Archaeologists on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi have unearthed two shark-tooth blades estimated to be around 7,000 years old.
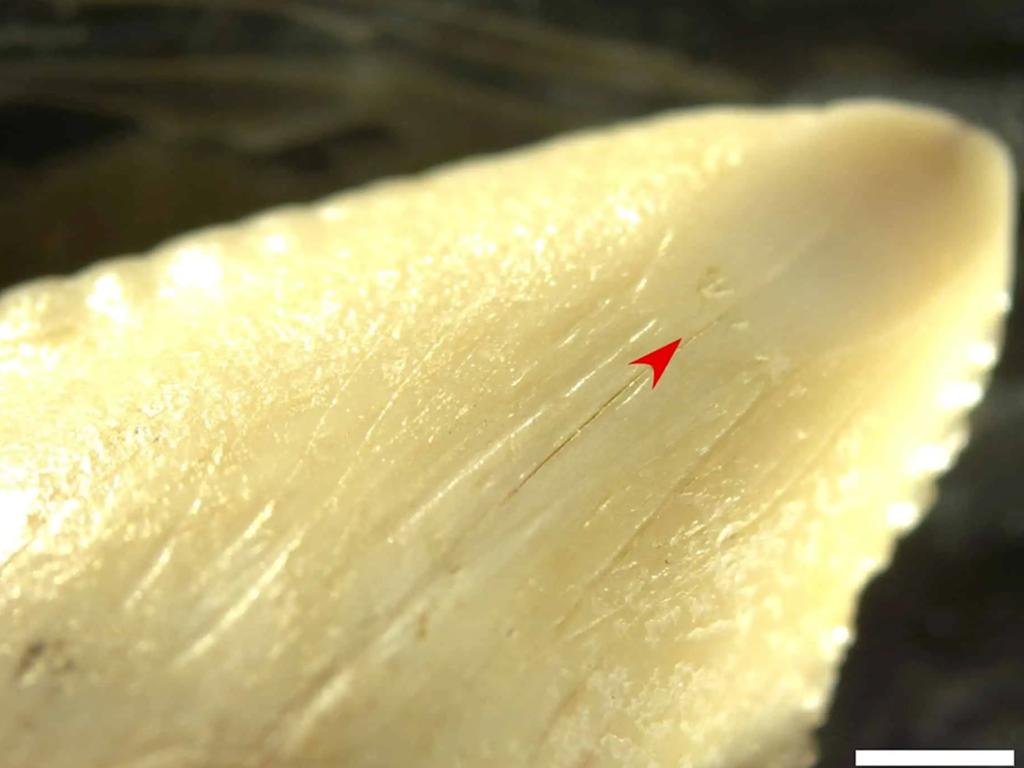 Scratches on the shark teeth suggest they were used by humans, likely as weapons or in rituals. Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
Scratches on the shark teeth suggest they were used by humans, likely as weapons or in rituals. Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
The artifacts, identified as tiger shark teeth, were fashioned into lethal weapons and provide some of the earliest global evidence of the use of shark teeth in composite weaponry. The findings, detailed in the journal Antiquity, reveal intriguing insights into the Toalean culture, an enigmatic foraging society that inhabited southwestern Sulawesi from approximately 8,000 years ago until an unknown recent period.
The international team of researchers, comprising scientists from Indonesia and Australia, made the discovery during excavations ᴀssociated with the Toalean culture. The tiger shark teeth, originating from sharks around six feet in length, displayed unique characteristics. One tooth, recovered from the Leang Panninge cave site, possessed two holes drilled through the root, while the other, found in the Leang Bulu’ Sipong 1 cave, had one hole, though it was damaged, likely originally featuring two holes.
The teeth, examined under a microscope, revealed traces of their attachment to handles using plant-based threads and a glue-like substance comprising mineral, plant, and animal materials.
