Archaeologists from Southern Methodist University (SMU) have uncovered a small flaked-stone obsidian blade in the Texas panhandle, suggesting a link to the historic expedition led by Spanish explorer Francisco Vázquez de Coronado in the mid-16th century.
 Coronado Sets Out to the North. oil painting by Frederic Remington, c. 1900. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Coronado Sets Out to the North. oil painting by Frederic Remington, c. 1900. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Coronado’s expedition, spanning from 1540 to 1542, aimed to uncover the mythical Cibola, believed to hold immense riches. This legend, often ᴀssociated with a Portuguese myth of seven cities on the mythical island of Antillia, captivated imaginations for centuries. However, the expedition’s origin lies in the tales of survivors from the ill-fated Narváez expedition of 1527, which aimed to establish settlements in Florida.
The obsidian blade, measuring just over 5 centimeters in length, was discovered in the Texas panhandle and is thought to have been dropped by a member of Coronado’s entourage, which included Indigenous Mexicans. Analyzing its chemical composition, researchers traced its origins to Central Mexico’s Sierra de Pachuca mountain range, where Indigenous peoples crafted similar tools before the Spanish conquest.
SMU anthropologist Matthew Boulanger, who led the study, said: “This small unᴀssuming artifact fits all of the requirements for convincing evidence of a Coronado presence in the Texas panhandle.” He further noted that the blade’s discovery aligns with other central Mexican obsidian artifacts discarded along the expedition’s route.
 The small piece of obsidian was found by Charlene Erwin’s father-in-law in the Texas Panhandle in the 1930s. Credit: Southern Methodist University
The small piece of obsidian was found by Charlene Erwin’s father-in-law in the Texas Panhandle in the 1930s. Credit: Southern Methodist University
The expedition’s journey through the American Southwest and Great Plains has long puzzled historians. While the path through New Mexico is relatively well-documented, the journey eastward poses challenges due to the lack of clear landmarks. Boulanger’s research, published in the Journal of the North Texas Archeological Society, suggests that artifacts like the obsidian blade could provide physical evidence to fill in these gaps.
The blade’s discovery came to light after a chance encounter with Charlene Erwin, whose family possessed the artifact since the 1930s. Boulanger’s examination, coupled with interviews and historical research, led to the conclusion that the artifact likely originated from Coronado’s expedition.
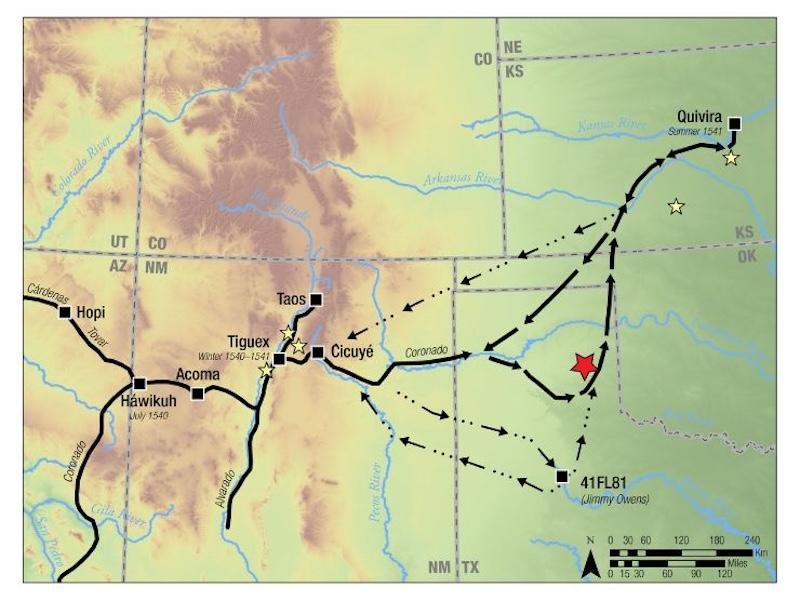 A map shows the reconstructed paths of the Francisco Vázquez de Coronado expedition (1540-1542). Credit: Southern Methodist University
A map shows the reconstructed paths of the Francisco Vázquez de Coronado expedition (1540-1542). Credit: Southern Methodist University
While the exact route of Coronado’s journey remains uncertain, researchers speculate that Indigenous allies accompanying the expedition may have left behind such artifacts. These brittle blades, essential for cutting and crafting, were often discarded when broken, leaving traces of the expedition’s path.
Coronado’s quest, immortalized in history and literature, ultimately ended in disappointment, as the fabled city of gold remained elusive. Nevertheless, artifacts like the obsidian blade serve as reminders of the expedition’s ambitious trek across the American Southwest.





