Archaeologists have unearthed a finely crafted, intricate necklace from an ancient child’s grave at the Neolithic village of Ba’ja in Jordan.
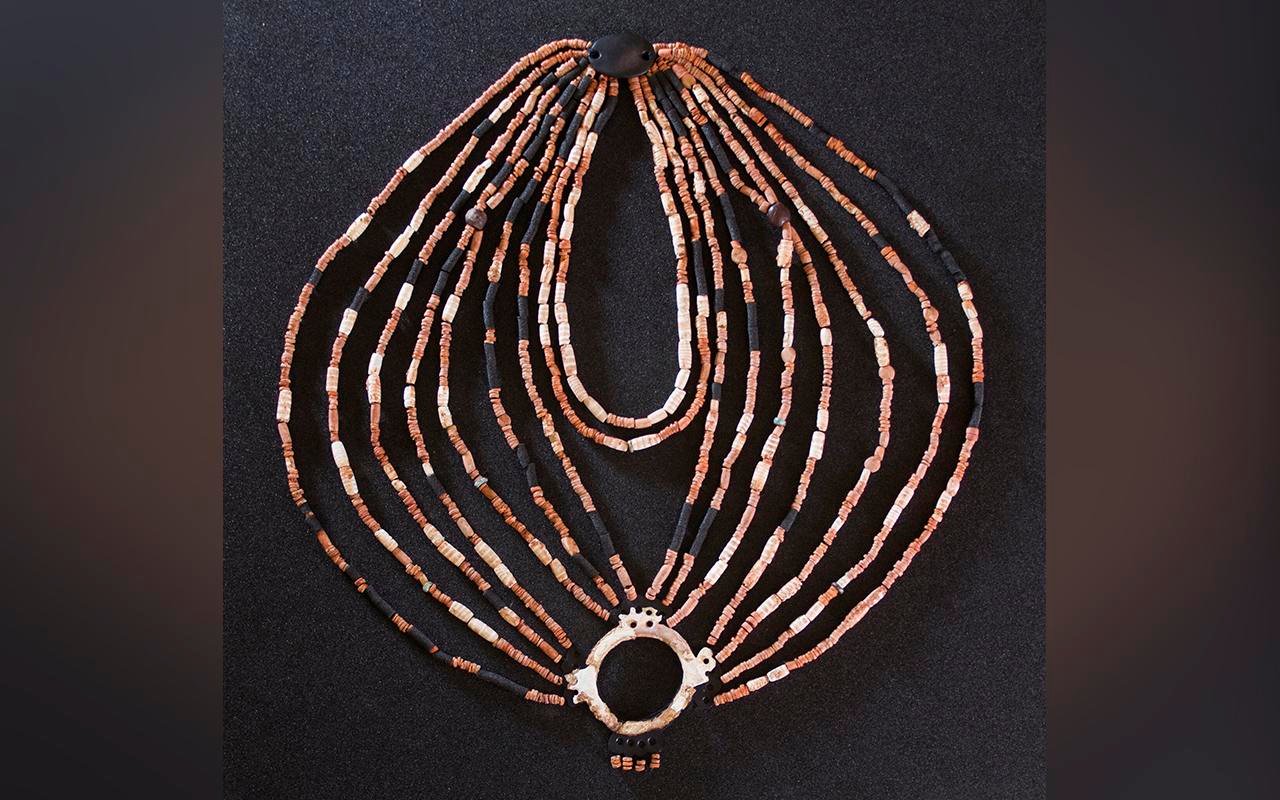 Physical reconstruction of the necklace, today exposed at the new museum of Petra in Jordan. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
Physical reconstruction of the necklace, today exposed at the new museum of Petra in Jordan. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
The ornate necklace, composed of over 2,500 colorful stones and shells, a large stone pendant, a delicately engraved mother-of-pearl ring, and the oldest known amber beads in the Levant region, is believed to be part of an elaborate funerary ritual that highlighted the high social status of the child.
