In a remarkable underwater excavation off the coast of Agrigento in Sicily, a team comprised of the Subacquei Nucleus of the Carabinieri Command, the Superintendence of the Sea, and the Diving Group of BCSicilia, a volunteer organization dedicated to protecting Sicily’s cultural heritage, has successfully recovered sculptural fragments believed to belong to the Temple of Olympian Zeus.
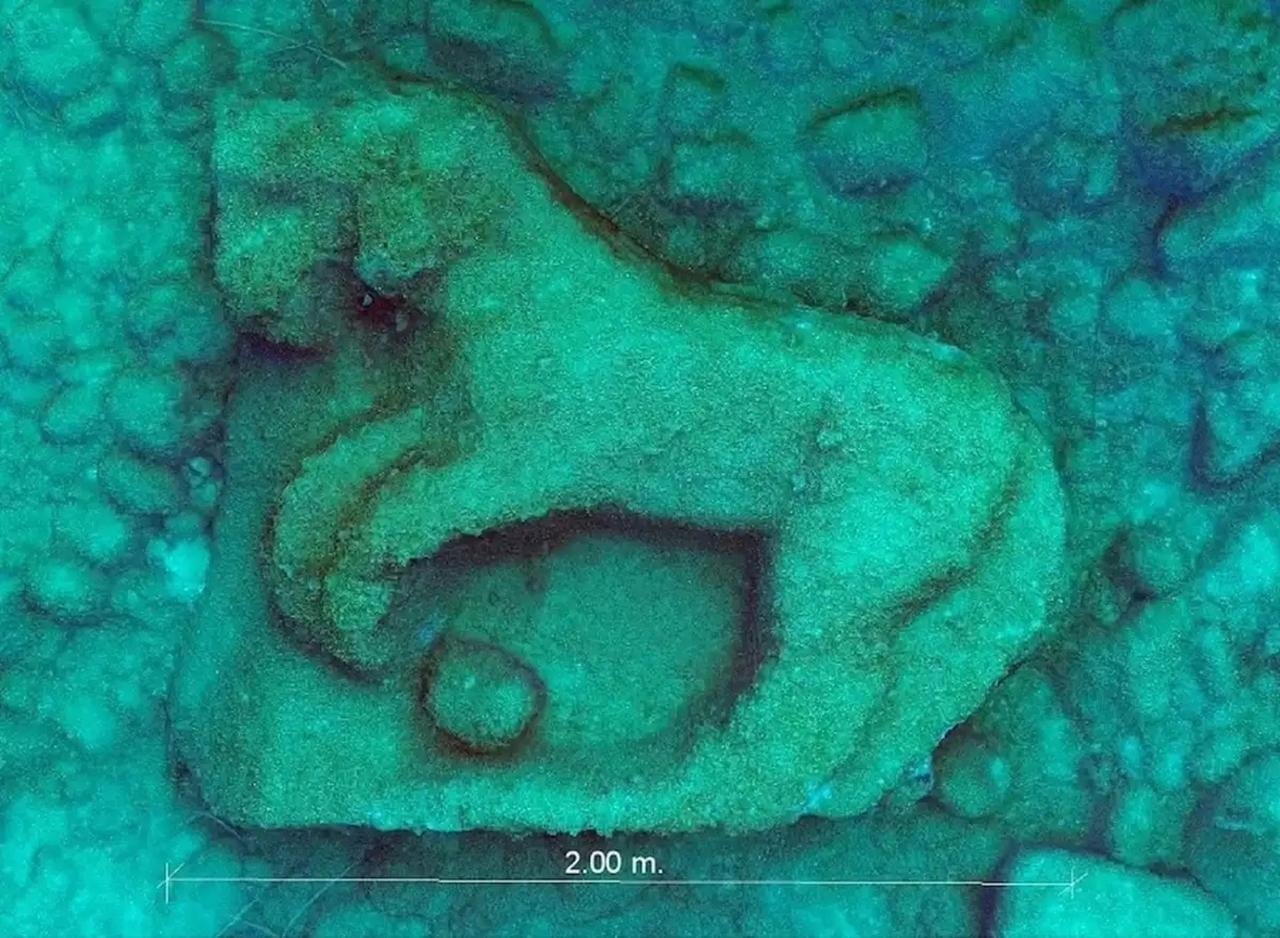 Fragment of the horse frieze from the Temple of Zeus in Agrigento, Sicily. Credit: BCSicilia
Fragment of the horse frieze from the Temple of Zeus in Agrigento, Sicily. Credit: BCSicilia
This temple considered the most amazing and bizarre of all Greek temples, was built in the ancient Greek city of Akragas (now Agrigento) by the tyrant Theron after his victory in the Battle of Himera in 480 BCE.
The discovery made about 300 meters from the coast and at a depth of 9 meters, includes a marble-carved piece depicting a prancing horse, a classic motif in Greek sculpture. Measuring 2 x 1.6 meters and 35 centimeters thick, this slab of Proconnesian marble is believed to be part of the temple frieze, declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The BCSicilia Subgroup, led by engineer Gaetano Lino, recognized its potential value through pH๏τogrammetric studies in October, leading to its successful recovery.
 One of the gigantic Atlanteans of the temple in Agrigento. Credit: Palickap, Wikimedia Commons
One of the gigantic Atlanteans of the temple in Agrigento. Credit: Palickap, Wikimedia Commons
This find is crucial in shedding new light on the grand construction from the 5th century BCE. The Temple of Zeus is characterized by its 38 huge atlantes, some of which can be seen today lying on the ground. It stands as an essentially Doric building with pseudoperipteral architecture, featuring no free-standing columns but rather semi-columns, seven by fourteen, engaged into a continuous wall. The intercolumni, spaces between the columns, held giant statues called Telamons or Atlantes, standing 7.61 meters high.
The find, covered with concretions, was almost certainly made of Proconnesian marble. The significance of this discovery is further emphasized by its ᴀssociation with Zeus, as the prancing horse depicted in the relief is iconographically linked to Zeus, whose chariot was drawn by the Four Winds in the form of horses. The Temple of Zeus itself was renowned for its proportions, being one of the largest structures of antiquity.
Sicily’s Superintendency of the Sea played a crucial role in ordering the recovery of the relief fragment so that the thick layers of concretions could be cleaned off, revealing its intricate details. The extensive pH๏τogrammetric studies and 3D imaging conducted in October 2022 highlighted the true significance of the piece.
Despite facing challenges with sea turbulence during the recovery attempts, the dedicated team succeeded in bringing this exceptional find back to shore.





