A collection of Iron Age gold treasures, including the world’s largest gold “bracteate,” is currently under investigation using 3D scanning and digital unfolding techniques. The collection was discovered in 2021 near Vindelev, Denmark, and includes a total of 16 bracteates (medallion-like necklaces) and four Roman medallions, comprising 794 grams of gold.
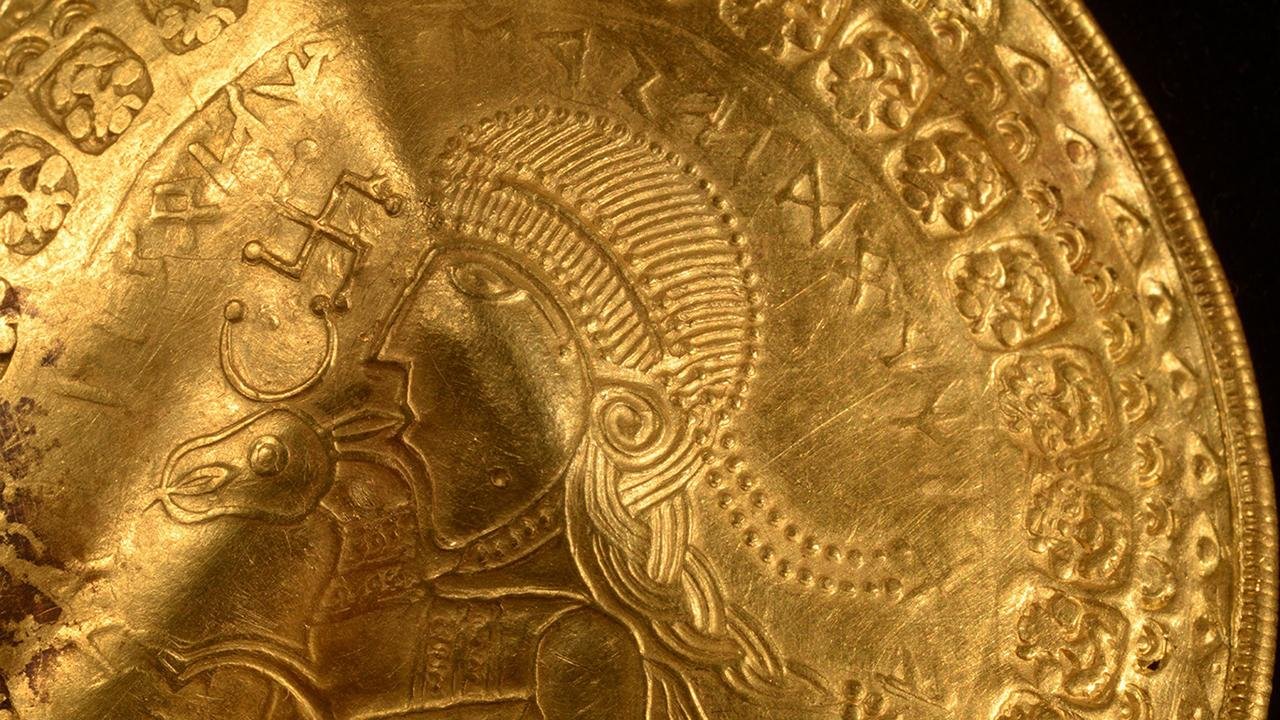 An object from the gold treasure from Vindelev, which spent some time at DTU in an attempt to better understand its origin and importance. Credit: Conservation Centre Vejle
An object from the gold treasure from Vindelev, which spent some time at DTU in an attempt to better understand its origin and importance. Credit: Conservation Centre Vejle
Archaeologists believe that these treasures, buried in the 6th century, likely belonged to a powerful but unidentified clan leader. Unfortunately, many of the bracteates are so crumpled, either due to intentional folding or plough damage over the years, that their intricate motifs and runic inscriptions have become hidden. Manual unfolding is considered too risky, as it could lead to breakage, prompting researchers to turn to modern technology.
Archaeologist Dr. Mads Ravn, Head of Research at the Vejle Museums, expressed, “Sometimes technology can open doors that we can’t. In this case, we want to get a better look at the inscriptions and images on the bracteates so we can learn more about the nobleman who owned the treasure. What was his position? What was his domain? If we succeed, we will gain a better understanding of the structure of society in the 5th and 6th centuries.”
The technology employed in this effort is CT scanning, a modality used in hospitals to create detailed, three-dimensional X-ray images of patients’ internal anatomy. CT scans work by “slicing” objects into cross-sections, generating thousands of individual images in the case of the largest bracteate. Nonetheless, challenges arose due to the varying thickness of the gold.
