A collection of Iron Age gold coins has been unearthed in the vicinity of Llangoed, Anglesey, marking a pivotal moment in Welsh history.
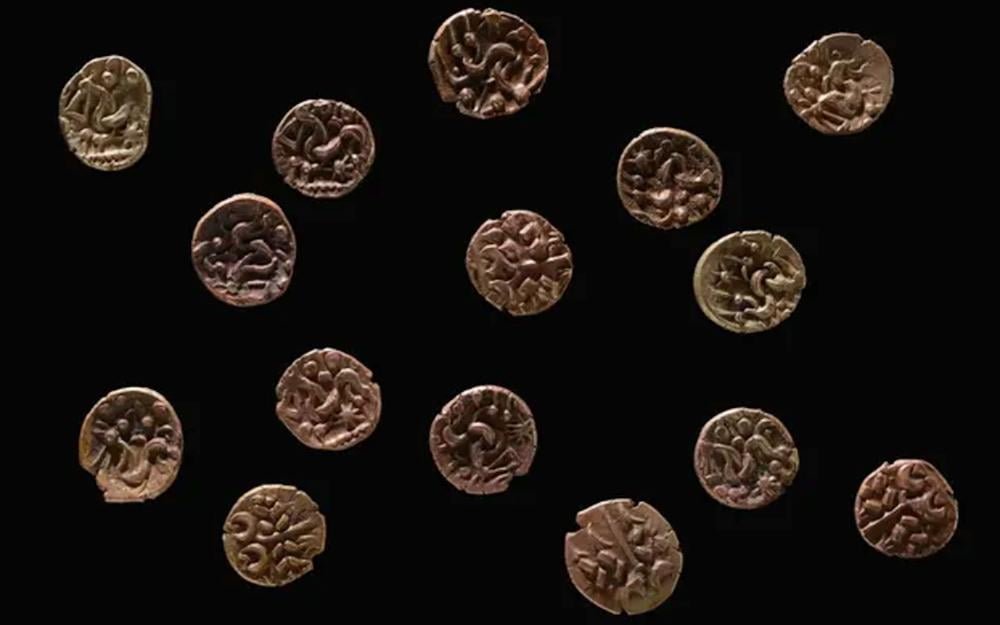 The collection of gold coins found in Wales. Credit: Amgueddfa Cymru — National Museum Wales
The collection of gold coins found in Wales. Credit: Amgueddfa Cymru — National Museum Wales
The hoard, consisting of fifteen intricately designed gold coins referred to as staters, dates back to the period between 60 BCE and 20 BCE. The remarkable discovery was reported to the Portable Antiquities Scheme by metal detectorists Peter Cockton, Lloyd Roberts, and Tim Watson. This unique find has been designated as treasure by the HM Senior Coroner for North West Wales.
The coins, known for their artistic stylization, depict the bust of Apollo on one side and a chariot drawn by two horses with a charioteer on the reverse. Their design draws inspiration from the gold coins of Phillip II of Macedonia.
While each coin exhibits Apollo’s wreath and hair in a distinctive manner, the reverse showcases a stylized triangular-headed horse, often accompanied by various symbols. These staters offer a rare glimpse into the aesthetics and craftsmanship of the Iron Age.
Lloyd Roberts, one of the metal detectorists, expressed his astonishment at discovering these treasures, saying, “Finding a gold stater was always number one on my wish list. Having never expected to actually find one, let alone in Anglesey, can you imagine my shock, delight, and surprise as I called out to my friend Peter, having dug up a beautiful full gold stater in mint condition? That one coin alone would have made my year.”
Roberts and his colleague Peter Cockton were responsible for uncovering five of the coins, while Tim Watson, who was new to metal detecting, discovered the remaining ten.
The hoard’s significance goes beyond the coins themselves. Sean Derby, Historic Environment Record Archaeologist and PAS Cymru Finds Recording Officer at Gwynedd Archaeological Trust, emphasized that this discovery sheds light on the rich archaeological landscape of North-West Wales.
Though the immediate area provided no direct clues to the hoard’s origin, the findspot is located within a region known for prehistoric and early Roman activities. Gwynedd Archaeological Trust, in collaboration with the landowner Gwyn Jones, conducted a site visit to better understand the historical context.
Archaeological experts believe that these coins were used by the Corieltavi tribe, who inhabited the East Midlands region during the Iron Age. It’s notable that these tribes in Wales rarely used coins from other regions, making finds from this era exceptionally rare. As such, these coins were likely not used for everyday transactions but might have been employed for ceremonial or symbolic purposes.
The coins were minted across different mints in Lincolnshire, and their discovery has provided fresh insights into the complex interactions and exchanges between tribes during the Iron Age.
The Art Newspaper’s Gareth Harris reports that Oriel Môn, a museum and gallery in Anglesey, is interested in acquiring the coins and placing them on public display.





