The mystery surrounding the ancient “Vittrup Man,” whose remains were discovered in a peat bog in northwest Denmark over a century ago, has been unraveled by a collaborative effort of international scientists. Through advanced genetic analyses and cutting-edge research techniques, a detailed portrait of this 5,000-year-old individual’s life has emerged.
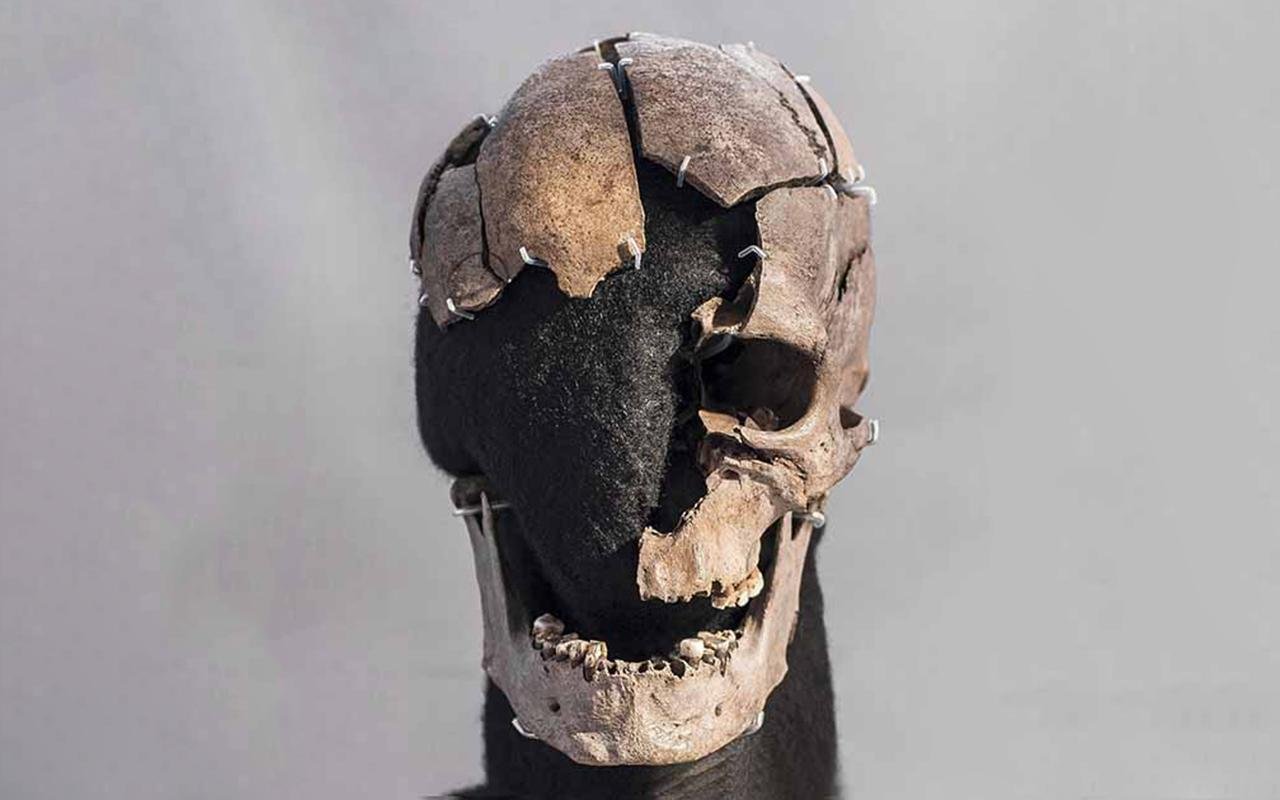 The cranial remains of Vittrup Man, who ended up in a bog after his skull had been crushed by at least eight heavy blows. Credit: Stephen Freiheit, PLOS One (2024)
The cranial remains of Vittrup Man, who ended up in a bog after his skull had been crushed by at least eight heavy blows. Credit: Stephen Freiheit, PLOS One (2024)
Originally found in 1915 by peat diggers near the village of Vittrup, the skeletal remains, including a fragmented skull and jaw, hinted at a violent end, with evidence of at least eight blows to the head. However, it wasn’t until recent studies that the full extent of Vittrup Man’s story began to unfold.
Led by Anders Fischer of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and his team, researchers delved into Vittrup Man’s genetics, diet, and geographical origins, uncovering surprising details about his life. Analyses revealed that he was born along the Scandinavian coast, likely in northern Norway or Sweden, around 5,200 years ago.
Despite this coastal upbringing, Vittrup Man’s journey took him to Denmark in his late teens, where he integrated into a farming community. This transition in diet and lifestyle, from a hunter-gatherer reliant on marine resources to a farmer consuming domesticated animals, was evident from isotopic and protein analyses of his teeth and bones.
 A cartoon included with the new research depicts how Vittrup Man was possibly sacrificed in a swamp. Credit: Anders Fischer/Niels Bach / CC-BY 4.0
A cartoon included with the new research depicts how Vittrup Man was possibly sacrificed in a swamp. Credit: Anders Fischer/Niels Bach / CC-BY 4.0
The reasons behind Vittrup Man’s migration remain speculative, with researchers proposing scenarios ranging from voluntary relocation for trade or adventure to possible captivity or enslavement. Regardless of the circumstances, his presence in Denmark marked a significant departure from his ancestral homeland.