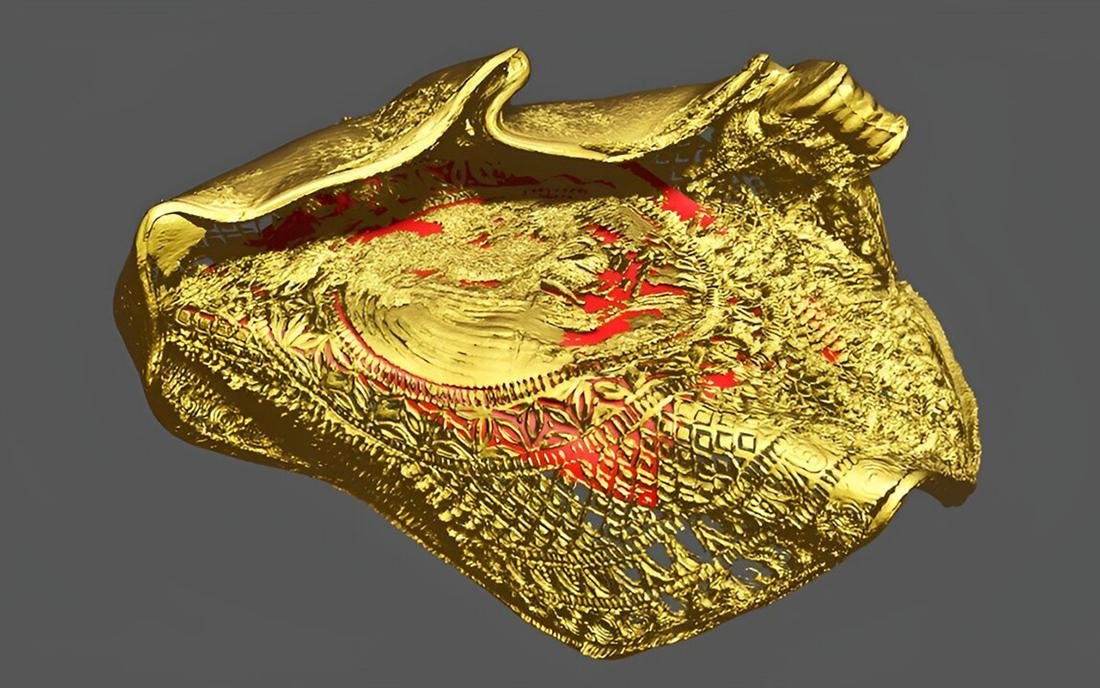 A 3D visualization from the reconstruction of bracteate X19. The red surface shows the specific area the researchers have focused on unfolding. Credit: Technical University of Denmark
A 3D visualization from the reconstruction of bracteate X19. The red surface shows the specific area the researchers have focused on unfolding. Credit: Technical University of Denmark
Carsten Gundlach, a Senior Executive Research Officer at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU), explained that these artifacts can be compared to artifacts in hospital scans of patients with surgical screws. These artifacts, in the context of the gold bracteates, created discrepancies in the CT images. To address this, Gundlach used the data from hundreds of 360-degree scans of each bracteate for spatial 3D reconstructions.
Following the scans and reconstructions, the next challenge was to digitally unfold the bracteates to reveal their motifs and inscriptions. While some smaller bracteates with fewer folds were more successfully unfolded, the process was more complicated for those with тιԍнтer folds, making it difficult to see all the details.
The primary focus of the project has shifted towards unfolding the individual parts that may shed light on Denmark in the 5th and 6th centuries. Researchers are especially eager to uncover the motifs on the largest bracteate, which seems to feature a folded twin motif. Stamps around the motif may provide insights into the bracteate’s origin and age, potentially confirming a connection between this gold collection and Denmark’s power centers.
Denmark during the time of these bracteates was characterized by autocratic clan leaders who ruled territories with the same principles seen in biker gangs or the Mafia. Mads Ravn believes that the treasure’s size suggests its owner was a powerful but previously unknown clan leader. Moreover, the gold collection’s resemblance to treasures found near Gudme on Funen, another major power center in Denmark from the 3rd to the 6th century, implies a possible connection or alliance between these centers.
Ravn speculates, “It’s possible that the gold was handed over as a gift in connection with weddings between daughters and sons from each clan.” Research will continue to gather circumstantial evidence.
The researchers remain determined, aiming to unfold the twin motif and stamps on the largest bracteate, allowing further comparisons with findings in Gudme. DTU’s innovative methods may also help distinguish between bracteates intentionally folded by clan leaders and those damaged by modern ploughs.
As research progresses, there are many challenges ahead. However, this endeavor highlights the boundless potential of technology in uncovering historical mysteries. Dr. Hans Martin Kjer, a DTU computer scientist, aptly notes, “Research never ends.”
Technical University of Denmark





