Archaeologists have unearthed an eleventh-century Islamic astrolabe adorned with both Arabic and Hebrew inscriptions, in a museum in Verona, Italy.
 The astrolabe of Verona. Credit: Federica Gigante
The astrolabe of Verona. Credit: Federica Gigante
This rare find, considered one of the oldest of its kind, demonstrates a centuries-long narrative of scientific exchange among Arabs, Jews, and Christians, spanning regions from Spain and North Africa to Italy.
The astrolabe, a sophisticated astronomical instrument resembling a pocket computer, was identified by Dr. Federica Gigante of Cambridge University’s History Faculty during her visit to the Fondazione Museo Miniscalchi-Erizzo. Initially, the museum was unaware of the object’s significance, with some even suspecting it to be a forgery. However, Dr. Gigante’s meticulous analysis revealed its true importance, now ranking it as the museum’s most prized possession.
The astrolabe, often referred to as the world’s first smartphone for its multifunctional capabilities, served as a portable model of the universe, allowing users to calculate time, distances, plot star positions, and even predict the future through horoscopes.
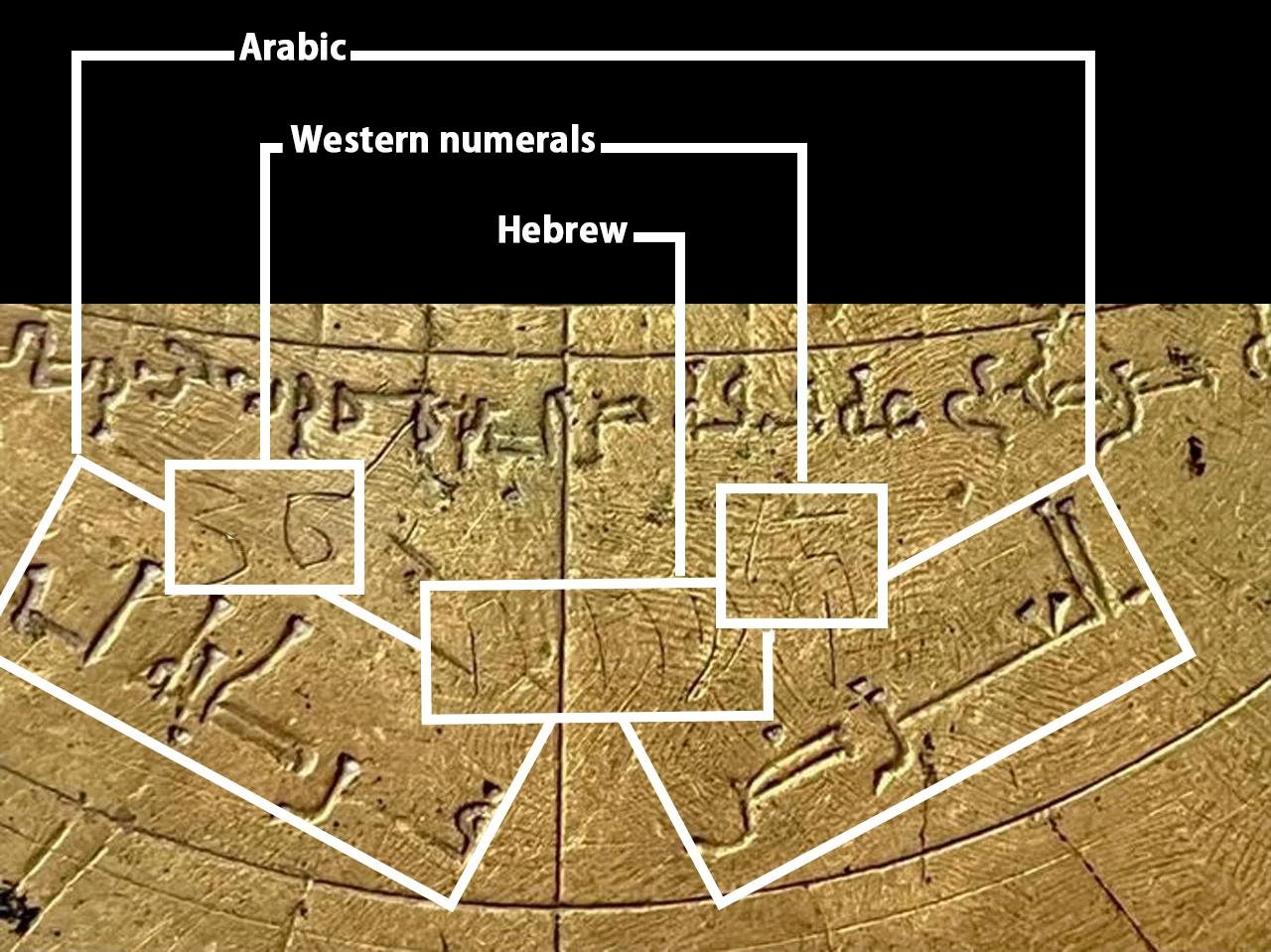 Close up of the Verona astrolabe features inscriptions in Arabic, Hebrew, and Western numerals. Credit: Federica Gigante
Close up of the Verona astrolabe features inscriptions in Arabic, Hebrew, and Western numerals. Credit: Federica Gigante
Through meticulous analysis of the astrolabe’s design, construction, and inscriptions, Dr. Gigante determined its origins in eleventh-century Muslim-ruled Spain, particularly in regions like Toledo, known for their diverse population of Muslims, Jews, and Christians. The instrument’s journey reveals a story of adaptation and translation, with subsequent modifications made by various users across different regions and linguistic communities.
Notably, Hebrew inscriptions added to the astrolabe suggest its circulation among Jewish diaspora communities in Italy, where Arabic was not widely understood.
 Close up of the Verona astrolabe showing Hebrew inscribed above Arabic inscriptions. Credit: Federica Gigante
Close up of the Verona astrolabe showing Hebrew inscribed above Arabic inscriptions. Credit: Federica Gigante
The Verona astrolabe symbolizes a profound collaboration between diverse cultures, fostering advancements in science and knowledge exchange. Dr. Gigante emphasizes, “This isn’t just an incredibly rare object. It’s a powerful record of scientific exchange between Arabs, Jews, and Christians over hundreds of years.”
“This object is Islamic, Jewish, and European,” Dr. Gigante remarked, emphasizing the inseparable nature of its cultural heritage. From its origins in medieval Spain to its eventual place in a Veronese nobleman’s collection, the astrolabe embodies a narrative of shared knowledge and mutual enrichment across borders and centuries.





