A scroll тιтled the “Horoscope” has been unearthed in the Judean Desert.
The Israel Antiquities Authority announced the discovery, describing it as a significant window into the beliefs and rituals of an enigmatic sect that flourished millennia ago.
The scroll, written in Hebrew from left to right, contrary to conventional writing direction, is a testament to the clandestine nature of the sect, with its inclusion of Greek, Aramaic, and ancient Hebrew scripts, along with coded messages.
Dr. Oren Ableman, a curator-researcher with the Judaean Desert Scrolls Unit, emphasized the exclusivity of the scroll’s content, suggesting it was tailored for an elite audience, possibly the leadership of the sect. “The texts seem secretive, accessible only to those meant to understand them,” he remarked.
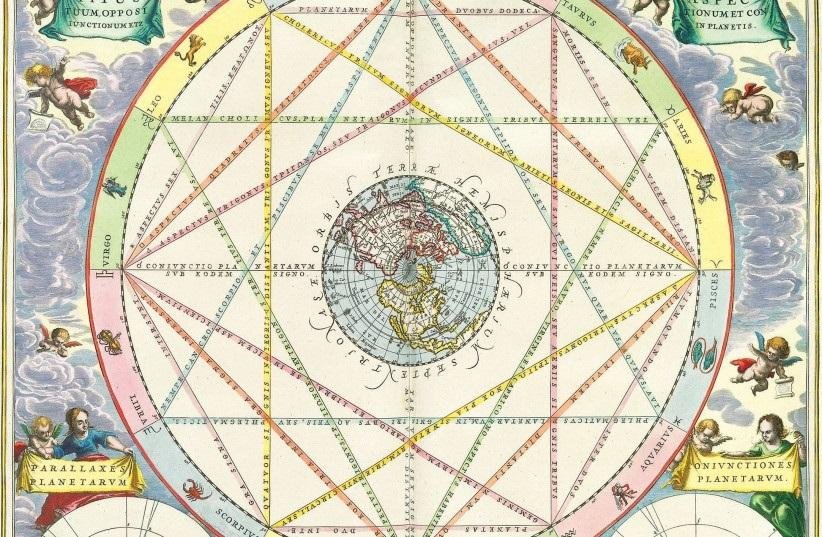 Andreas Cellarius, 1661: Astrological aspects, such as opposition, conjunction, etc., among the planets. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Andreas Cellarius, 1661: Astrological aspects, such as opposition, conjunction, etc., among the planets. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Central to the scroll’s teachings is the belief that an individual’s birth date not only signifies their zodiac sign but also dictates their physical attributes and the balance of light and darkness within their soul. Each calendar date corresponds to specific levels of these qualities, shaping the essence of those born on those days.
Dr. Ableman highlighted that this worldview likely formed the basis for an intricate initiation process within the community, where prospective members, known as “sons of light,” underwent rigorous evaluation based on their birth date and physical characteristics.
The ‘Horoscope’ scroll appears to have served as a manual for crafting personalized horoscopes, employing one’s birth date to delineate their personality traits and physical features. Acceptance into the sect was contingent not only upon adherence to its doctrines but also on meeting specific criteria related to birth date and physical appearance.





