Czech archaeologists from Masaryk University in Brno have revealed a bronze belt buckle dating back to the eighth century, depicting a snake devouring a frog-like creature.
 A bronze belt buckle dating back to the eighth century, depicting a snake devouring a frog-like creature. Credit: Masaryk University Brno
A bronze belt buckle dating back to the eighth century, depicting a snake devouring a frog-like creature. Credit: Masaryk University Brno
The find, made near the town of Břeclav in Southern Moravia, could significantly enhance our understanding of the spiritual life of people in the pre-Christian era, a period about which little is currently known.
Jiří Macháček, head of the university’s department of Archeology and Museology, told Radio Prague that such ornaments were worn by elites in East Central Europe during the early Middle Ages.
This particular belt buckle, ᴀssociated with the Avars, a nomadic people settled in the Carpathian basin (present-day Hungary), was also worn by neighboring nations or groups of people. Notably, it was discovered in the context of excavating a settlement of early Slavs, adding a layer of complexity to its cultural significance.
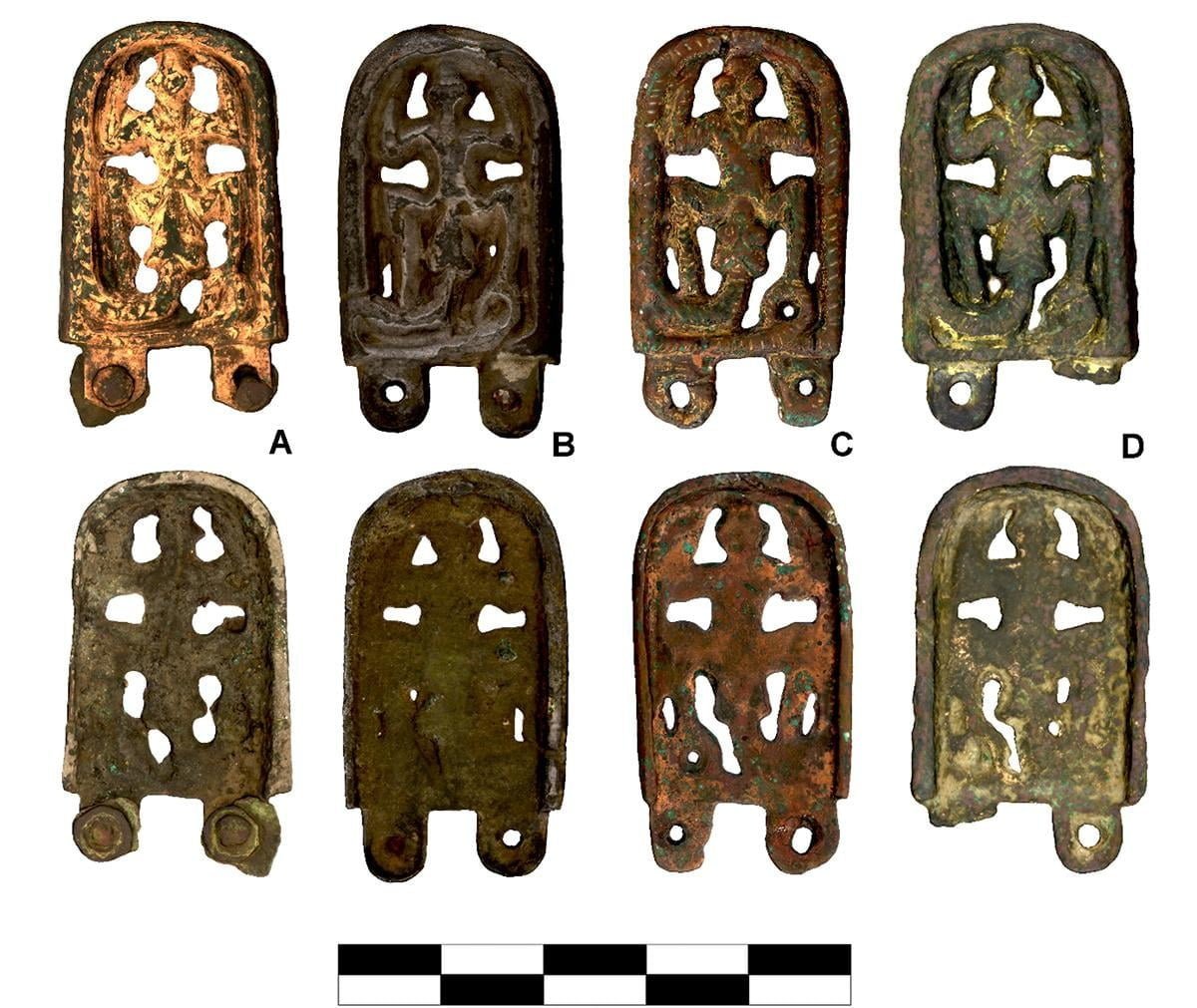 Nearly identical belt buckles have been discovered in Central Europe: A – Lány (Czech Republic), B – Zsámbék (Hungary), C – Iffelsdorf (Germany), and D – Nový Bydžov (Czech Republic). Credit: Masaryk University Brno, Journal of Archaeological Science
Nearly identical belt buckles have been discovered in Central Europe: A – Lány (Czech Republic), B – Zsámbék (Hungary), C – Iffelsdorf (Germany), and D – Nový Bydžov (Czech Republic). Credit: Masaryk University Brno, Journal of Archaeological Science
The motif depicted on the belt buckle, showcasing a snake devouring a frog-like creature, is a recurring theme in Germanic, Avar, and Slavic mythologies. Scholars believe it is likely linked to narratives surrounding the world’s creation or fertility cults.
This discovery is particularly significant because nearly identical belt buckles have been found hundreds of kilometers apart in various parts of Central Europe. The widespread distribution implies the motif played a pivotal role in the religious and spiritual life of the early Middle Ages inhabitants in this region.
Macháček emphasized the scarcity of knowledge about the pre-Christian religions of Germanic and Slavic people, given the lack of written sources. He stated, “We believe that this scene of the fighting snake could be connected with the pre-Christian religion of the people of central Europe. Therefore, such archaeological discoveries could be very important to the discussion about the religion of these people before Christianity.”
Following this extraordinary find, an international team of experts was swiftly ᴀssembled, collaborating with researchers from other countries where similar artifacts had been discovered. The team, as reported by Radio Prague International, used advanced analytical methods such as lead isotope analysis and scanning electron microscopy to examine five specimens. Their goal is to identify the origin of these ornaments, exploring the possibility that they were produced in the same workshop and distributed across central Europe.
 Credit: Masaryk University Brno, Journal of Archaeological Science
Credit: Masaryk University Brno, Journal of Archaeological Science
The team’s findings, detailed in the Journal of Archaeological Science, provide valuable insights into the shared cultural and religious practices of diverse communities in East Central Europe during the early Middle Ages.
The recurring motif in Germanic, Avar, and Slavic mythologies suggests a shared cultural narrative, and the widespread distribution of similar artifacts across Central Europe underscores its significance in the religious and spiritual practices of the early Middle Ages.
More information: Macháček, J., Eichert, S., Nosek, V., & Pernicka, E. (2024). Copper-alloy belt fittings and elite networking in Early Medieval Central Europe. Journal of Archaeological Science, 161, 105895. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2023.105895





