Declassified Cold War-era spy satellite images have led researchers to identify 396 previously unknown Roman forts in Syria and Iraq.
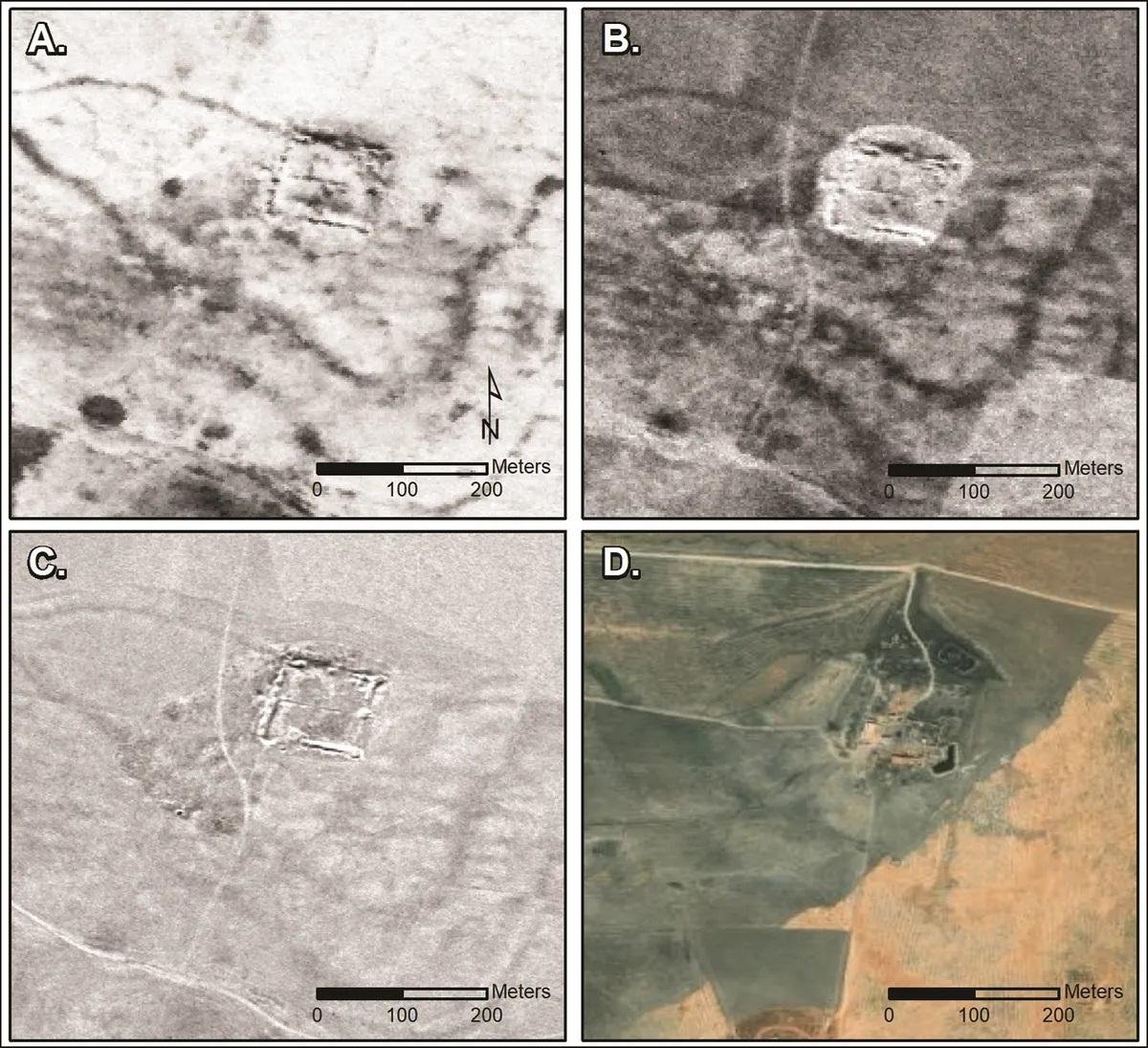 Older and more modern satellite imagery of a fort at Tell Brak, northern Syria. Credit: Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
Older and more modern satellite imagery of a fort at Tell Brak, northern Syria. Credit: Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
The research, led by Professor Jesse Casana from Dartmouth College, challenges long-held ᴀssumptions about the purpose of these structures, pointing towards a vibrant network supporting trade and cultural exchange rather than a rigid border defense system.