The research team, led by Hala Alarashi of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas in Spain and the Université Côte d’Azur in France, meticulously reconstructed the necklace, now displayed at the Petra Museum in southern Jordan.
This ancient adornment offers a window into the multifaceted aspects of Neolithic society, where body adornments held significant symbolic meaning, conveying cultural values and individual idenтιтies.
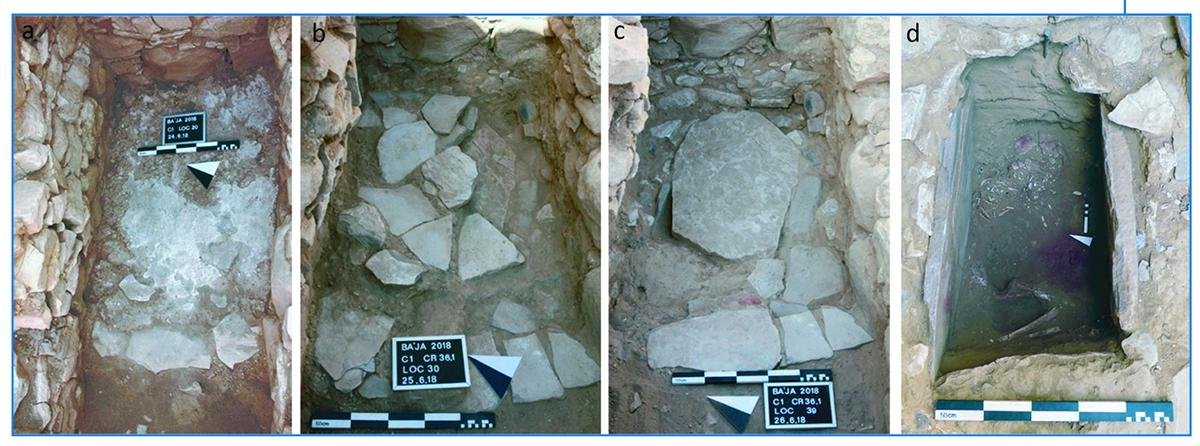 Excavation stages of of the cist-type grave CG7 at Ba`ja, Jordan. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
Excavation stages of of the cist-type grave CG7 at Ba`ja, Jordan. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
The beads, each a testament to meticulous craftsmanship, were made from various materials, including shells, stones, and even fossilized amber—highlighting an extensive trading network that spanned the Levant region during the Neolithic period.
The complexity of the necklace’s design and the use of rare materials suggest a community that involved skilled artisans, traders, and high-status individuals.
“Beyond the symbolic functions related to idenтιтy, the necklace is believed to have played a key role in performing the inhumation rituals, understood as a public event gathering families, relatives and people from other villages,” the authors write.
“The lavishly endowed child laying down in an impressive burial, and the extraordinary ornament decorating the chest was intended to be shown, probably for a last sight,” the researchers noted. “In this sense, the death of the child should be seen as a public event gathering the people of Ba‘ja, families, friends, and probably members from other villages too.”
