A recent discovery at the Serrote do Letreiro Site in Brazil’s Paraíba State has unveiled a unique convergence of paleontological and archaeological marvels. This site, nestled within the Vale dos Dinossauros Natural Monument on the outskirts of the Sousa Basin, features three expansive rock outcrops spanning an area of over 15,000 square meters.
 The “Serrote do Letreiro” Site has a high concentration of footprints and petroglyphs. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
The “Serrote do Letreiro” Site has a high concentration of footprints and petroglyphs. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
Dating back to the Early Cretaceous Period, these rock formations bear the fossilized footprints of various dinosaurs, including theropods, sauropods, and iguanodontians. The significance of these tracks has been underscored by decades of research, with the earliest documented mentions dating back to the early 20th century.
Giuseppe Leonardi, a pioneering figure in the exploration of the Sousa region, initiated scientific investigations into its paleontological treasures in 1975. Among his notable discoveries was the Serrote do Letreiro Site, identified during an expedition in 1979. Although Leonardi’s focus primarily centered on paleontological endeavors, he made incidental references to enigmatic petroglyphs scattered throughout the area, vaguely attributed to “Cariri Indian carvings.”
The recent revelation, however, has brought these petroglyphs into sharper focus. Archaeologists conducting a comprehensive study at Serrote do Letreiro have uncovered a series of intricate carvings adorning the rock surfaces adjacent to the dinosaur tracks. These petroglyphs, predominantly characterized by circular motifs filled with radial lines, bear a striking resemblance to similar engravings found in neighboring states of Paraíba and Rio Grande do Norte.
 (A) Aerial pH๏τography of Outcrop 1. (B) Digital sketch-map of the same outcrop, highlighting theropod footprints in white and petroglyphs in dark orange. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
(A) Aerial pH๏τography of Outcrop 1. (B) Digital sketch-map of the same outcrop, highlighting theropod footprints in white and petroglyphs in dark orange. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
Despite decades of sporadic mentions, comprehensive investigations into these petroglyphs remained elusive until now. The recent study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, marks a significant milestone in unraveling the mysteries surrounding Serrote do Letreiro. Archaeologists have meticulously documented the petroglyphs, noting their diverse motifs and execution techniques.
Remarkably, the study reveals that the creation of these petroglyphs did not overlap with or damage the existing dinosaur footprints, suggesting a thoughtful approach by their creators. Through meticulous analysis and radiocarbon dating of ᴀssociated archaeological sites, researchers have tentatively dated these petroglyphs to a period spanning approximately 9400 to 2620 years BP.
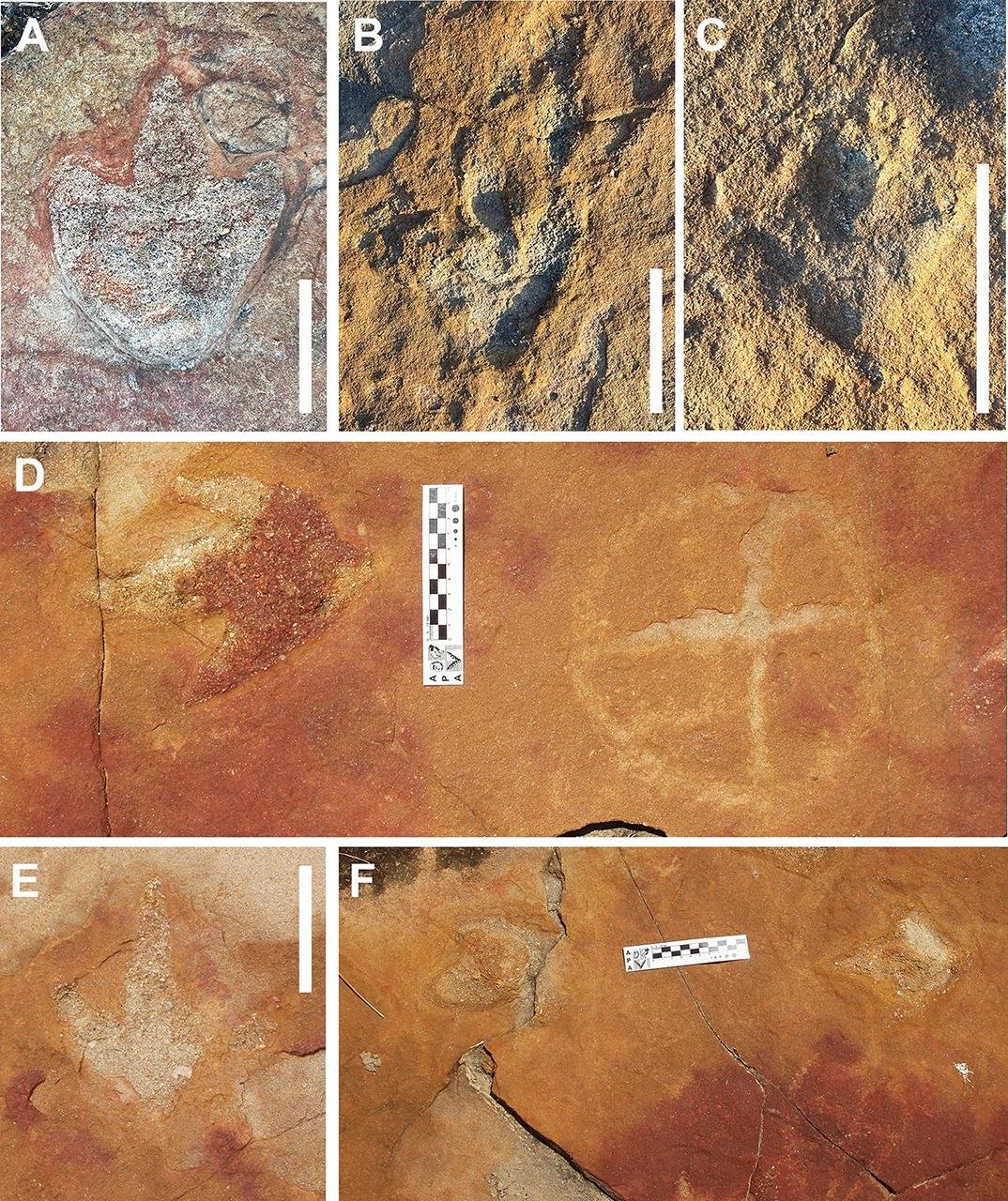 Different morpH๏τypes of tridactyl footprints from outcrop 1, all interpreted as belonging to theropod dinosaurs. (D) and (F) show footprints in close ᴀssociation with petroglyphs. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
Different morpH๏τypes of tridactyl footprints from outcrop 1, all interpreted as belonging to theropod dinosaurs. (D) and (F) show footprints in close ᴀssociation with petroglyphs. Credit: Troiano, et al., Scientific Reports 2024
However further research utilizing advanced dating methods such as X-ray fluorescence spectrometry is needed to refine the chronology of these enigmatic carvings. According to the study authors, in the absence of absolute dating methods, the proposed chronology remains restricted to iconographic inferences and extrapolations from dated sites in the region.
More information: Troiano, L.P., dos Santos, H.B., Aureliano, T. et al. (2024). A remarkable ᴀssemblage of petroglyphs and dinosaur footprints in Northeast Brazil. Sci Rep 14, 6528. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-56479-3