The discovery builds upon the pioneering work of French Jesuit priest Father Antoine Poidebard, who, in the 1920s, conducted one of the world’s first aerial archaeological surveys, documenting 116 forts along what was believed to be the eastern boundary of the Roman Empire. However, the recent analysis, based on declassified imagery from the Corona and Hexagon spy satellite programs of the 1960s and 70s, challenges Poidebard’s interpretation.
Casana’s team identified 396 forts scattered across the Syrian steppe, far exceeding Poidebard’s count. The newfound forts, distributed both east-to-west and north-to-south, challenge the notion of a strict border and indicate a more fluid and interconnected Roman frontier.
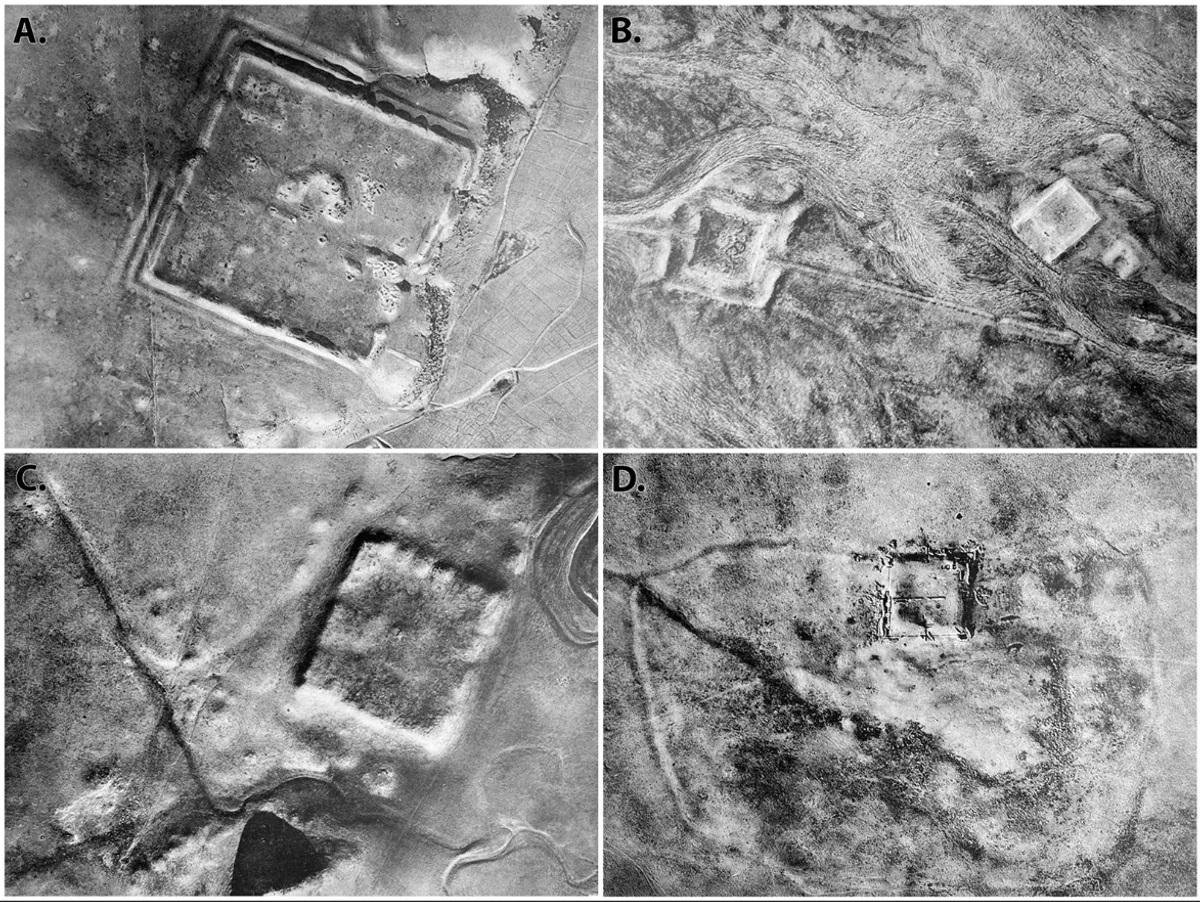 Aerial pH๏τography from 1934 of select Roman forts in the region surveyed. Credit: Father Antoine Poidebard / Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
Aerial pH๏τography from 1934 of select Roman forts in the region surveyed. Credit: Father Antoine Poidebard / Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
The distinct square shape, typically 50-80 meters per side, classifies these structures as probable forts, distinguishable from modern buildings by their lower, eroded walls. The findings challenge the idea of a rigid Roman border, indicating that the empire’s eastern extent was more about facilitating commerce than strict territorial defense.
