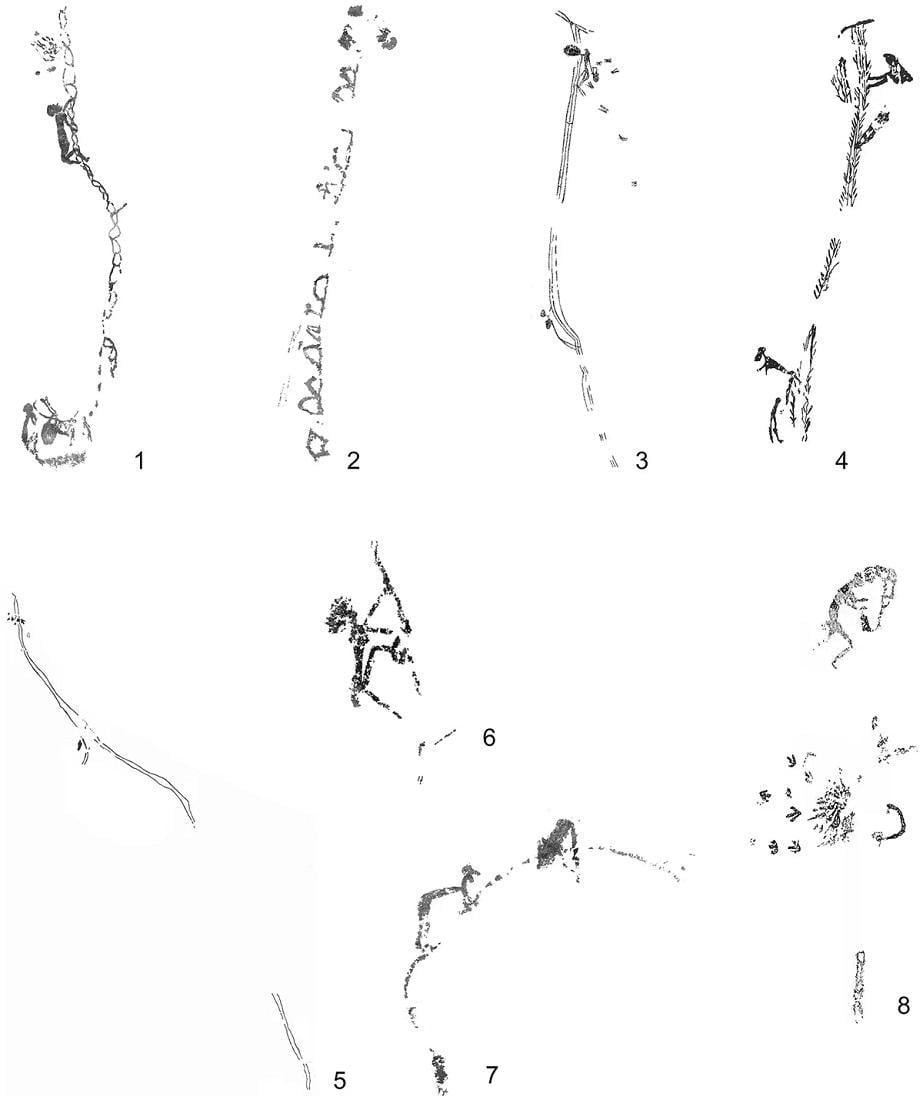 The variety of different flexible climbing systems found in Levantine rock art. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
The variety of different flexible climbing systems found in Levantine rock art. Credit: Bea et al, 2023, Cambridge Archaeological Journal (CC BY 4.0)
The research team conducted the study funded by the European Research Council, the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, the Valencian Government, and the Ministry of Economy and Compeтιтiveness.
The study’s findings published in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal, expand our understanding of the advanced skills and knowledge possessed by ancient societies in Spain.
More information: Bea, M., Roman, D., & Domingo, I. (2023). Hanging over the Void. Uses of Long Ropes and Climbing Rope Ladders in Prehistory as Illustrated in Levantine Rock Art. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 1-19. doi:10.1017/S0959774323000173