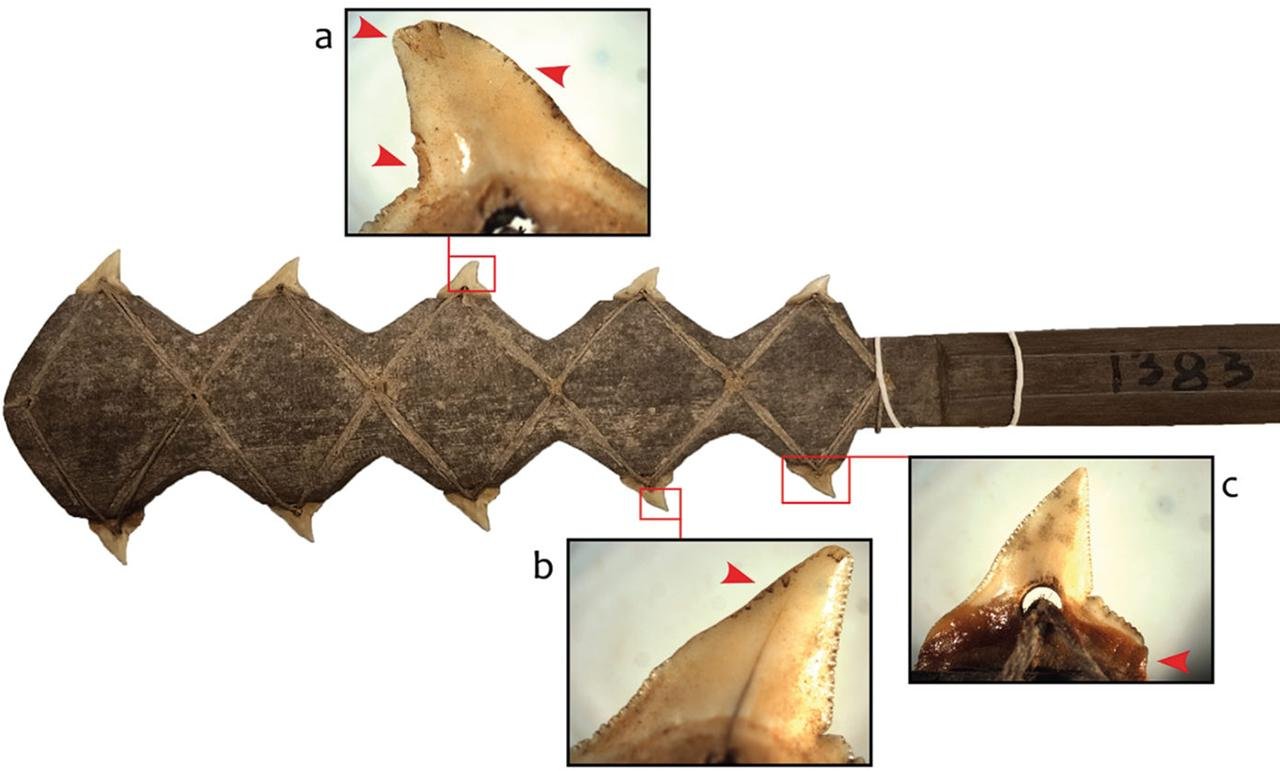 A knife with a shark tooth blade from Aua Island, Papua New Guinea. Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
A knife with a shark tooth blade from Aua Island, Papua New Guinea. Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
These blades, believed to be used in warfare or rituals, represent some of the oldest evidence of such composite weapons globally. Previous instances of modified shark teeth date back to less than 5,000 years ago, making these Sulawesi discoveries a remarkable leap into the past.
Michelle Langley, a professor of archaeology at Griffith University and one of the study’s authors, emphasized the rarity of finding evidence of shark teeth being modified and used by ancient cultures. She told Newsweek, “in the Pacific region, shark-tooth knives are very culturally significant in the recent and present day, so finding evidence that this form of tool is at least several thousand years old is incredible. It just goes to show how deep these traditions are in this region.”
The Toalean people, an elusive group of hunter-gatherers, inhabited Sulawesi long before the arrival of Neolithic farmers from mainland Asia. The shark-tooth blades, with their intricate attachment method and signs of wear suggesting use beyond everyday cutting needs, challenge the notion of these tools as mere ornaments.
 Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
Credit: M.C. Langley, Antiquity (2023)
Anthropological observations of contemporary societies, combined with experimental data, suggest that shark teeth were commonly fashioned into weapons for warfare or ceremonial purposes, emphasizing the reverence communities had for these oceanic predators.
The blades’ effectiveness in creating deep incisions, as demonstrated in experimental reproductions, was counteracted by their quick dulling, making them impractical for everyday use. This led researchers to propose that the shark-tooth blades were likely reserved for special events or conflicts rather than mundane tasks. The findings also connect the Toalean people to global cultures that incorporated shark teeth into their weaponry.
More information: Langley, M., Duli, A., Stephenson, B., Nur, M., Matherson, C., Burhan, B., . . . Brumm, A. (2023). Shark-tooth artefacts from middle Holocene Sulawesi. Antiquity, 1-16. doi:10.15184/aqy.2023.144





