A team of scientists, including Kari A. Guilbault of Purdue University, was studying a 1,300-year-old body unearthed in a cemetery near the Ghazali monastery in Sudan, which is known for its historical significance and sits approximately 9.3 miles from the Nile River. The individual, who likely lived between 667 and 774 CE, had a remarkable tattoo on their right foot.
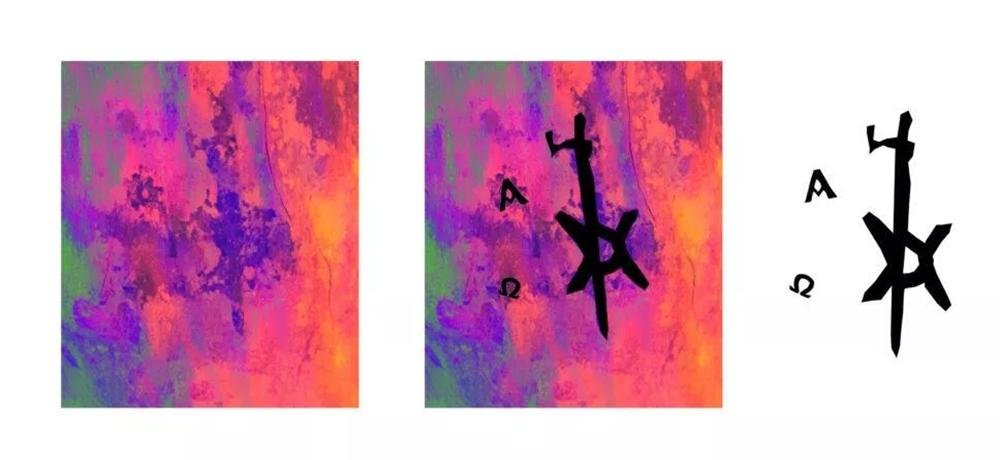 A digital illustration of the tattoos found on the body at Ghazali. Credit: Kari A. Guilbault, Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology
A digital illustration of the tattoos found on the body at Ghazali. Credit: Kari A. Guilbault, Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology
The tattoo contains a Christogram, an ancient Christian symbol, made by combining the Greek letters “chi” and “rho” to form an abbreviation for Christ. Additional Greek letters, alpha (A) and omega (Ω), representing the beginning and end, enhance the Christogram. This orientation is intriguing as it is reminiscent of the possibility that it references the crucifixion of Christ or symbolizes a spiritual journey.
This Christogram tattoo signifies not only the individual’s faith but also provides a unique historical glimpse into the prevalence of Christianity in medieval Nubia. At the time, Christianity was widespread in the region. The person was likely between 35 and 50 years old when they pᴀssed away. Notably, this is only the second instance of a tattoo discovered in medieval Nubia.
The location of the tattoo on the right foot is significant, as it may allude to the crucifixion of Christ, a detail that Robert Stark, a bioarchaeologist with the Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology at the University of Warsaw, and Kari Guilbault noted during their research. Although it’s clear the individual was Christian, their role in society is less certain. They were buried in a cemetery separate from the monastery’s monks, suggesting they were part of local communities.
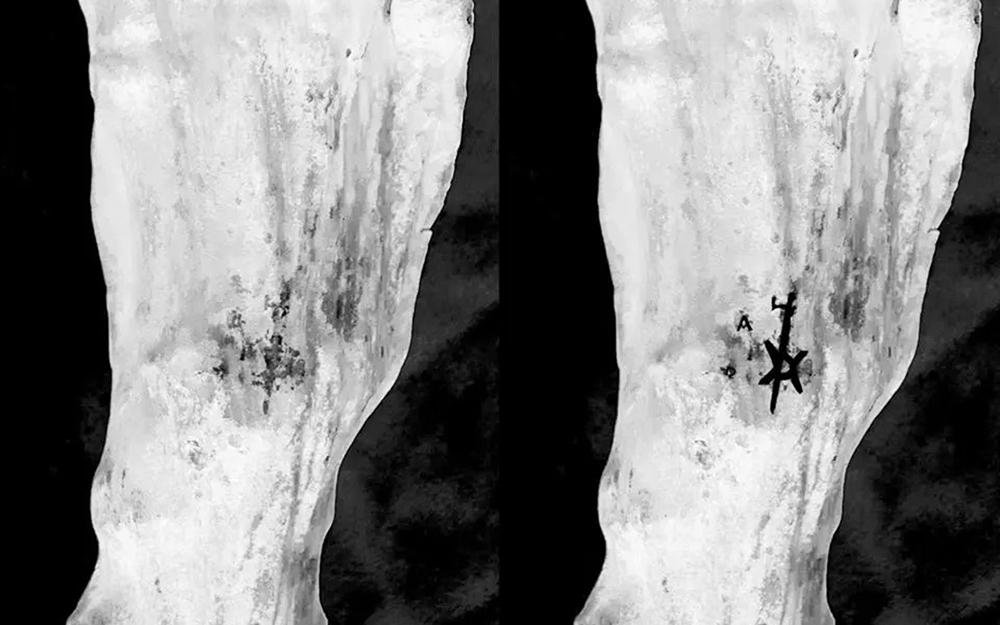 In the image captured with a full-spectrum camera on the left, the toes extend past the top. On the right, an overlay of the tattoo is superimposed onto the image. Credit: Kari A. Guilbault, Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology at the University of Warsaw
In the image captured with a full-spectrum camera on the left, the toes extend past the top. On the right, an overlay of the tattoo is superimposed onto the image. Credit: Kari A. Guilbault, Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology at the University of Warsaw
The Ghazali monastery has a rich history, with excavations revealing several significant findings, including a basilica-style church, cemeteries, a settlement, and evidence that the site was involved in iron smelting. The research team made this discovery in 2016 while conducting an ongoing investigation of Ghazali, and the tattoo came to light after additional post-excavation analysis and full-spectrum pH๏τography.
Guilbault, who has expertise in medieval tattooing practices, found the tattoo by chance while pH๏τographing the remains. She noted that earlier Nubian tattoos, dating back around 4,000 years, were often abstract in design and found on females. The latest discovery, however, is a well-defined religious symbol, and it’s also the first tattoo found on male remains.
In addition to its cultural and religious significance, the preserved tattoo itself is remarkable. Tattoos typically break down in the body over time, as they are seen as foreign substances. However, this breakdown process is paused upon death, which is why the tattoo on this 1,300-year-old body remains intact.
The discovery adds an intriguing chapter to the understanding of early Christian symbolism and practices in Nubia.