The discovery of Vittrup Man’s distinct genetic signature, closely linked to populations in northern Scandinavia, challenges previous ᴀssumptions about the homogeneity of ancient Danish inhabitants.
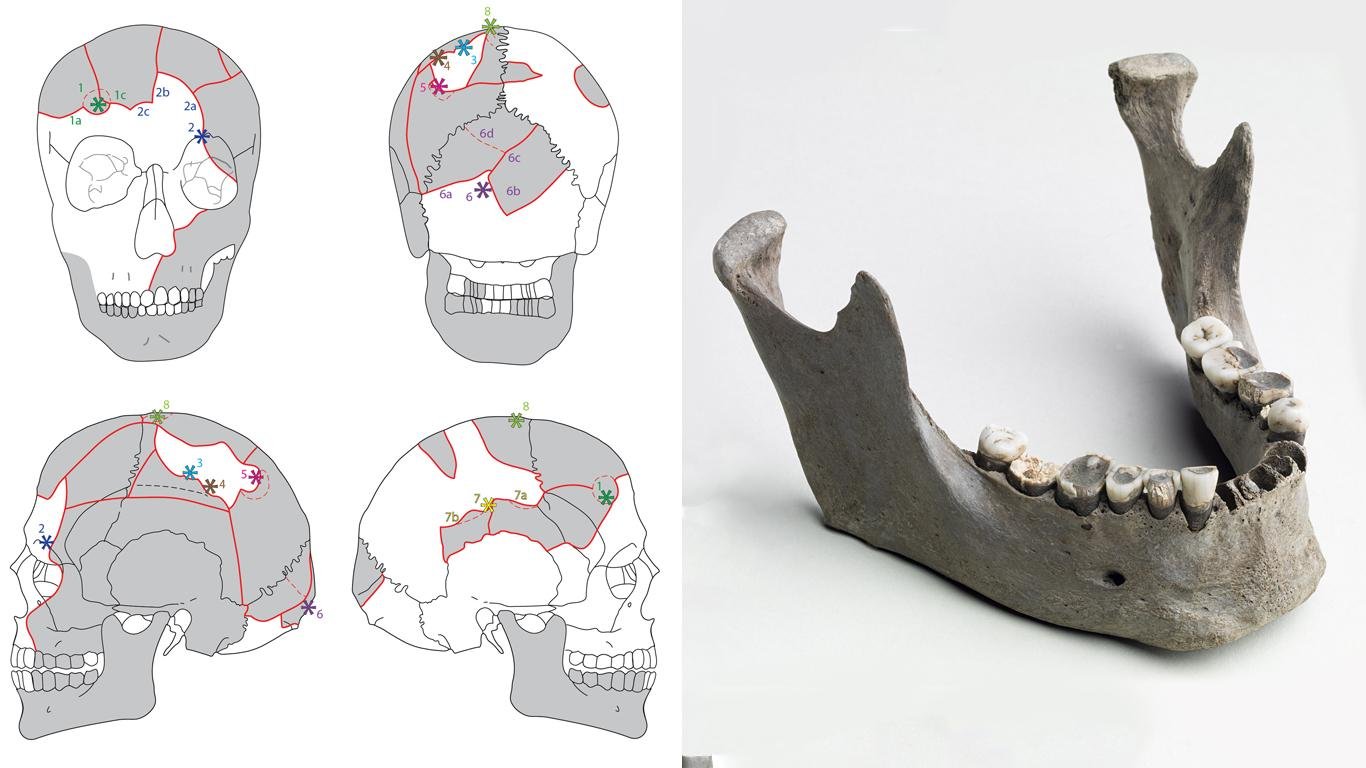 (Left) Principal drawing of the cranium with indications of eight impact lesions and radiating fracture lines. Credit: Marie Louise Jørkov, Anders Fischer and Sidsel Wåhlin, graphically finalised by Rich Potter, University of Gothenburg. (Right) The jawbone of Vittrup Man. Several of the teeth are corroded due to soil chemical processes. All are clearly worn as a result of chewing. Credit: Arnold Mikkelsen.
(Left) Principal drawing of the cranium with indications of eight impact lesions and radiating fracture lines. Credit: Marie Louise Jørkov, Anders Fischer and Sidsel Wåhlin, graphically finalised by Rich Potter, University of Gothenburg. (Right) The jawbone of Vittrup Man. Several of the teeth are corroded due to soil chemical processes. All are clearly worn as a result of chewing. Credit: Arnold Mikkelsen.
One prevailing theory regarding Vittrup Man’s demise suggests that he may have been a victim of ritual sacrifice, a common practice in Neolithic Europe. The brutal nature of his death, evidenced by the multiple cranial fractures, aligns with archaeological findings of sacrificial activity in the region.
The study of Vittrup Man not only sheds light on individual life histories but also offers broader insights into the dynamics of ancient societies. By examining the transition from hunter-gatherer to agricultural lifestyles and the genetic interplay between different populations, researchers gain a deeper understanding of human migration and cultural exchange in prehistoric Europe.
More information: Fischer A, Sjögren K-G, Jensen TZT, Jørkov ML, Lysdahl P, Vimala T, et al. (2024) Vittrup Man–The life-history of a genetic foreigner in Neolithic Denmark. PLoS ONE 19(2): e0297032. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297032





