A new study of the Hand of Irulegi has revealed the oldest and most extensive example of Vasconic script to date.
 The engraved bronze hand from Irulegi. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
The engraved bronze hand from Irulegi. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
The hand, measuring approximately 5.5 by six inches, was discovered during excavations in 2021 at the site, believed to have been a settlement during the Roman Sertorian Wars. Upon closer examination, researchers determined that the inscription on the hand is written in Vasconic, a language family that includes Basque, which is spoken in modern-day Basque Country at the western edge of the Pyrenees.
The Vasconic language, spoken by the pre-Roman Vascones, holds significant implications for understanding Europe’s linguistic and cultural evolution. The location of the artifact, found at the entrance of a domestic building within the Irulegi settlement, suggests its ritualistic significance. Analysis of the inscription revealed a word resembling the Basque term for ‘good fortune,’ suggesting the artifact may have served as a charm or dedication to a deity.
Lead author of the study, Mattin Aiestaran from the University of the Basque Country, said: “The Irulegi hand is the only long written text retrieved to date, alongside several coins minted in the Vasconic territory.” He added: “The Irulegi hand must be considered as a well-integrated element within the cultural context of the settlement.”
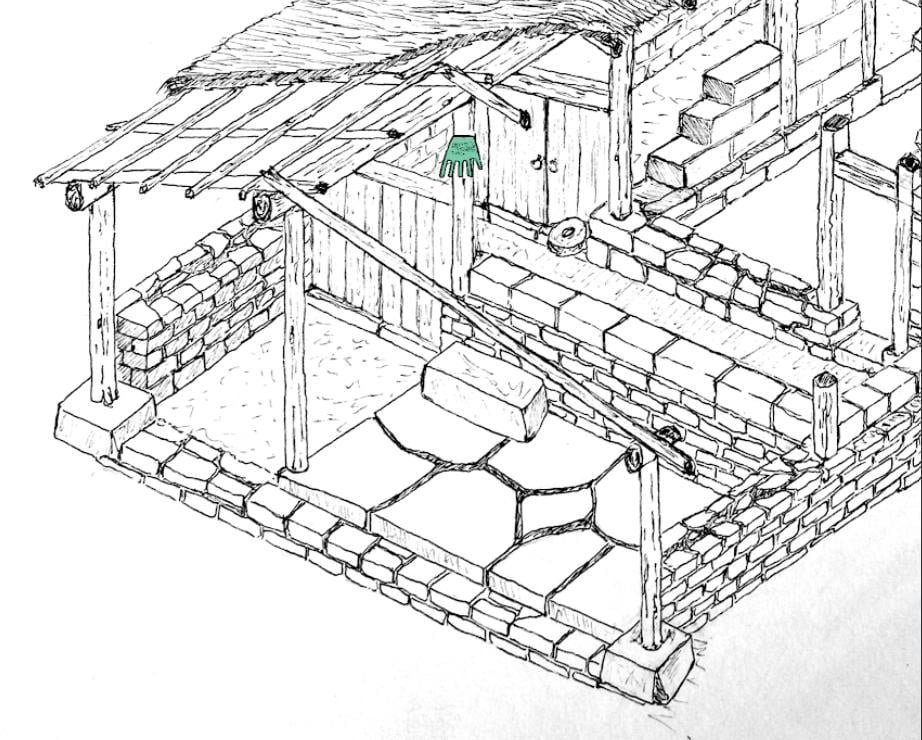 Sketch of a house, indicating where the bronze hand was likely displayed. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
Sketch of a house, indicating where the bronze hand was likely displayed. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
The discovery challenges previous ᴀssumptions about the literacy of ancient Vasconic communities, providing evidence that they were familiar with writing. While the connection between the Vasconic language of Irulegi and modern Basque remains to be definitively proven due to the scarcity of comparative texts, researchers believe the inscription offers tantalizing evidence of a linguistic link.
Mikel Edeso Egia from the Aranzadi Science Society, which coordinated the research team, said: “The discovery of the Hand of Irulegi has opened a new horizon to unravel the history behind the most enigmatic language still alive in Europe: the Basque language.” He emphasized the importance of further research to unravel the mysteries surrounding the Basque language and its ancient origins.
 Sequence of pH๏τographs illustrating the excavation (1–4) and restoration (5–6) of the Irulegi hand. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
Sequence of pH๏τographs illustrating the excavation (1–4) and restoration (5–6) of the Irulegi hand. Credit: Aiestaran, M. et al., Antiquity Journal (2024)
This find not only advances our understanding of ancient languages and cultures but also raises new questions about the origins and development of Basque, a language isolate with no known living relatives.
More information: Aiestaran M, Velaza J, Gorrochategui J, et al. (2024). A Vasconic inscription on a bronze hand: writing and rituality in the Iron Age Irulegi settlement in the Ebro Valley. Antiquity;98(397):66-84. doi:10.15184/aqy.2023.199