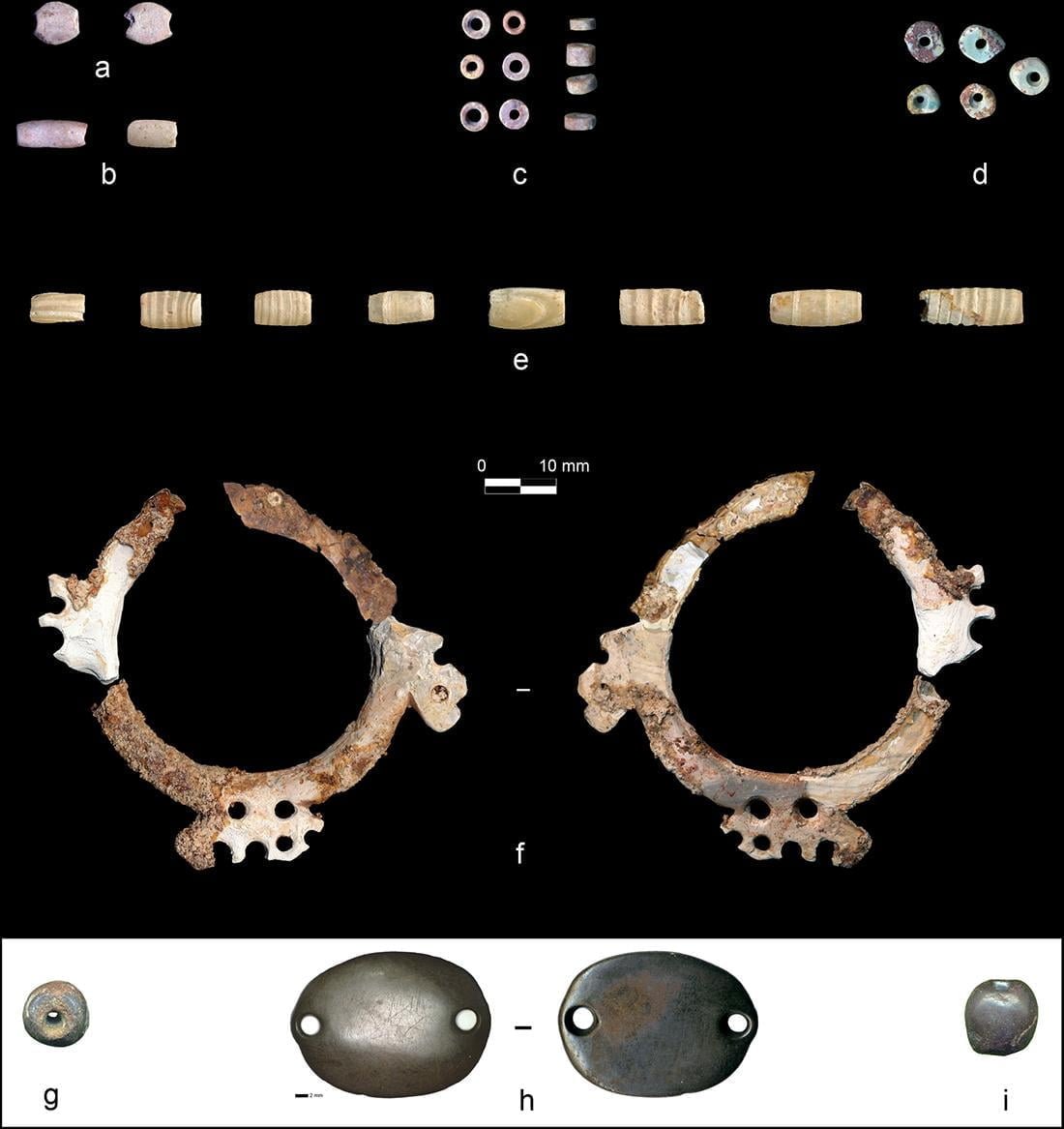 Diversity of items compositing the ornamental ᴀssemblage of CG7. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
Diversity of items compositing the ornamental ᴀssemblage of CG7. Credit: Alarashi et al., 2023, PLOS ONE
The Neolithic village of Ba’ja, dating between 7,400 and 6,800 BCE, has provided a unique opportunity for archaeologists to delve into the lives and rituals of prehistoric societies. The burial practices and exquisite artifacts discovered within children’s graves, including this intricate necklace, speak volumes about the cultural values and shared emotions of the community.
This remarkable discovery, detailed in a study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, sheds light on the social complexities, artistic prowess, and trading networks of Neolithic culture.
More information: Alarashi H et al. (2023). Threads of memory: Reviving the ornament of a ᴅᴇᴀᴅ child at the Neolithic village of Ba’ja (Jordan), PLoS ONE. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288075