According to Professor Casana, “Historically, as an archaeologist, I can say that there have been many attempts by ancient states to build walls across borders, and it has been a universal failure. If there’s any way that archaeology contributes to modern discourse, I would hope it is that building giant walls to keep people out is a bad plan.”
The research emphasizes the importance of satellite imagery for recording archaeological features before they are lost due to urban development and agriculture. Unfortunately, many of the newly identified Roman forts have already been destroyed.
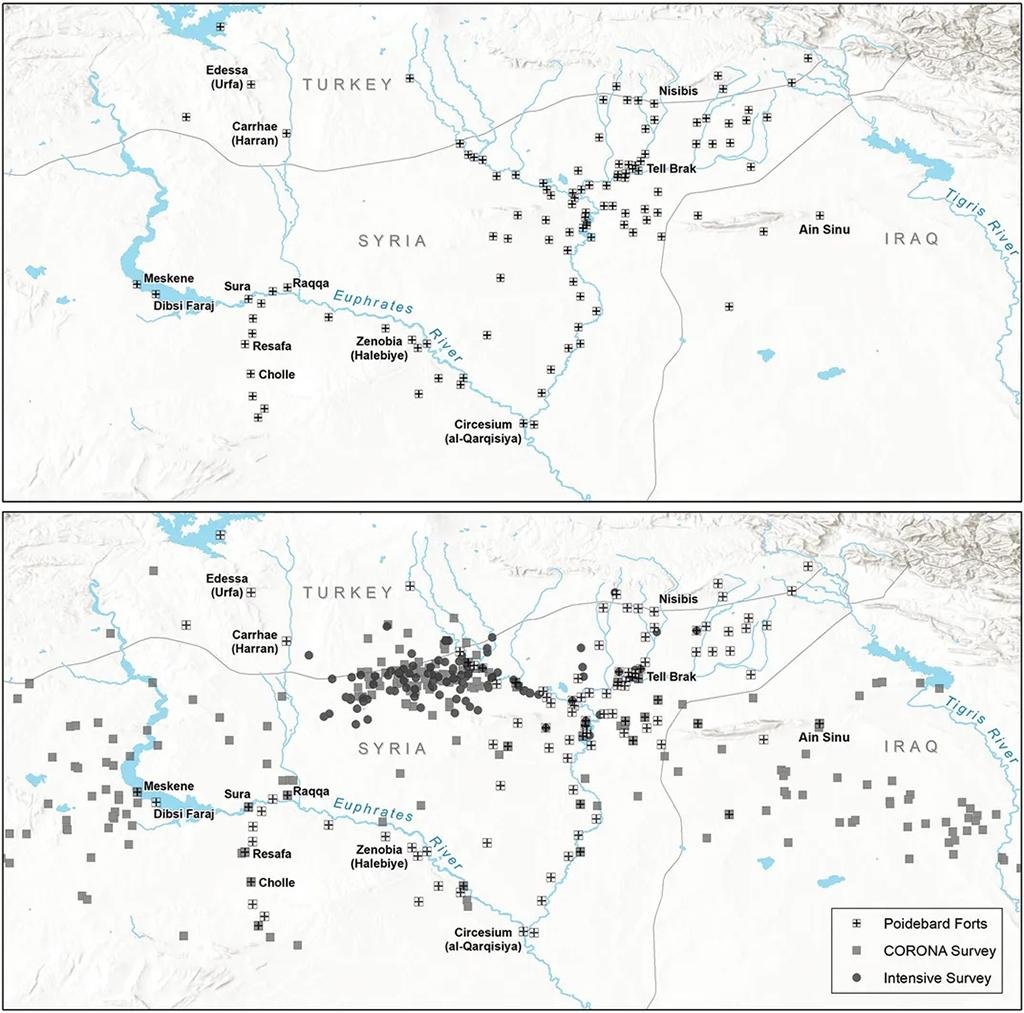 Map showing distribution of forts as documented by Poidebard (above) and the authors (below). Credit: Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
Map showing distribution of forts as documented by Poidebard (above) and the authors (below). Credit: Casana et al, Antiquity 2023 (CC BY 4.0)
In the words of Professor Casana, “Careful analysis of these powerful data holds enormous potential for future discoveries in the Near East and beyond.” With more declassified imagery, such as U2 spy plane pH๏τographs, becoming available, the researchers anticipate additional archaeological revelations.
More information: Casana, J. et al, (2023), A wall or a road? A remote sensing-based investigation of fortifications on Rome’s eastern frontier, Antiquity. DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2023.153





